一、
题目描述
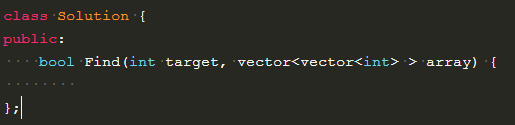
1、vector<vector<int> > array
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector< vector<int> > m(6);//m[i]返回的是第i个向量。同理,mmm6[i][j]返回的是第i个向量中第j个元素
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
m[i].resize(2); //指定向量大小,定义了一个6*2的数组
}
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
m[i][0]=i;
m[i][1]=i+1;
}//全部初始化为0</span>
for(int i=0;i<6;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<2;j++)
{
cout<<m[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
int n,r;
cout<<endl;
n=m.size();
r=m[0].size();
cout<<n<<" "<<r<<endl;
}

容器嵌套容器,获取二维数组的方式。通过这种方式可以为二维数据赋初值。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector< vector<int> > test; //输入n*n的方阵
vector<int> v;
int n,temp;
cin >> n;
test.clear();
//输入
for (int i = 0; i<n; i++) {
v.clear(); //每次记得clear:)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
cin >> temp;
v.push_back(temp); //插入temp
}
test.push_back(v);//整体插入 v
}
//输出
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0;j < n; j++)
{
cout << test[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
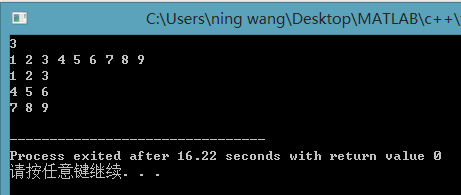
2、暴力解法
class Solution
{
public:
bool Find(int target, vector<vector<int> > array)
{
int n,m,x,y;
n=array.size();//行
m=array[0].size();//列
for (int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
{
if(array[i][j]==target)
{
return true;
break;
}
}
}
return false;
}
};
遍历一遍,全部输出。
时间复杂度(n^2)
3、利用矩阵已经从左到右从上到下排好序的特点,从左下角开始,如果比目标值大则上一行,如果比目标值小则向右移动。
class Solution
{
public:
bool Find(int target, vector<vector<int> > array)
{
int n,m,x=0,y;
n=array.size();//行
m=array[0].size();//列
n--;
while(x<m && n>=0)
{
if(target>array[n][x])
{
x++;
}
else if(target<array[n][x])
{
n--;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
class Solution
{
public:
bool Find(int target, vector<vector<int> > array)
{
int n,m,x=0,y;
n=array.size();//行
m=array[0].size();//列
n--;
while(x<m && n>=0 && target!=array[n][x])
{
if(target>array[n][x])
{
x++;
}
else if(target<array[n][x])
{
n--;
}
}
if(n<0 || x==m)
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
};
4、剑指offer书中的源程序

该程序传递的是位置指针,所以需要对位置特别清楚才行。不是下标[a][b],而是连续的a*b的空间。
二、
题目描述
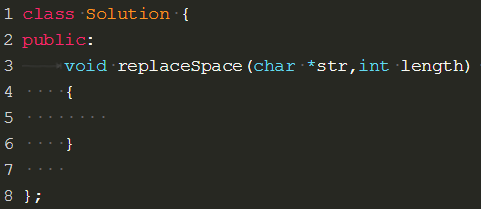
这是定义了一个字符型的变量空间,是char类型,而非string。所以处理起来注意地址位置的判断。
1、

越界的情况。


#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char a[]="hello world";
char b[]="hello world";
//cout<<a<<endl;
if(a==b)
cout<<"char a=b"<<endl;
else
cout<<"char a!=b"<<endl;
cout<<endl;
char a3[]="h";
char b3[]="h";
//cout<<a<<endl;
if(a==b)
cout<<"char a3=b3"<<endl;
else
cout<<"char a3!=b3"<<endl;
cout<<endl;
char a2='h';
char b2='h';
//cout<<a<<endl;
if(a2==b2)
cout<<"char a=b"<<endl;
else
cout<<"char a!=b"<<endl;
cout<<endl;
string a1="hello world";
string b1="hello world";
if(a1==b1)
cout<<"string a=b"<<endl;
else
cout<<"string a!=b"<<endl;
cout<<endl;
int A=5,B=5;
if(A==B)
cout<<"int A=B"<<endl;
else
cout<<"int A!=B"<<endl;
}
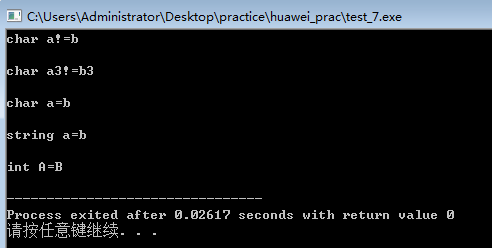
从加黄的代码可以看出,用常量内存初始化数组时,判断会将地址考虑到内。
2、
替换空格的实际应用

