1、异常:
(1)错误:
错误是绝症,只能修改代码;
(2)异常
编译时期异常Exception是小病,可以处理;
运行时期异常RuntimeException不能处理,也需要修改代码;
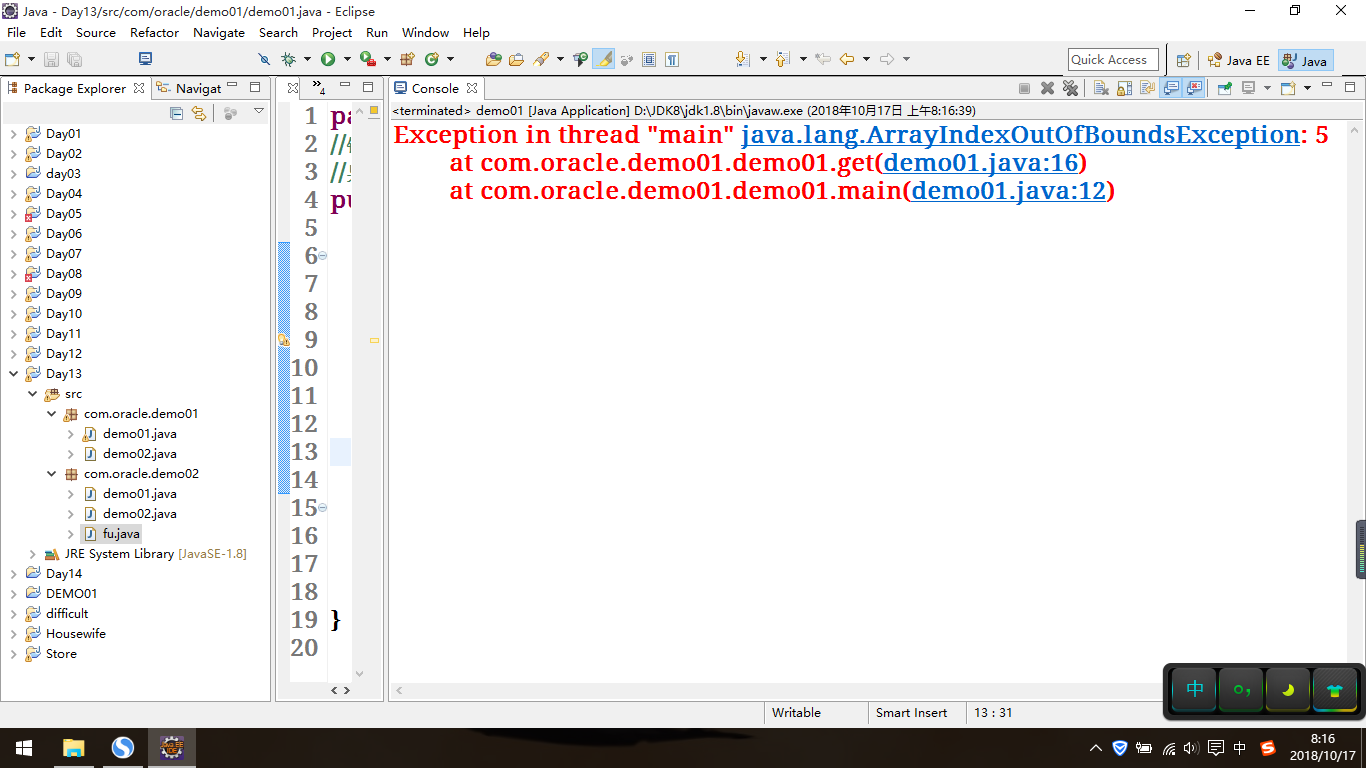
package com.oracle.demo01; //错误:绝症(只能修改代码) //异常:编译时期异常Exception 小病(可以处理);运行时期异常RuntimeException不能处理 public class demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //数组长度过大,会产生内存溢出错误 //int[] arr = new int[999999999]; int[] arr = new int[999]; //异常 int[] arr1 = new int[5]; int i = get(arr1); System.out.println(i); } public static int get(int[] arr){ int i = arr[5]; return i; } }
效果如下:
(3)throw new Exception();抛出异常对象;
throws Exception;抛出异常类;
(4)try{可能会发生异常的语句
}catch(可能会发生异常的类名 变量名){
异常的处理方式
}finally{
不管发不发生异常都会执行的语句
释放资源的语句
}
package com.oracle.demo01; /*try{ 可能会发生异常的语句 }catch(可能会发生异常的类名 变量名){ 异常的处理方式 }finally{ 不管发不发生异常都会执行的语句 释放资源的语句 }*/ public class demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {1,2,2,2}; try{ int i = get(arr); System.out.println(i); }catch(NullPointerException ex){ System.out.println(ex); }catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex){ System.out.println(ex); }finally{ System.out.println("finally执行语句"); } System.out.println("你好呀"); } public static int get(int[] arr) { if(arr == null){ throw new NullPointerException("数组为空"); } if(arr.length == 0){ throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("数组长度为零"); } int i = arr[arr.length-1]; return i; } }
效果如下:

(5)对于RuntimeException运行时期异常:不需要throws,也不需要try,catch处理
一旦出现,程序员修改代码;
对于编译时期异常Exception及Exception的子类(不包括RuntimeException)
2种处理方式:一个throws,一个是try/catch
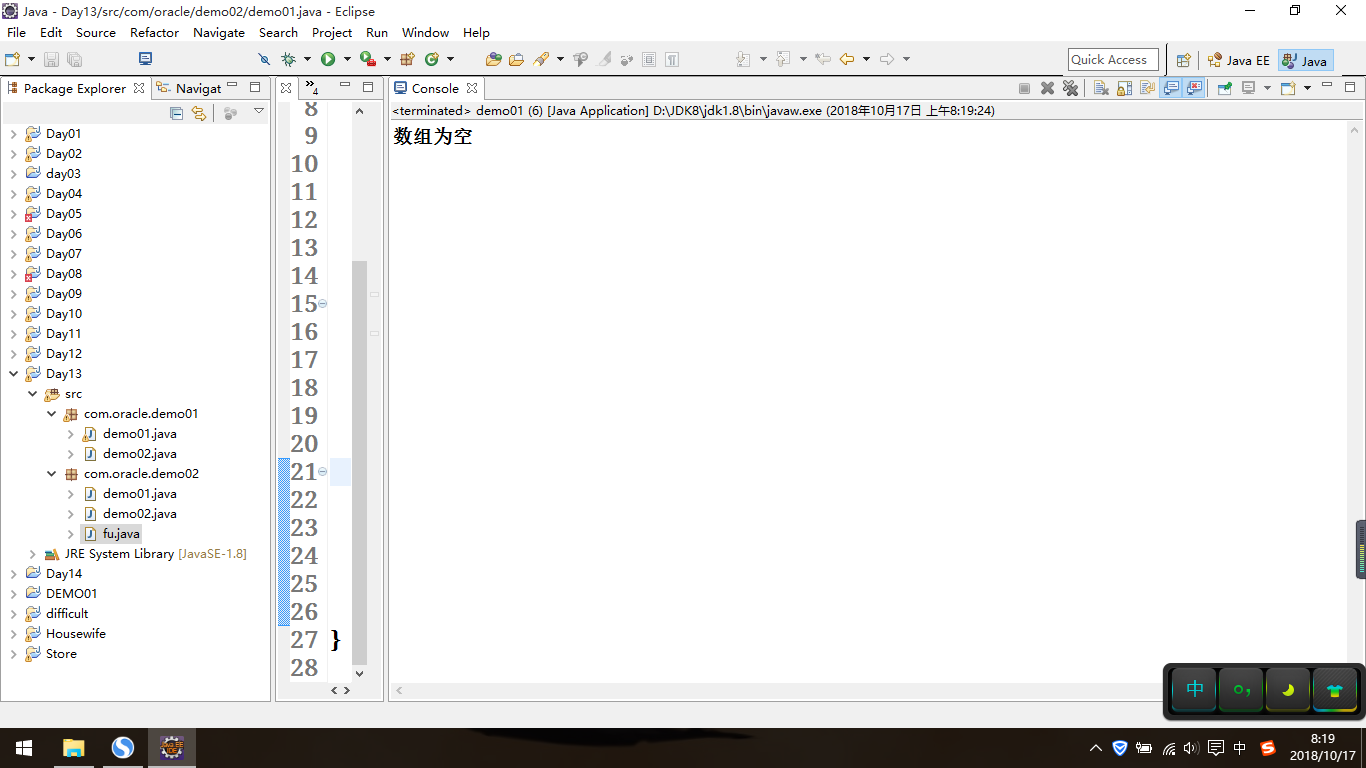
package com.oracle.demo02; //RuntimeException运行时期异常:不需要throws,也不需要try,catch处理 // 一旦出现,程序员修改代码; //对于编译时期异常Exception及Exception的子类(不包括RuntimeException) // 2种处理方式:一个throws,一个是try/catch public class demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = null; try { System.out.println(get2(arr)); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } public static int get(int[] arr){ if(arr == null){ throw new NullPointerException("数组为空"); } return arr[1]; } public static int get2(int[] arr) throws Exception { if(arr == null){ throw new Exception("数组为空"); } return arr[1]; } }
效果如下:
(6)1当父类方法有异常时,子类继承重写后可以不抛异常,
也可以抛异常,该异常不得超过父类异常
2当父类方法没有异常,子类重写该方法不得抛出异常
如果该方法调用了一个抛出编译异常的方法,只能try,catch;
package com.oracle.demo02; //1当父类方法有异常时,子类继承重写后可以不抛异常, //也可以抛异常,该异常不得超过父类异常 //2当父类方法没有异常,子类重写该方法不得抛出异常 //如果该方法调用了一个抛出编译异常的方法,只能try,catch; import java.text.ParseException; public class fu { public void f() throws ParseException{} //重载不会 public void f(String a){}; } class zi extends fu{ public void f(){ try { z(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } }; public void z() throws Exception{} }