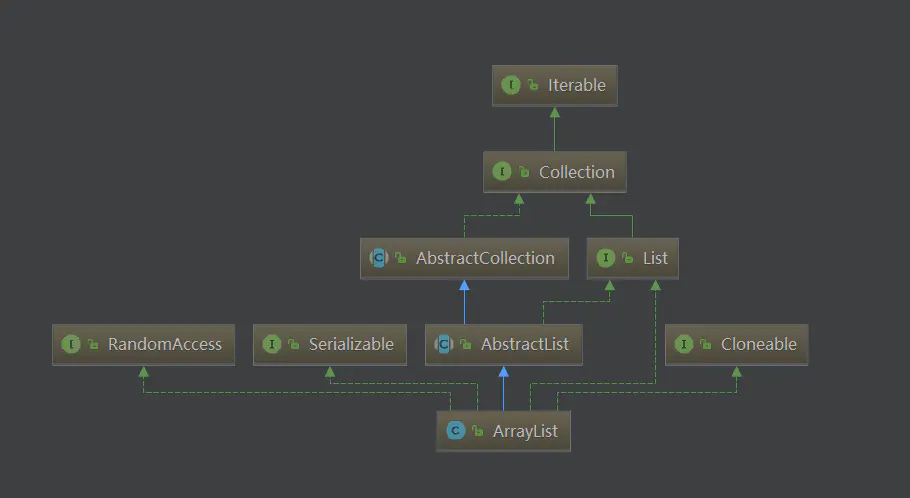
- 基于数组实现,是一个动态数组,其容量能自动增长。
- ArrayList不是线程安全的,建议在单线程中使用,多线程可以选择Vector或CopyOnWriteArrayList。
- 实现了RandomAccess接口,可以通过下标序号进行快速访问。
- 实现了Cloneable接口,能被克隆。
- 实现了Serializable接口,支持序列化。
ArrayList源码分析
展示部分源码:

public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { /** * Default initial capacity. 默认初始容量 */ private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; /** * Shared empty array instance used for empty instances. */ private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; /** * Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when first element is added. */ private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; /** * The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any empty ArrayList with * elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added. 使用DEFAULT**的集合,添加第一个元素时,扩展到默认容量 */ transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access /** * The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains). * @serial */ private int size; /** * Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity. 有参构造函数 * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity is negative */ public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity > 0) { this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); } } /** * Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten. 无参构造函数 */ public ArrayList() { this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } /** * Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's iterator. 有参构造函数,集合转成ArrayList * @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null */ public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { elementData = c.toArray(); if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) { // c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652) if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); } else { // replace with empty array. this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } } /** * The maximum size of array to allocate. Some VMs reserve some header words in an array. Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in * OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit 最大数组大小 */ private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; /** * Returns the number of elements in this list. * @return the number of elements in this list */ public int size() { return size; } /** * Returns <tt>true</tt> if this list contains no elements. * @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contains no elements */ public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; } /** * Returns <tt>true</tt> if this list contains the specified element. More formally, returns <tt>true</tt> if and only if this list contains * at least one element <tt>e</tt> such that <tt>(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))</tt>. * @param o element whose presence in this list is to be tested * @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contains the specified element */ public boolean contains(Object o) { return indexOf(o) >= 0; } /** * Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element. * More formally, returns the lowest index <tt>i</tt> such that <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>, or -1 if there is no such index. */ public int indexOf(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (elementData[i]==null) return i; } else { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1; } /** * Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element. * More formally, returns the highest index <tt>i</tt> such that <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>, or -1 if there is no such index. */ public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--) if (elementData[i]==null) return i; } else { for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1; } /** * Returns a shallow copy of this <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance. (The elements themselves are not copied.) 浅拷贝 * @return a clone of this <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance */ public Object clone() { try { ArrayList<?> v = (ArrayList<?>) super.clone(); v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); v.modCount = 0; return v; } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { // this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable throw new InternalError(e); } } /** * Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list in proper sequence (from first to last element). * @return an array containing all of the elements in this list in proper sequence */ public Object[] toArray() { return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); } /** * Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list in proper sequence (from first to last element); the runtime type of the returned * array is that of the specified array. If the list fits in the specified array, it is returned therein. Otherwise, a new array is * allocated with the runtime type of the specified array and the size of this list. 数组长度大于list长度,多余的会被赋值null * @param a the array into which the elements of the list are to be stored, if it is big enough; otherwise, a new array of the * same runtime type is allocated for this purpose. * @return an array containing the elements of the list*/ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { if (a.length < size) // Make a new array of a's runtime type, but my contents: return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, a.getClass()); System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, a, 0, size); if (a.length > size) a[size] = null; return a; } // Positional Access Operations @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E elementData(int index) { return (E) elementData[index]; } /** * Returns the element at the specified position in this list. * @param index index of the element to return * @return the element at the specified position in this list * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E get(int index) { rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index); } /** * Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the specified element. set方法会返回旧值 * * @param index index of the element to replace * @param element element to be stored at the specified position * @return the element previously at the specified position * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E set(int index, E element) { rangeCheck(index); E oldValue = elementData(index); elementData[index] = element; return oldValue; } /** * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. * * @param e element to be appended to this list * @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) */ public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! elementData[size++] = e; return true; } /** * Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and * any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices). 