#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
class A:
arr=[]
@classmethod
def push(cls,i):
cls.arr=[i]+cls.arr
@classmethod
def pop(cls):
ret=cls.arr[0]
cls.arr=cls.arr[1:]
return ret
A.arr=[66,661,662,663]
for i in range(10):
A.push(i)
import pprint
pprint.pprint(A.arr)
ret=A.pop()
pprint.pprint(A.arr)
小结:
1、
借助linkedlist,每次添加元素后,反转,取逆序
Implement Stack using Queues - LeetCode
https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-stack-using-queues/solution/
Implement Stack using Queues - LeetCode Articles
https://leetcode.com/articles/implement-stack-using-queues/
使用队列实现栈的下列操作:
- push(x) -- 元素 x 入栈
- pop() -- 移除栈顶元素
- top() -- 获取栈顶元素
- empty() -- 返回栈是否为空
注意:
- 你只能使用队列的基本操作-- 也就是
push to back,peek/pop from front,size, 和is empty这些操作是合法的。 - 你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
- 你可以假设所有操作都是有效的(例如, 对一个空的栈不会调用 pop 或者 top 操作)。
Approach #1 (Two Queues, push - O(1), pop O(n))
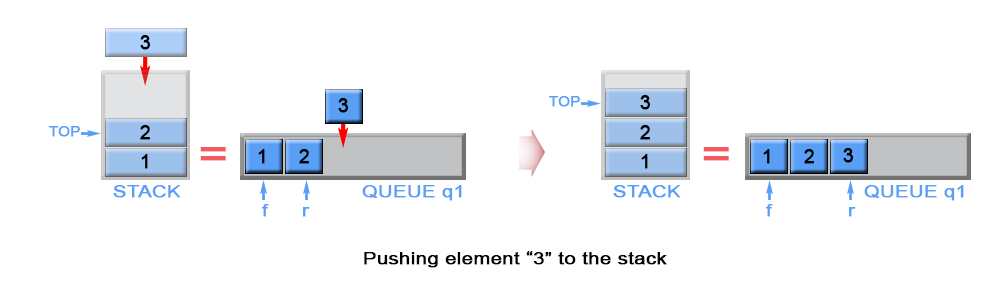
Approach #2 (Two Queues, push - O(n), pop O(1) )
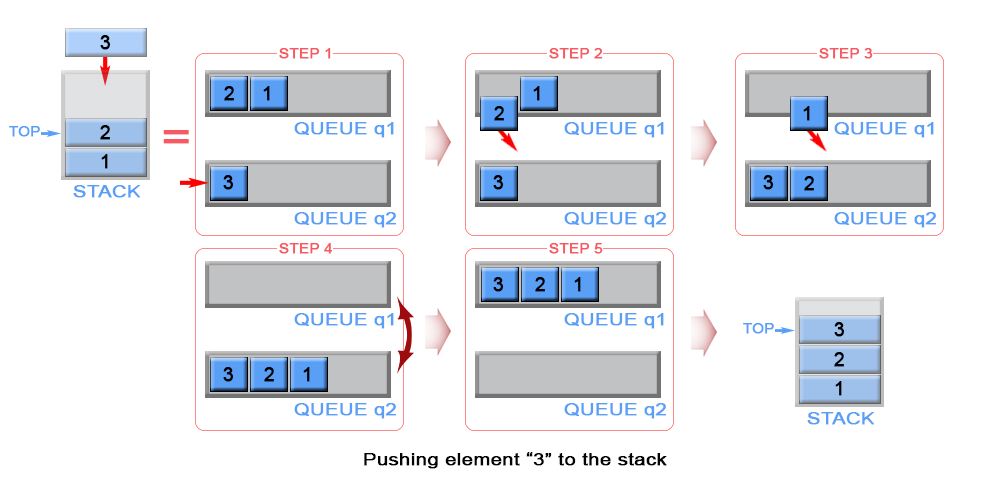
Approach #3 (One Queue, push - O(n), pop O(1))

package leetcode;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class MyStack {
//one Queue solution
private Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyStack myStack = new MyStack();
myStack.push(-2);
myStack.push(0);
myStack.push(-3);
myStack.push(13);
myStack.pop();
myStack.top();
}
// Push element x onto stack.
public void push(int x) {
q.add(x);
for (int i = 1; i < q.size(); i++) { //rotate the queue to make the tail be the head
q.add(q.poll());
}
}
// Removes the element on top of the stack.
public int pop() {
return q.poll();
}
// Get the top element.
public int top() {
return q.peek();
}
// Return whether the stack is empty.
public boolean empty() {
return q.isEmpty();
}
}
class MyStack:
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize your data structure here.
"""
self.myqueue=[]
def push(self, x: int) -> None:
"""
Push element x onto stack.
"""
self.myqueue=[x]+self.myqueue
def pop(self) -> int:
"""
Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element.
"""
ret=self.myqueue[0]
self.myqueue=self.myqueue[1:]
return ret
def top(self) -> int:
"""
Get the top element.
"""
ret=self.myqueue[0]
return ret
def empty(self) -> bool:
"""
Returns whether the stack is empty.
"""
return len(self.myqueue)==0
# Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = MyStack()
# obj.push(x)
# param_2 = obj.pop()