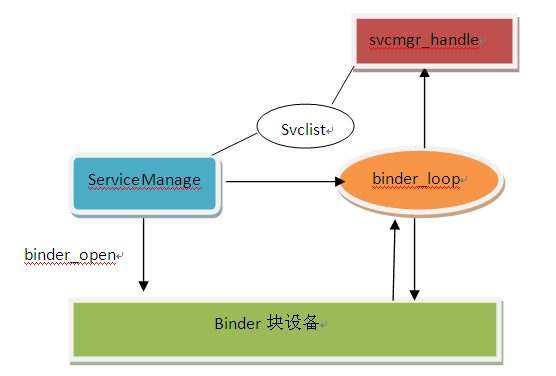
ServiceMananger是android中比较重要的一个进程,它是在init进程启动之后启动,从名字上就可以看出来它是用来管理系统中的service。比如:InputMethodService、ActivityManagerService等。在ServiceManager中有两个比较重要的方法:add_service、check_service。系统的service需要通过add_service把自己的信息注册到ServiceManager中,当需要使用时,通过check_service检查该service是否存在。
主函数
从它的主函数代码开始:
- int main(int argc, char **argv)
- {
- struct binder_state *bs;
- void *svcmgr = BINDER_SERVICE_MANAGER;
- bs = binder_open(128*1024);
- if (binder_become_context_manager(bs)) {
- LOGE("cannot become context manager (%s) ", strerror(errno));
- return -1;
- }
- svcmgr_handle = svcmgr;
- binder_loop(bs, svcmgr_handler);
- return 0;
- }
从main函数中可以看出,它主要做了三件事情:
- 打开/dev/binder设备,并在内存中映射128K的空间。
- 通知Binder设备,把自己变成context_manager
- 进入循环,不停的去读Binder设备,看是否有对service的请求,如果有的话,就去调用svcmgr_handler函数回调处理请求。
服务注册
再来看看ServiceManager中是怎么样去注册服务的。先来看先,当有对service的请求时,调用的回调函数svcmgr_handler:
- int svcmgr_handler(struct binder_state *bs,
- struct binder_txn *txn,
- struct binder_io *msg,
- struct binder_io *reply)
- {
- struct svcinfo *si;
- uint16_t *s;
- unsigned len;
- void *ptr;
- uint32_t strict_policy;
- // LOGI("target=%p code=%d pid=%d uid=%d ",
- // txn->target, txn->code, txn->sender_pid, txn->sender_euid);
- if (txn->target != svcmgr_handle)
- return -1;
- // Equivalent to Parcel::enforceInterface(), reading the RPC
- // header with the strict mode policy mask and the interface name.
- // Note that we ignore the strict_policy and don't propagate it
- // further (since we do no outbound RPCs anyway).
- strict_policy = bio_get_uint32(msg);
- s = bio_get_string16(msg, &len);
- if ((len != (sizeof(svcmgr_id) / 2)) ||
- memcmp(svcmgr_id, s, sizeof(svcmgr_id))) {
- fprintf(stderr,"invalid id %s ", str8(s));
- return -1;
- }
- switch(txn->code) {
- case SVC_MGR_GET_SERVICE:
- case SVC_MGR_CHECK_SERVICE:
- s = bio_get_string16(msg, &len);
- ptr = do_find_service(bs, s, len);
- if (!ptr)
- break;
- bio_put_ref(reply, ptr);
- return 0;
- case SVC_MGR_ADD_SERVICE:
- s = bio_get_string16(msg, &len);
- ptr = bio_get_ref(msg);
- if (do_add_service(bs, s, len, ptr, txn->sender_euid))
- return -1;
- break;
- case SVC_MGR_LIST_SERVICES: {
- unsigned n = bio_get_uint32(msg);
- si = svclist;
- while ((n-- > 0) && si)
- si = si->next;
- if (si) {
- bio_put_string16(reply, si->name);
- return 0;
- }
- return -1;
- }
- default:
- LOGE("unknown code %d ", txn->code);
- return -1;
- }
- bio_put_uint32(reply, 0);
- return 0;
- }
在该回调函数中会判断Service有什么需要,如果是请求注册service,那么久执行:
- case SVC_MGR_ADD_SERVICE:
- s = bio_get_string16(msg, &len);
- ptr = bio_get_ref(msg);
- if (do_add_service(bs, s, len, ptr, txn->sender_euid))
- return -1;
- break;
我们再来看看do_add_service中做了什么事情:
- int do_add_service(struct binder_state *bs,
- uint16_t *s, unsigned len,
- void *ptr, unsigned uid)
- {
- struct svcinfo *si;
- // LOGI("add_service('%s',%p) uid=%d ", str8(s), ptr, uid);
- if (!ptr || (len == 0) || (len > 127))
- return -1;
- if (!svc_can_register(uid, s)) {
- LOGE("add_service('%s',%p) uid=%d - PERMISSION DENIED ",
- str8(s), ptr, uid);
- return -1;
- }
- si = find_svc(s, len);
- if (si) {
- if (si->ptr) {
- LOGE("add_service('%s',%p) uid=%d - ALREADY REGISTERED ",
- str8(s), ptr, uid);
- return -1;
- }
- si->ptr = ptr;
- } else {
- si = malloc(sizeof(*si) + (len + 1) * sizeof(uint16_t));
- if (!si) {
- LOGE("add_service('%s',%p) uid=%d - OUT OF MEMORY ",
- str8(s), ptr, uid);
- return -1;
- }
- si->ptr = ptr;
- si->len = len;
- memcpy(si->name, s, (len + 1) * sizeof(uint16_t));
- si->name[len] = '�';
- si->death.func = svcinfo_death;
- si->death.ptr = si;
- si->next = svclist;
- svclist = si;
- }
- binder_acquire(bs, ptr);
- binder_link_to_death(bs, ptr, &si->death);
- return 0;
- }
在该函数中,首先会去检查是否有权限注册service,如果没有权限就直接返回,不能注册。
- if (!svc_can_register(uid, s)) {
- LOGE("add_service('%s',%p) uid=%d - PERMISSION DENIED ",
- str8(s), ptr, uid);
- return -1;
- }
然后会去检查该service是否已经注册过了,如果已经注册过,那么就不能再注册了:
- si = find_svc(s, len);
- if (si) {
- if (si->ptr) {
- LOGE("add_service('%s',%p) uid=%d - ALREADY REGISTERED ",
- str8(s), ptr, uid);
- return -1;
- }
- si->ptr = ptr;
- }
再判断内存是否足够:
- si = malloc(sizeof(*si) + (len + 1) * sizeof(uint16_t));
- if (!si) {
- LOGE("add_service('%s',%p) uid=%d - OUT OF MEMORY ",
- str8(s), ptr, uid);
- return -1;
- }
如果都没什么问题,会注册该service,加入到svcList中来。注意,在ServiceManager中维护service信息的地方就是svclist。里面存了service的name和handler。
服务获取
通过以上几个步骤,service就算注册成功了。那么当要获得该service的时候又是怎么去处理的。还是来看下回调函数中的判断:
- case SVC_MGR_CHECK_SERVICE:
- s = bio_get_string16(msg, &len);
- ptr = do_find_service(bs, s, len);
- if (!ptr)
- break;
- bio_put_ref(reply, ptr);
- return 0;
如果是获取service,那么执行SVC_MGR_CHECK_SERVICE,并把返回的数据写入reply,返回给客户端。
do_find_service函数中主要执行service的查找。
- void *do_find_service(struct binder_state *bs, uint16_t *s, unsigned len)
- {
- struct svcinfo *si;
- si = find_svc(s, len);
- // LOGI("check_service('%s') ptr = %p ", str8(s), si ? si->ptr : 0);
- if (si && si->ptr) {
- return si->ptr;
- } else {
- return 0;
- }
- }
这样在ServiceManager中就完成了服务的注册和查找。来看下ServiceManager的功能图: