一、指针
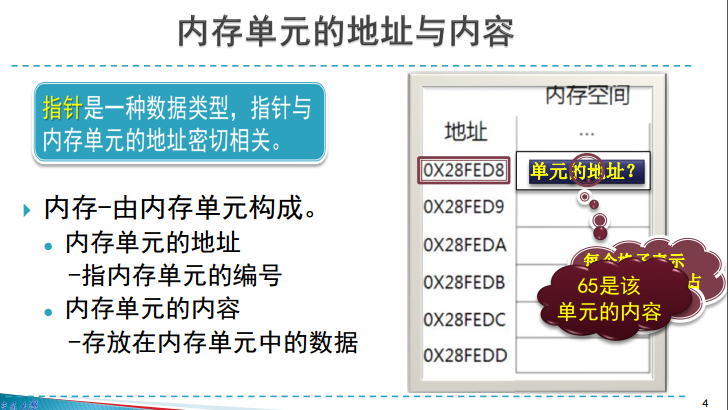

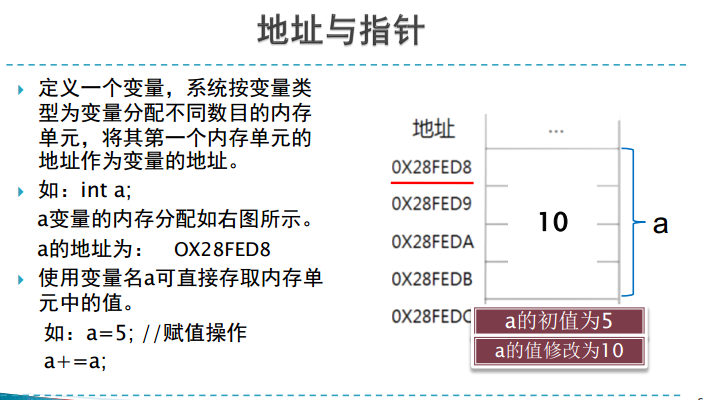
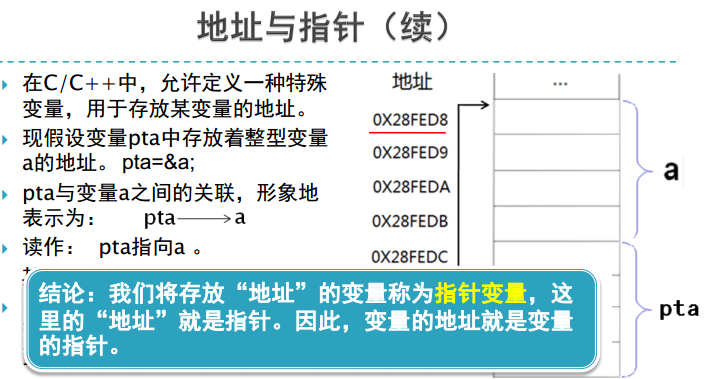
二、变量与指针
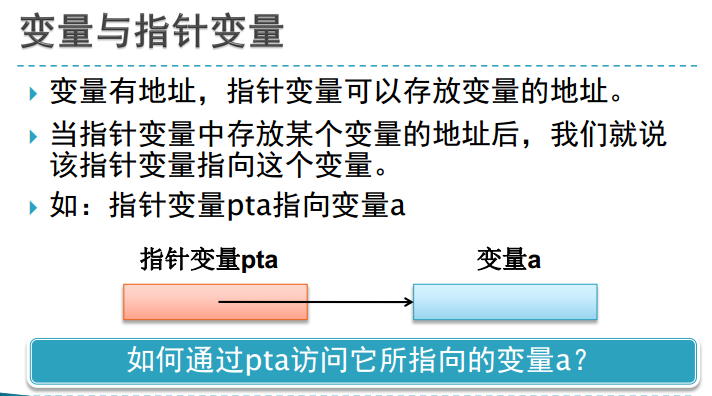


 注意区别char 和char *。
注意区别char 和char *。

 !!!!!!!
!!!!!!!



