文章转载自:https://elasticstack.blog.csdn.net/article/details/111692444
前提条件
在继续执行本教程中概述的步骤之前,你需要具备一个关键的先决条件:你需要一个稳定且受支持的 Docker 版本,才能使用 Dockerfile 创建 Elasticsearch 映像。你可以使用如下的命令来检查你的 Docker 的版本:
$ docker --version
Docker version 20.10.0, build 7287ab3
Elasticsearch YAML 文件
针对定制的 Docker image,我们通常需要定制自己的 elasticsearch.yml 文件。然后,你需要使用 Dockerfile 的 COPY 命令将文件内容复制到容器中。我们首先来创建一个文件目录:
mkdir elasticsearch-docker && cd elasticsearch-docker
使用 Elasticsearch 和 Dockerfile 时,你可以使用 YAML 进行许多不同的配置更改。 以下 YAML 命令仅显示了你可以为在 Docker 中运行的 Elasticsearch 集群修改的一些内容:
elasticsearch.yml
# ---------------------------------- Cluster -----------------------------------
#
# Use a descriptive name for your cluster:
#
cluster.name: cluster-liuxg
#
# ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------
#
# Use a descriptive name for the node:
#
node.name: node1
#
# Add custom attributes to the node:
#
#node.attr.rack: r1
#
# ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------
#
# Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma):
#
path.data: /var/lib/elasticsearch
#
# Path to log files:
#
path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch
#
# ----------------------------------- Memory -----------------------------------
#
# Lock the memory on startup:
#
#bootstrap.memory_lock: true
#
# Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available
# on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this
# limit.
#
# Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory.
#
# ---------------------------------- Network -----------------------------------
#
# Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6):
#
network.host: 0.0.0.0
#
# Set a custom port for HTTP:
#
http.port: 9200
#
# For more information, consult the network module documentation.
#
# --------------------------------- Discovery ----------------------------------
#
# Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when this node is started:
# The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"]
#
#discovery.seed_hosts: ["host1", "host2"]
#
# Bootstrap the cluster using an initial set of master-eligible nodes:
#
#cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1", "node-2"]
#
# For more information, consult the discovery and cluster formation module documentation.
#
# ---------------------------------- Gateway -----------------------------------
#
# Block initial recovery after a full cluster restart until N nodes are started:
#
#gateway.recover_after_nodes: 3
#
# For more information, consult the gateway module documentation.
#
# ---------------------------------- Various -----------------------------------
#
# Require explicit names when deleting indices:
#
#action.destructive_requires_name: true
discovery.type: single-node
在上面我修改了 cluster.name 以及 node.name。更重要的是我修改了 network.host 为 0.0.0.0,这样可以使得 Elasticsearch 可以被外部所访问。你可以根据自己实际的需求配置这个文件。
Elasticsearch Dockerfile
你可以通过多种方式在 Dockerfile 中构建 Elasticsearch 映像。 在以下示例中,Ubuntu 镜像使用 wget 下载 Elasticsearch 服务的 DEB 软件包:
Dockerfile
FROM ubuntu:20.04
# container creator
LABEL maintainer="liu_xiao_guo@yahoo.com"
# copy the configuration file into the container
COPY logging.yml /usr/share/elasticsearch/config/
RUN groupadd -g 1000 elasticsearch && useradd elasticsearch -u 1000 -g 1000
# install APT transport and wget
RUN apt-get update &&
apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends
apt-transport-https
curl
wget -y
RUN wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-7.10.1-amd64.deb --no-check-certificate && dpkg -i elasticsearch-7.10.1-amd64.deb
COPY --chown=elasticsearch:elasticsearch elasticsearch.yml /etc/elasticsearch/
# start elasticsearch service
USER elasticsearch
ENV PATH=$PATH:/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin
CMD ["elasticsearch"]
# expose the default Elasticsearch port
EXPOSE 9200 9300
注意:请确保在同一行中运行 apt-get update 和 apt-get install 命令,如上例所示。 如果你不这样做,它将被缓存并且不会每次都更新。
我们使用如下的命令来 build docker image:
docker build -t liuxg/liuxg-elasticsearch $PWD
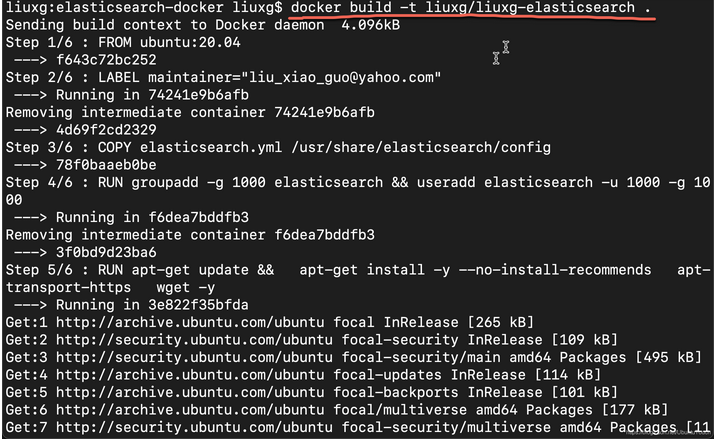
上面的 -t 是给这个镜像一个名称。我们使用 . 来表示当前的目录。等运行完上面的命令后,我们可以使用如下的命令来进行检查:
docker images
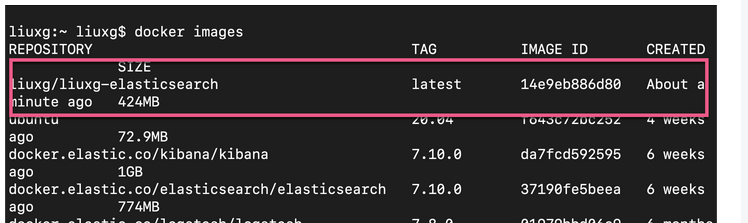
上面的命令显示:
我们可以看到一个新增加的 docker image。
另外一种方法是我们通过下载已经创建好的 Elasticsearch 镜像,然后把我们的配置文件直接拷入到镜像的容器中。下面的例子展示如何实现:
Dockerfile
FROM elasticsearch:7.10.1
# container creator
MAINTAINER orkb
# copy the configuration file into the container
COPY elasticsearch.yml /usr/share/elasticsearch/config
# expose the default Elasticsearch port
EXPOSE 9200 9300
注意:Docker 仅允许你从每个 Dockerfile 提取一个镜像,因此请确保不要使用多个 FROM 命令。 如果你确实尝试使用 FROM 提取多个镜像,它将仅使用最后一个命令构建一个镜像,而忽略之前的任何命令。
至此,我们已经成功地创建了我们的 docker 镜像。我们可以使用如下的命令来检查是否有刚才被创建的镜像运行的容器:
docker ps -a
docker ps -a | grep liuxg
上面的命令显示没有任何运行的容器。这是因为到目前为止仅创建了镜像。 你需要使用 docker run 命令从镜像创建容器。
启动一个 Elasticsearch 容器
你可以使用以下命令来运行先前创建的 liuxg/iuxg-elasticsearch Docker 镜像:
docker run --rm -it liuxg/liuxg-elasticsearch /bin/bash
你还可以使用 -p 选项公开默认的 Elasticsearch 端口 9200。以下是如何使用此选项的示例:
docker run --rm -p 9200:9200 liuxg/liuxg-elasticsearch
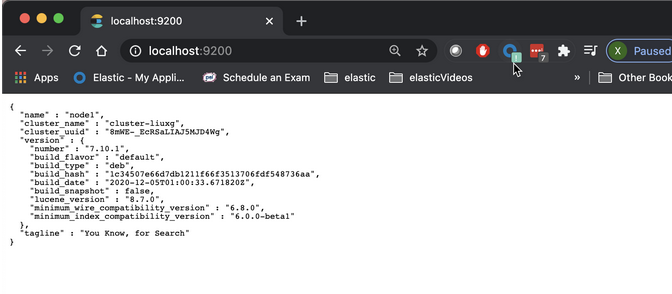
一旦我们启动这个容器,我们可以在 host 机器的命令行中打入如下的命令来进行查看:
curl -XGET http://localhost:9200
上面命令显示的结果为:
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200
{
"name" : "node1",
"cluster_name" : "cluster-liuxg",
"cluster_uuid" : "8mWE-_EcRSaLIAJ5MJD4Wg",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.10.1",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "deb",
"build_hash" : "1c34507e66d7db1211f66f3513706fdf548736aa",
"build_date" : "2020-12-05T01:00:33.671820Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.7.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
从上面我们可以看出来 cluster_name 以及 node 名字都是我们之前在 elasticsearch.yml 中所设置的。我们可以在浏览器中访问 localhost:9200 查看: