实践:
1)
vim /lib/systemd/system/WebSvc.service
[Unit]
Description=WebSvc service
[Service]
Type=forking
RemainAfterExit=no
ExecStart=/bin/sh /home/testWebSvc/systemctWebSvc.sh
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
CMD
systemctl enable WebSvc;
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/WebSvc.service to /lib/systemd/system/WebSvc.service.
#!/bin/bash
sleep 1s
/usr/bin/nohup /home/test/WebSvc -conf /home/test/WebSvc/configs/config.yaml > /dev/null 2>&1 &
systemctl --help
systemctl [OPTIONS...] {COMMAND} ...
Query or send control commands to the systemd manager.
-h --help Show this help
--version Show package version
--system Connect to system manager
--user Connect to user service manager
-H --host=[USER@]HOST
Operate on remote host
-M --machine=CONTAINER
Operate on local container
-t --type=TYPE List units of a particular type
--state=STATE List units with particular LOAD or SUB or ACTIVE state
-p --property=NAME Show only properties by this name
-a --all Show all loaded units/properties, including dead/empty
ones. To list all units installed on the system, use
the 'list-unit-files' command instead.
-l --full Don't ellipsize unit names on output
-r --recursive Show unit list of host and local containers
--reverse Show reverse dependencies with 'list-dependencies'
--job-mode=MODE Specify how to deal with already queued jobs, when
queueing a new job
--show-types When showing sockets, explicitly show their type
-i --ignore-inhibitors
When shutting down or sleeping, ignore inhibitors
--kill-who=WHO Who to send signal to
-s --signal=SIGNAL Which signal to send
--now Start or stop unit in addition to enabling or disabling it
-q --quiet Suppress output
--no-block Do not wait until operation finished
--no-wall Don't send wall message before halt/power-off/reboot
--no-reload Don't reload daemon after en-/dis-abling unit files
--no-legend Do not print a legend (column headers and hints)
--no-pager Do not pipe output into a pager
--no-ask-password
Do not ask for system passwords
--global Enable/disable unit files globally
--runtime Enable unit files only temporarily until next reboot
-f --force When enabling unit files, override existing symlinks
When shutting down, execute action immediately
--preset-mode= Apply only enable, only disable, or all presets
--root=PATH Enable unit files in the specified root directory
-n --lines=INTEGER Number of journal entries to show
-o --output=STRING Change journal output mode (short, short-iso,
short-precise, short-monotonic, verbose,
export, json, json-pretty, json-sse, cat)
--firmware-setup Tell the firmware to show the setup menu on next boot
--plain Print unit dependencies as a list instead of a tree
lines 27-49
--kill-who=WHO Who to send signal to
-s --signal=SIGNAL Which signal to send
--now Start or stop unit in addition to enabling or disabling it
-q --quiet Suppress output
--no-block Do not wait until operation finished
--no-wall Don't send wall message before halt/power-off/reboot
--no-reload Don't reload daemon after en-/dis-abling unit files
--no-legend Do not print a legend (column headers and hints)
--no-pager Do not pipe output into a pager
--no-ask-password
Do not ask for system passwords
--global Enable/disable unit files globally
--runtime Enable unit files only temporarily until next reboot
-f --force When enabling unit files, override existing symlinks
When shutting down, execute action immediately
--preset-mode= Apply only enable, only disable, or all presets
--root=PATH Enable unit files in the specified root directory
-n --lines=INTEGER Number of journal entries to show
-o --output=STRING Change journal output mode (short, short-iso,
short-precise, short-monotonic, verbose,
export, json, json-pretty, json-sse, cat)
--firmware-setup Tell the firmware to show the setup menu on next boot
--plain Print unit dependencies as a list instead of a tree
Unit Commands:
list-units [PATTERN...] List loaded units
list-sockets [PATTERN...] List loaded sockets ordered by address
list-timers [PATTERN...] List loaded timers ordered by next elapse
start NAME... Start (activate) one or more units
stop NAME... Stop (deactivate) one or more units
reload NAME... Reload one or more units
restart NAME... Start or restart one or more units
try-restart NAME... Restart one or more units if active
reload-or-restart NAME... Reload one or more units if possible,
otherwise start or restart
try-reload-or-restart NAME... If active, reload one or more units,
if supported, otherwise restart
isolate NAME Start one unit and stop all others
kill NAME... Send signal to processes of a unit
is-active PATTERN... Check whether units are active
is-failed PATTERN... Check whether units are failed
status [PATTERN...|PID...] Show runtime status of one or more units
show [PATTERN...|JOB...] Show properties of one or more
units/jobs or the manager
cat PATTERN... Show files and drop-ins of one or more units
set-property NAME ASSIGNMENT... Sets one or more properties of a unit
help PATTERN...|PID... Show manual for one or more units
reset-failed [PATTERN...] Reset failed state for all, one, or more
units
list-dependencies [NAME] Recursively show units which are required
or wanted by this unit or by which this
unit is required or wanted
Unit File Commands:
list-unit-files [PATTERN...] List installed unit files
enable NAME... Enable one or more unit files
disable NAME... Disable one or more unit files
reenable NAME... Reenable one or more unit files
preset NAME... Enable/disable one or more unit files
based on preset configuration
preset-all Enable/disable all unit files based on
preset configuration
is-enabled NAME... Check whether unit files are enabled
mask NAME... Mask one or more units
unmask NAME... Unmask one or more units
link PATH... Link one or more units files into
the search path
add-wants TARGET NAME... Add 'Wants' dependency for the target
on specified one or more units
add-requires TARGET NAME... Add 'Requires' dependency for the target
on specified one or more units
edit NAME... Edit one or more unit files
get-default Get the name of the default target
set-default NAME Set the default target
Machine Commands:
list-machines [PATTERN...] List local containers and host
Job Commands:
list-jobs [PATTERN...] List jobs
cancel [JOB...] Cancel all, one, or more jobs
Environment Commands:
show-environment Dump environment
set-environment NAME=VALUE... Set one or more environment variables
unset-environment NAME... Unset one or more environment variables
import-environment [NAME...] Import all or some environment variables
Manager Lifecycle Commands:
daemon-reload Reload systemd manager configuration
daemon-reexec Reexecute systemd manager
System Commands:
is-system-running Check whether system is fully running
default Enter system default mode
rescue Enter system rescue mode
emergency Enter system emergency mode
halt Shut down and halt the system
poweroff Shut down and power-off the system
reboot [ARG] Shut down and reboot the system
kexec Shut down and reboot the system with kexec
exit [EXIT_CODE] Request user instance or container exit
switch-root ROOT [INIT] Change to a different root file system
suspend Suspend the system
hibernate Hibernate the system
hybrid-sleep Hibernate and suspend the system
lines 91-132/132 (END)
systemctl开机启动设置_龙哥哥的博客-CSDN博客_systemctl 开机启动 https://blog.csdn.net/tl4832194/article/details/109781230
常用的systemctl命令
以sshd服务为例,列出常用systemctl命令:
启动sshd服务:systemctl start ssh.service
停止sshd服务:systemctl stop ssh.service
查看sshd服务状态:systemctl status ssh.service
重启sshd服务:systemctl restart ssh.service
设置开机自启动:systemctl enable ssh.service
禁止开机自启动:systemctl disable ssh.service
查看所有已经启动的服务:systemctl list-units --type=service
重新加载配置文件:systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl启动服务编写
Centos7的服务systemctl脚本存放在:/usr/lib/systemd/目录下,有系统(system)和用户(user)之分,一般需要开机不登录就能运行的程序,就存放在/usr/lib/systemd/system/目录下
每一个服务以.service结尾,一般会分为3部分:[Unit]、[Service]和[Install],以sshd为实例如下:
[Unit]
Description=OpenSSH server daemon
Documentation=man:sshd(8) man:sshd_config(5)
After=network.target sshd-keygen.service
Wants=sshd-keygen.service
[Service]
Type=notify
EnvironmentFile=/etc/sysconfig/sshd
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/sshd -D $OPTIONS
ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID
KillMode=process
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=42s
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
[Unit]部分主要是对这个服务的说明,内容包括Description和After,Description 用于描述服务,After用于描述服务类别;
[Service]部分是服务的关键,是服务的一些具体运行参数的设置;
[Install]部分是服务安装的相关设置,可设置为多用户的;
配置文件详解
Unit
After 表示服务需要在***服务启动之后执行 无依赖
Before 表示服务需要在***服务启动之前执行 无依赖
Wants 弱依赖关系
Requires 强依赖关系 ***停止之后本服务也必须停止
Service
ExecStart 启动进程时执行的命令
ExecReload 重启服务时执行的命令
ExecStop 停止服务时执行的命令
ExecStartPre 启动服务之前执行的命令
ExecStartPost 启动服务之后执行的命令
ExecStopPost 停止服务之后执行的命令
所有的启动设置之前,都可以加上一个 连词号(-),表示"抑制错误", 即发生错误的时候,不影响其他命令的执行。比如,EnvironmentFile=-/etc/sysconfig/sshd(注意等号后面的那个连词号),就表示即使/etc/sysconfig/sshd文件不存在,也不会抛出错误。
type参数说明
simple(默认值) ExecStart字段启动的进程为主进程
forking ExecStart字段将以fork()方式启动,此时父进程将会退出,子进程将成为主进程
oneshot 类似于simple,但只执行一次,Systemd 会等它执行完,才启动其他服务
dbus 类似于simple,但会等待 D-Bus 信号后启动
notify 类似于simple,启动结束后会发出通知信号,然后 Systemd 再启动其他服务
idle 类似于simple,但是要等到其他任务都执行完,才会启动该服务。一种使用场合是为让该服务的输出,不与其他服务的输出相混合
KillMode参数说明
control-group(默认值) 当前控制组里面的所有子进程,都会被杀掉
process 只杀主进程
mixed 主进程将收到 SIGTERM 信号,子进程收到 SIGKILL 信号
none 没有进程会被杀掉,只是执行服务的 stop 命令。
Restart参数说明
no(默认值) 退出后不会重启
on-success 只有正常退出时(退出状态码为0),才会重启
on-failure 非正常退出时(退出状态码非0),包括被信号终止和超时,才会重启
on-abnormal 只有被信号终止和超时,才会重启
on-abort 只有在收到没有捕捉到的信号终止时,才会重启
on-watchdog 超时退出,才会重启
always 不管是什么退出原因,总是重启
修改配置文件以后,需要重新加载配置文件,然后重新启动相关服务。
重新加载配置文件
systemctl daemon-reload
1
Linux 服务管理两种方式service和systemctl - 迪米特 - 博客园 https://www.cnblogs.com/shijingjing07/p/9301590.html
Linux 服务管理两种方式service和systemctl
1.service命令
service命令其实是去/etc/init.d目录下,去执行相关程序
# service命令启动redis脚本
service redis start
# 直接启动redis脚本
/etc/init.d/redis start
# 开机自启动
update-rc.d redis defaults
其中脚本需要我们自己编写
2.systemctl命令
systemd是Linux系统最新的初始化系统(init),作用是提高系统的启动速度,尽可能启动较少的进程,尽可能更多进程并发启动。
systemd对应的进程管理命令是systemctl
1)systemctl命令兼容了service
即systemctl也会去/etc/init.d目录下,查看,执行相关程序
systemctl redis start
systemctl redis stop
# 开机自启动
systemctl enable redis
2)systemctl命令管理systemd的资源Unit
systemd的Unit放在目录/usr/lib/systemd/system(Centos)或/etc/systemd/system(Ubuntu)
主要有四种类型文件.mount,.service,.target,.wants
.mount文件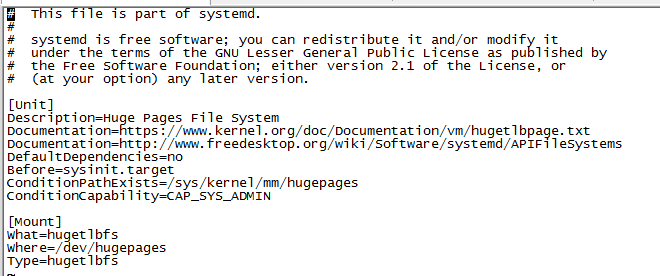
.mount文件定义了一个挂载点,[Mount]节点里配置了What,Where,Type三个数据项
等同于以下命令:
mount -t hugetlbfs /dev/hugepages hugetlbfs
.service文件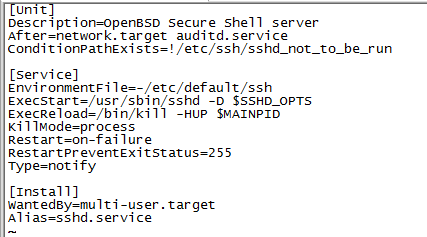
.service文件定义了一个服务,分为[Unit],[Service],[Install]三个小节
[Unit]
Description:描述,
After:在network.target,auditd.service启动后才启动
ConditionPathExists: 执行条件
[Service]
EnvironmentFile:变量所在文件
ExecStart: 执行启动脚本
Restart: fail时重启
[Install]
Alias:服务别名
WangtedBy: 多用户模式下需要的
.target文件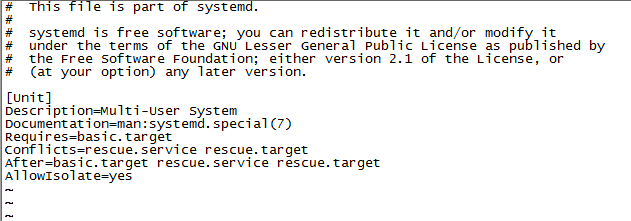
.target定义了一些基础的组件,供.service文件调用
.wants文件
.wants文件定义了要执行的文件集合,每次执行,.wants文件夹里面的文件都会执行
Web进程的服务化
cd /lib/systemd/system;
vim WebSvc.service
[Unit]
Description=WebSvc service
[Service]
Type=forking
RemainAfterExit=no
ExecStart=/bin/sh /home/test/WebSvc/LinuxWebSvc.sh
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
开机启动
systemctl enable WebSvc
sudo systemctl daemon-reload;sudo systemctl start WebSvc;
sudo systemctl daemon-reload;sudo systemctl restart WebSvc;
sudo systemctl status WebSvc.service;
sudo systemctl stop WebSvc;
cat LinuxWebSvc.sh
sleep 8s # TODO 等待启动依赖的程序启动
/usr/bin/nohup /home/test/WebSvc -conf /home/test/configs/config.yaml > /dev/null&
Linux使用systemctl设置程序开机自启动_sayyy的专栏-CSDN博客_systemctl 开机自启动 https://blog.csdn.net/sayyy/article/details/79276575
/etc/init.d$ cat mysql
# Start MySQL!
su - mysql -s /bin/sh -c "/usr/bin/mysqld_safe > /dev/null 2>&1 &"
/etc/init.d$ cat mysql
#!/bin/bash
#
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: mysql
# Required-Start: $remote_fs $syslog
# Required-Stop: $remote_fs $syslog
# Should-Start: $network $time
# Should-Stop: $network $time
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: Start and stop the mysql database server daemon
# Description: Controls the main MySQL database server daemon "mysqld"
# and its wrapper script "mysqld_safe".
### END INIT INFO
#
set -e
set -u
${DEBIAN_SCRIPT_DEBUG:+ set -v -x}
test -x /usr/bin/mysqld_safe || exit 0
. /lib/lsb/init-functions
SELF=$(cd $(dirname $0); pwd -P)/$(basename $0)
CONF=/etc/mysql/my.cnf
MYADMIN="/usr/bin/mysqladmin --defaults-file=/etc/mysql/debian.cnf"
# priority can be overriden and "-s" adds output to stderr
ERR_LOGGER="logger -p daemon.err -t /etc/init.d/mysql -i"
# Safeguard (relative paths, core dumps..)
cd /
umask 077
# mysqladmin likes to read /root/.my.cnf. This is usually not what I want
# as many admins e.g. only store a password without a username there and
# so break my scripts.
export HOME=/etc/mysql/
## Fetch a particular option from mysql's invocation.
#
# Usage: void mysqld_get_param option
mysqld_get_param() {
/usr/sbin/mysqld --print-defaults \
| tr " " "\n" \
| grep -- "--$1" \
| tail -n 1 \
| cut -d= -f2
}
## Do some sanity checks before even trying to start mysqld.
sanity_checks() {
# check for config file
if [ ! -r /etc/mysql/my.cnf ]; then
log_warning_msg "$0: WARNING: /etc/mysql/my.cnf cannot be read. See README.Debian.gz"
echo "WARNING: /etc/mysql/my.cnf cannot be read. See README.Debian.gz" | $ERR_LOGGER
fi
# check for diskspace shortage
datadir=`mysqld_get_param datadir`
if LC_ALL=C BLOCKSIZE= df --portability $datadir/. | tail -n 1 | awk '{ exit ($4>4096) }'; then
log_failure_msg "$0: ERROR: The partition with $datadir is too full!"
echo "ERROR: The partition with $datadir is too full!" | $ERR_LOGGER
exit 1
fi
}
## Checks if there is a server running and if so if it is accessible.
#
# check_alive insists on a pingable server
# check_dead also fails if there is a lost mysqld in the process list
#
# Usage: boolean mysqld_status [check_alive|check_dead] [warn|nowarn]
mysqld_status () {
ping_output=`$MYADMIN ping 2>&1`; ping_alive=$(( ! $? ))
ps_alive=0
pidfile=`mysqld_get_param pid-file`
if [ -f "$pidfile" ] && ps `cat $pidfile` >/dev/null 2>&1; then ps_alive=1; fi
if [ "$1" = "check_alive" -a $ping_alive = 1 ] ||
[ "$1" = "check_dead" -a $ping_alive = 0 -a $ps_alive = 0 ]; then
return 0 # EXIT_SUCCESS
else
if [ "$2" = "warn" ]; then
echo -e "$ps_alive processes alive and '$MYADMIN ping' resulted in\n$ping_output\n" | $ERR_LOGGER -p daemon.debug
fi
return 1 # EXIT_FAILURE
fi
}
#
# main()
#
case "${1:-''}" in
'start')
sanity_checks;
# Start daemon
log_daemon_msg "Starting MySQL database server" "mysqld"
if mysqld_status check_alive nowarn; then
log_progress_msg "already running"
log_end_msg 0
else
# Could be removed during boot
test -e /var/run/mysqld || install -m 755 -o mysql -g root -d /var/run/mysqld
# Start MySQL!
su - mysql -s /bin/sh -c "/usr/bin/mysqld_safe > /dev/null 2>&1 &"
# 6s was reported in #352070 to be too few when using ndbcluster
# 14s was reported in #736452 to be too few with large installs
for i in $(seq 1 30); do
sleep 1
if mysqld_status check_alive nowarn ; then break; fi
log_progress_msg "."
done
if mysqld_status check_alive warn; then
log_end_msg 0
# Now start mysqlcheck or whatever the admin wants.
output=$(/etc/mysql/debian-start)
[ -n "$output" ] && log_action_msg "$output"
else
log_end_msg 1
log_failure_msg "Please take a look at the syslog"
fi
fi
;;
'stop')
# * As a passwordless mysqladmin (e.g. via ~/.my.cnf) must be possible
# at least for cron, we can rely on it here, too. (although we have
# to specify it explicit as e.g. sudo environments points to the normal
# users home and not /root)
log_daemon_msg "Stopping MySQL database server" "mysqld"
if ! mysqld_status check_dead nowarn; then
set +e
shutdown_out=`$MYADMIN shutdown 2>&1`; r=$?
set -e
if [ "$r" -ne 0 ]; then
log_end_msg 1
[ "$VERBOSE" != "no" ] && log_failure_msg "Error: $shutdown_out"
log_daemon_msg "Killing MySQL database server by signal" "mysqld"
killall -15 mysqld
server_down=
for i in 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10; do
sleep 1
if mysqld_status check_dead nowarn; then server_down=1; break; fi
done
if test -z "$server_down"; then killall -9 mysqld; fi
fi
fi
if ! mysqld_status check_dead warn; then
log_end_msg 1
log_failure_msg "Please stop MySQL manually and read /usr/share/doc/mysql-server-5.7/README.Debian.gz!"
exit -1
else
log_end_msg 0
fi
;;
'restart')
set +e; $SELF stop; set -e
$SELF start
;;
'reload'|'force-reload')
log_daemon_msg "Reloading MySQL database server" "mysqld"
$MYADMIN reload
log_end_msg 0
;;
'status')
if mysqld_status check_alive nowarn; then
log_action_msg "$($MYADMIN version)"
else
log_action_msg "MySQL is stopped."
exit 3
fi
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $SELF start|stop|restart|reload|force-reload|status"
exit 1
;;
esac
# Some success paths end up returning non-zero so exit 0 explicitly. See
# bug #739846.
exit 0