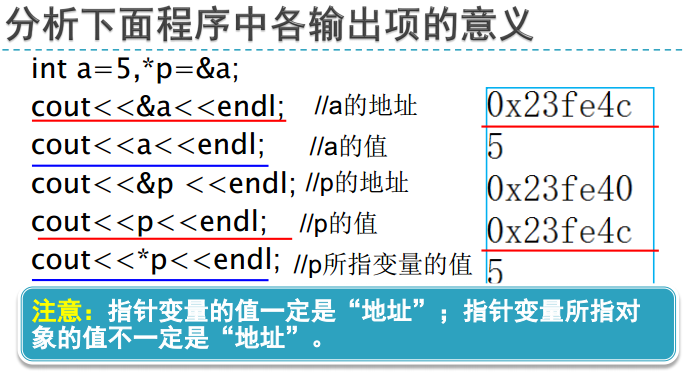

二、函数与指针


#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
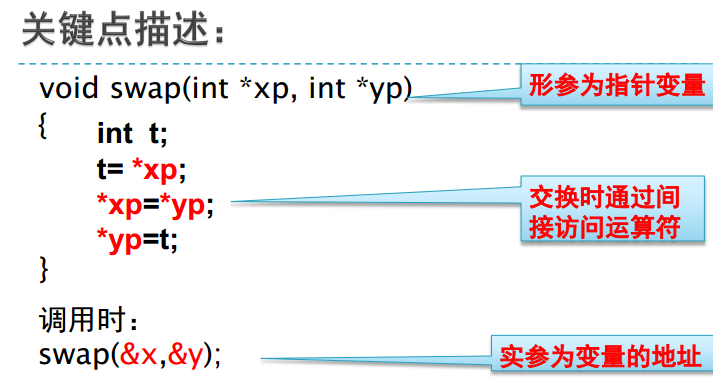
void swap(int *px,int *py)
{
int t;
t=*px;
*px=*py;
*py=t;
};
int main()
{
int x=2,y=3;
cout<<"调用前:x="<<x<<",y="<<y<<endl;
swap(&x,&y);
cout<<"调用后:x="<<x<<",y="<<y<<endl;
}

#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
double faver(int a[],int n,int *max,int *min)
{
double aver=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
aver+=a[i];
*max=*min=a[0];
if(*max<a[i])
*max=a[i];
if(*min>a[i])
*min=a[i];
}
return aver/n;
};
int main()
{
int s[]={1,3,5,6,7,8},min,max,n=6;
double aver;
aver=faver(s,n,&max,&min);
cout<<"average="<<aver<<endl;
cout<<"max="<<max<<" min="<<min<<endl;
}
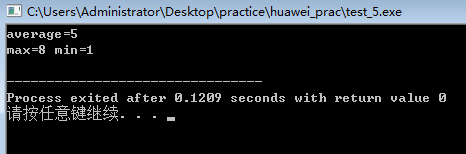
注意1、通过指针这种形式,可以将最大和最小值,平均值带回主函数,通过return的话只能带回一个数。2、调用就用&,定义就用*。


#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
char *noblank(char *str)
{
while(*str=='')
str++;
return str;
}
int main()
{
char *s1=" using namespace std;";
char *s2;
s2=noblank(s1);
cout<<s2<<endl;
return 0;
}
觉得这个例子有点扯

三、数组与指针

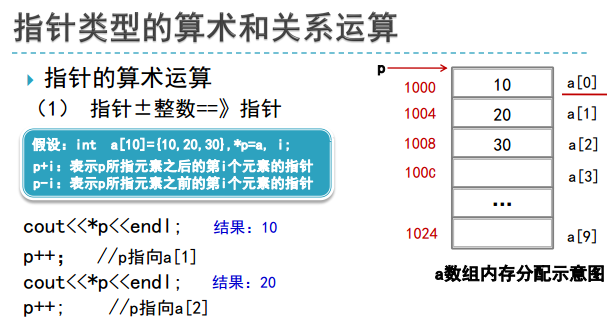
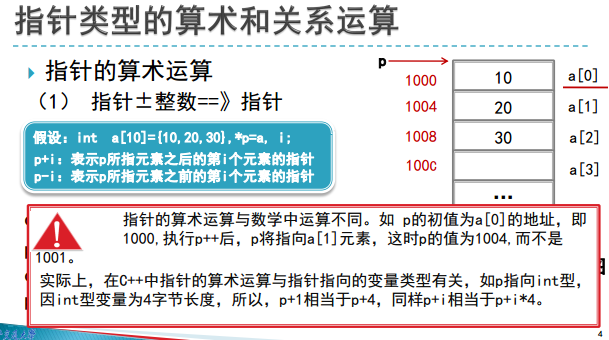
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//int a[10]={10,20,30},*p=a,i;
int a[10]={10,20,30},i,*p;
p=a;
cout<<p<<" "<<*p<<endl;
p++;
cout<<p<<" "<<*p<<endl;
}
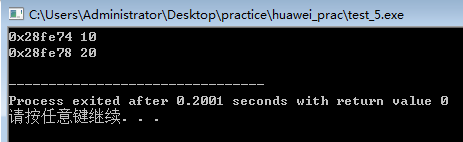

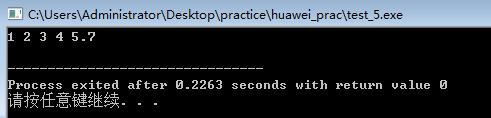
2、指针的关系运算

#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double x[5]={1,2,3,4,5.7},*p;
for(p=x;p<x+5;p++)
{
cout<<*p<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}


#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[5]={1,2,3,4,5},i;
cout<<"a[i]:";
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
cout<<"*(a+i):";
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<*(a+i)<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
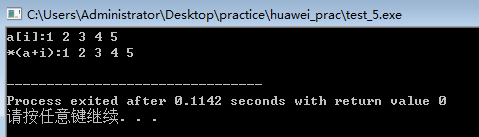
可以看到(a)是地址
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[5]={1,2,3,4,5},*p=a,i;
cout<<"a[i]:";
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
cout<<"*(a+i):";
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<*(a+i)<<" ";
cout<<endl;
cout<<"p[i]:";
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<p[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
cout<<"*(p+i):";
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<*(p+i)<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
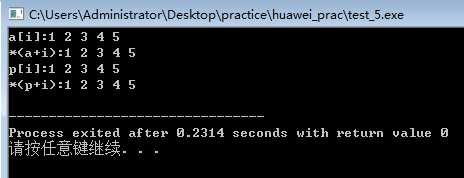
3、二维数组

#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[2][2]={1,2,4,5},*p;
int max=a[0][0];
for(p=&a[0][0];p<&a[0][0]+4;p++)
{
if(max<*p)
max=*p;
}
cout<<max<<endl;
}
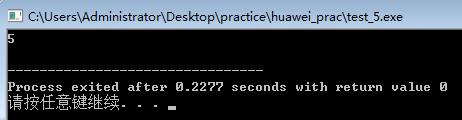




#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[2][3]={1,2,3,4,5,6},(*p)[3];
for(p=a;p<a+2;p++)
{
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
cout<<*(*p+i)<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
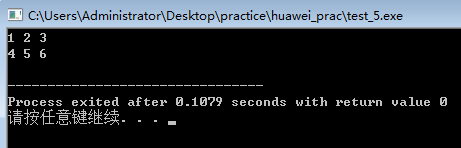


例子

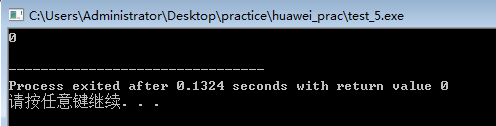
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
char *strchr(char *str,char c)
{
while(*str!='�')
{
if(*str==c)
return str;
str++;
}
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
char *str="abcdefghij";
char *p;
p=strchr(str,'a');
if(p==NULL)
cout<<"Null";
else
cout<<p-str<<endl;
}

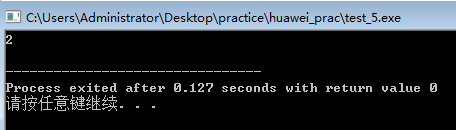
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
char *strchr(char *str,char c)
{
while(*str!='�')
{
if(*str==c)
return str;
str++;
}
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
char str[]="abcdefghij";
char *p;
p=strchr(str,'c');
if(p==NULL)
cout<<"Null";
else
cout<<p-str<<endl;
}

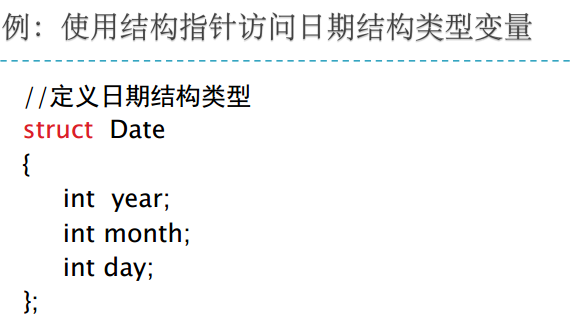
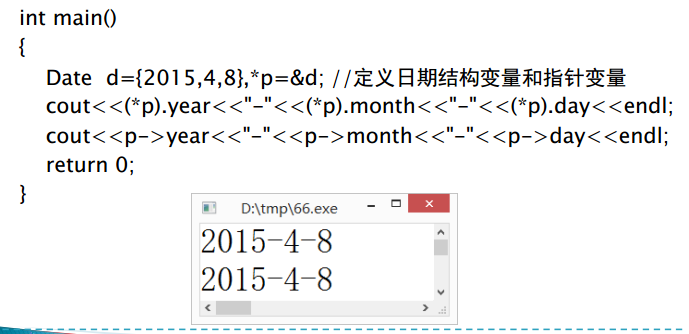
5、指针与结构体

6、动态数组





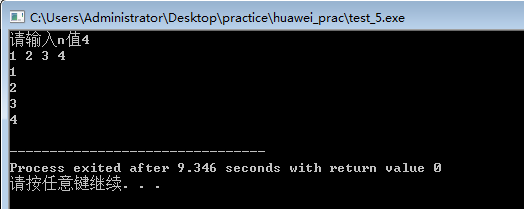
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n,*p;
cout<<"请输入n值";
cin>>n;
p=new int[n];
if(p==NULL)
{
cout<<"空间申请失败";
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
cin>>p[i];
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
cout<<p[j]<<" "<<endl;
return 0;
}