用string方法比较简单,遍历判断,+号连接。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
string ReplaceSpace(string str)
{
string s;
for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++)
{
if(str[i] == ' ')
s+="%20";
else
s+=str[i];
}
return s;
}
int main()
{
string str;
while(getline(cin,str))
{
cout<<ReplaceSpace(str);
}
}

还可以用find函数,string.erase() 和string.insert() 函数。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
string ReplaceSpace(string str)
{
int i=0;
while( (i=str.find(' ',i)) > -1)
{
str.erase(i,1);//从i开始,删除一个字符,即删除空格;
str.insert(i,"%20");
}
return str;
}
int main()
{
string str;
while(getline(cin,str))
{
cout<<ReplaceSpace(str);
}
}
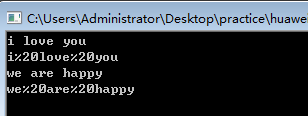
3、char 地址,并且void 没有返回,所以这是在原地址上修改字符串。
3.1

class Solution {
public:
void replaceSpace(char *str,int length)
{
for(int i=0;i<length;i++)
{
if(*(str+i)==' ')//长度加2,统一后移,由于只能一个一个位置移动,前面变化会对后面有硬性,所以得逆序
{
length+=2;
for(int j=length-1;j>=(i+3);j--)
{
*(str+j)=*(str+j-2); //逆序存放
}
*(str+i)='%';//空格部分替换
*(str+i+1)='2';
*(str+i+2)='0';
}
}
}
};
以上的方法是见一个空格移动一次,重复移动了很多次,时间复杂度太高。
class Solution {
public:
void replaceSpace(char *str,int length)
{
for(int i=0;i<length;i++)
{
if(str[i]==' ')//长度加2,统一后移,由于只能一个一个位置移动,前面变化会对后面有硬性,所以得逆序
{
length+=2;
for(int j=length-1;j>=(i+3);j--)
{
str[j]=str[j-2]; //逆序存放
}
str[i]='%';//空格部分替换
str[i+1]='2';
str[i+2]='0';
}
}
}
};
下标的方法。
3.2
首先就判断出所有的空格,进而判断出替换 后的总长度,再只需一次移动,和替换,完成任务。
class Solution {
public:
void replaceSpace(char *str,int length)
{
int n=0;
for(int i=0;i<length;i++)
{
if(str[i]==' ')
{
n++;
}
}
int L=length+n*2-1;//替换后的下标
for(int i=length-1;i>=0;i--)
{
if(str[i]!=' ')//添加字符
{
str[L]=str[i];
L--;
}
else //替换为%20
{
str[L]='0';
str[L-1]='2';
str[L-2]='%';
L=L-3;
}
}
}
};
两个数分别来表示替换前和替换后的下标的方法值得学习。
三、
题目描述
n<=39
1、1、2、3、5、8、13、21、34、……
1、递归计算,重复计算很多,但是代码简单
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int Dp(int n)
{
if(n==1 || n==2)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return Dp(n-1)+Dp(n-2);
}
}
int Fibonacci(int n)
{
return Dp(n);
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(cin>>n)
{
cout<<Fibonacci(n)<<endl;
}
}
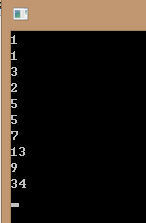
2、牛客中通过不了
class Solution {
public:
int Dp(int n)
{
if(n==1 || n==2)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return Dp(n-1)+Dp(n-2);
}
}
int Fibonacci(int n)
{
return Dp(n);
}
};
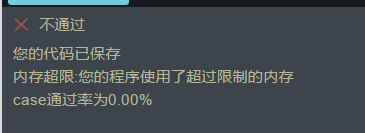
3、使用递推的代码
class Solution {
public:
int Fibonacci(int n)
{
if(n==0)
return 0;
else if(n==1 or n==2)
return 1;
int n1=1,n2=1,r=0;
for(int i=3;i<=n;i++)
{
r=n1+n2;
n1=n2;
n2=r;
}
return r;
}
};
四、
题目描述
class Solution {
public:
int Num[10000]={0};
int jumpFloor(int number)
{
Num[1]=1;
Num[2]=2;
for(int i=3;i<=number;i++)
{
Num[i]=Num[i-1]+Num[i-2];
}
return Num[number];
}
};
一定注意题目是求多少种方法,而不是求上了多少次台阶,所以递归关系中不用加1。
五、
题目描述
class Solution {
public:
int Num[10000]={0};
int jumpFloorII(int number)
{
Num[1]=1;
Num[2]=2;
for(int i=3;i<=number;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<i;j++)
Num[i]+=Num[j];
Num[i]++; //直接跳到n台阶的情况,加1
}
return Num[number];
}
};
递推关系发生变化f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2)+...+f(1)+1;
六、
题目描述

可以看出,n是在n-1和n-2的基础上进行扩展,所以递推关系还是f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2);
class Solution {
public:
int Num[10000]={0};
int rectCover(int number)
{
Num[1]=1;
Num[2]=2;
for(int i=3;i<=number;i++)
{
Num[i]=Num[i-1]+Num[i-2];
}
return Num[number];
}
};
七、