在指定位置增加元素,后面元素顺次后移 * * @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted * @param element element to be inserted * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public void add(int index, E element) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,size - index); elementData[index] = element; size++; } /** * Removes the element at the specified position in this list. Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their indices). * * @param index the index of the element to be removed * @return the element that was removed from the list * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E remove(int index) { rangeCheck(index); modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue; } /** * * @param o element to be removed from this list, if present * @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contained the specified element */ public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } else { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } return false; } /** * Removes all of the elements from this list. The list will be empty after this call returns. 清空集合 */ public void clear() { modCount++; // clear to let GC do its work for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null; size = 0; } /** * @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list * @return <tt>true</tt> if this list changed as a result of the call * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null */ public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0; } /** * Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this list, starting at the specified position. * * @param index index at which to insert the first element from the specified collection * @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list * @return <tt>true</tt> if this list changed as a result of the call*/ public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount int numMoved = size - index; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, numMoved); System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0; } /** * Removes from this list all of the elements whose index is between {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, and {@code toIndex}, exclusive.*/ protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { modCount++; int numMoved = size - toIndex; System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex, numMoved); // clear to let GC do its work int newSize = size - (toIndex-fromIndex); for (int i = newSize; i < size; i++) { elementData[i] = null; } size = newSize; }/** * Removes from this list all of its elements that are contained in the specified collection. * * @param c collection containing elements to be removed from this list * @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call * @see Collection#contains(Object) */ public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) { Objects.requireNonNull(c); return batchRemove(c, false); } /** * Retains only the elements in this list that are contained in the specified collection. In other words, removes from this list all * of its elements that are not contained in the specified collection. 从列表中删除所有未包含在指定集合中的元素 * * @param c collection containing elements to be retained in this list * @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call * @see Collection#contains(Object) */ public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) { Objects.requireNonNull(c); return batchRemove(c, true); } private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) { final Object[] elementData = this.elementData; int r = 0, w = 0; boolean modified = false; try { for (; r < size; r++) if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement) elementData[w++] = elementData[r]; } finally { // Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection, even if c.contains() throws. if (r != size) { System.arraycopy(elementData, r, elementData, w, size - r); w += size - r; } if (w != size) { // clear to let GC do its work for (int i = w; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null; modCount += size - w; size = w; modified = true; } } return modified; } /** * Save the state of the <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance to a stream (that is, serialize it).*/ private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)throws java.io.IOException{ // Write out element count, and any hidden stuff int expectedModCount = modCount; s.defaultWriteObject(); // Write out size as capacity for behavioural compatibility with clone() s.writeInt(size); // Write out all elements in the proper order. for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { s.writeObject(elementData[i]); } if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } /** * Reconstitute the <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance from a stream (that is, deserialize it). */ private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; // Read in size, and any hidden stuff s.defaultReadObject(); // Read in capacity s.readInt(); // ignored if (size > 0) { // be like clone(), allocate array based upon size not capacity ensureCapacityInternal(size); Object[] a = elementData; // Read in all elements in the proper order. for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { a[i] = s.readObject(); } } } @Override @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) { final int expectedModCount = modCount; Arrays.sort((E[]) elementData, 0, size, c); if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } modCount++; } }
总结:
- ArrayList 实际上是通过一个数组去保存数据的。当我们使用无参构造函数构造ArrayList时,则ArrayList的默认容量大小是10。
- 当ArrayList容量不足以容纳全部元素时,ArrayList会重新设置容量:新的容量=“(原始容量x3)/2 + 1”;如果设置后的新容量还不够,则直接把新容量设置为传入的参数。容量最大不超过 Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8
- ArrayList基于数组实现,可以通过下标索引直接查找到指定位置的元素,因此查找效率高,但每次插入或删除元素,就要大量地移动元素,插入删除元素的效率低。
- Object[] toArray()方法。该方法有可能会抛出java.lang.ClassCastException异常。toArray()返回的是 Object[] 数组,Java不支持向下转型。(例如,将Object[]转换为的Integer[])
- System.arraycopy()方法。该方法被标记了native,调用了系统的C/C++代码,该函数实际上最终调用了C语言的memmove()函数,因此它可以保证同一个数组内元素的正确复制和移动,比一般的复制方法的实现效率要高很多,很适合用来批量处理数组
