- 实验环境linux mint下面 QT5.11
- execlp失败时返回
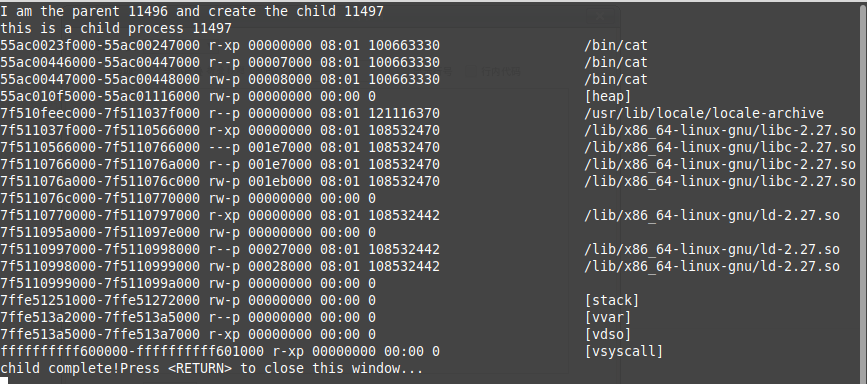
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<sys/types.h> int main() { pid_t pid; pid_t pid2; pid=fork(); char buf[1024]; if(pid==0) { pid2=getpid(); printf("this is a child process %d ",pid2); sprintf(buf,"/proc/%d/maps",pid2);//显示进程映射了的内存区域和访问权限 execlp("/bin/cat","cat",buf,NULL); } else { printf("I am the parent %d and create the child %d ",getpid(),pid); sleep(40); wait(NULL); printf("child complete!"); } return 0; }
输出结果:
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<sys/types.h> #include<fcntl.h> int main() { int fd; fd=open("monolog.txt",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0644); if(fd<0) { perror("open monolog.txt "); exit(1); } dup2(fd,STDOUT_FILENO);//把屏幕输出重定向到文件描述符 execlp("ps","ps","ax",NULL); return 0; }
操作结果:文件目录下生成文件,写入monolog.txt
- execv
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<sys/types.h> int main() { pid_t pid; pid=fork(); if(pid==-1) { perror("fork error"); exit(-1); } else if(pid>0) { sleep(10); printf("parent "); } else { char *argv[]={"ls","-1","-a","-h",NULL}; execv("/bin/ls",argv); } return 0; }