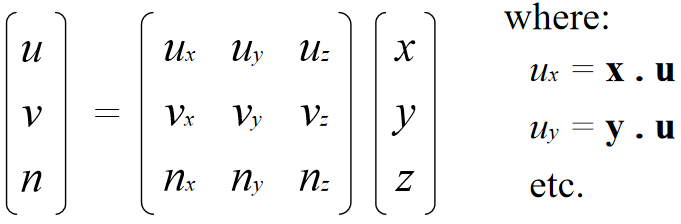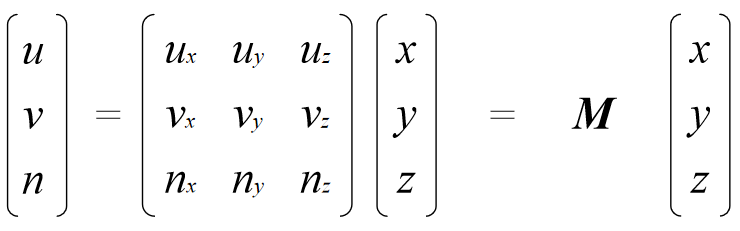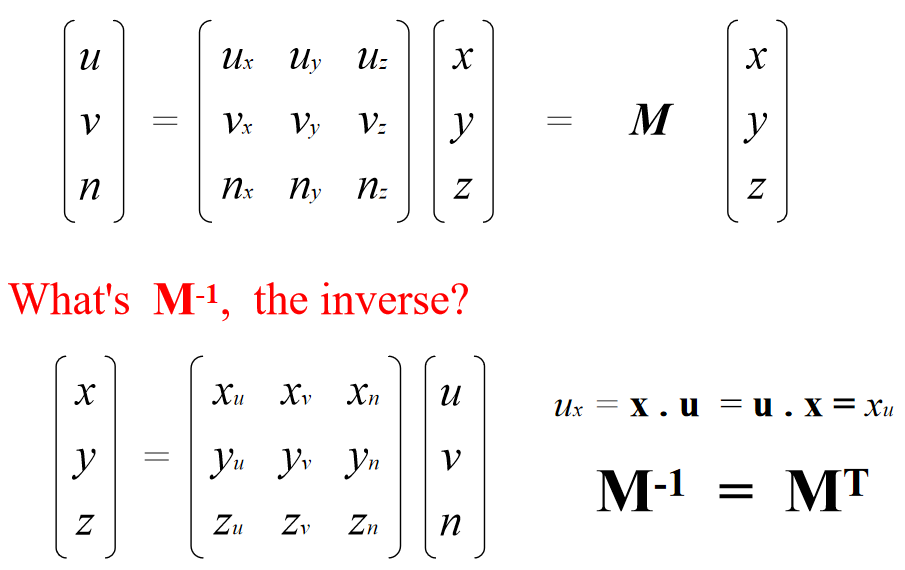http://groups.csail.mit.edu/graphics/classes/6.837/F03/lectures/04_transformations.ppt
https://groups.csail.mit.edu/graphics/classes/6.837/F03/lectures/
Maps points (x, y) in one coordinate system to points (x', y') in another coordinate system
x' = ax + by + c
y' = dx + ey + f
For example, IFS:


Can be combined
Are these operations invertible?
Yes, except scale = 0
恒等 平移 旋转 等比缩放
可逆,除非等比缩放系数为0
Classes of Transformations 变换分类
Rigid Body / Euclidean Transforms 刚体、欧式变换
Similitudes / Similarity Transforms 相似性变换
Linear 线性变换
Affine 放射
Projective 投影
保持不变量的对象
点点之间
距离
线线之间
角度
平行关系
保距变换
保角变换
平行变换
Rigid-Body / Euclidean Transforms
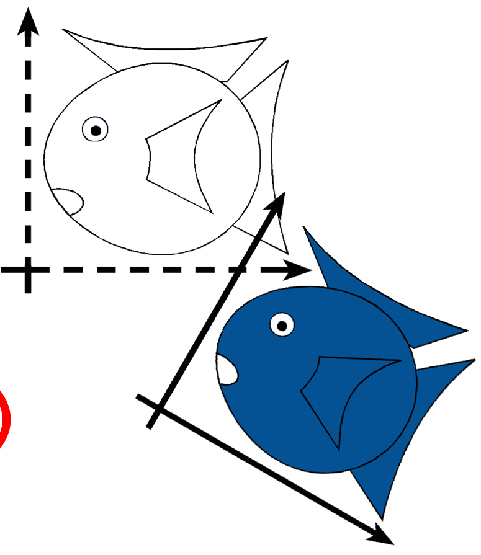
Preserves distances
Preserves angles
Rigid / Euclidean
Translation Identity Rotation
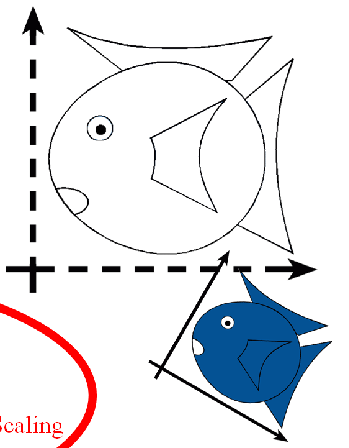
Similitudes / Similarity Transforms
Linear Transformations
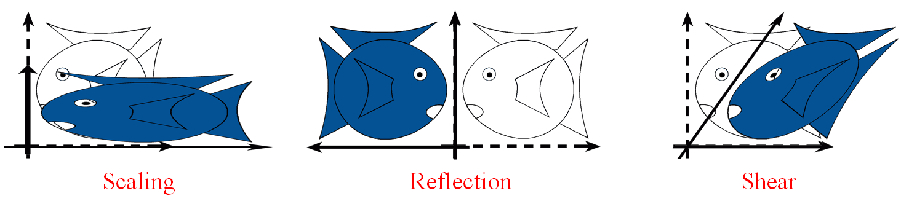
L(p + q) = L(p) + L(q)
L(ap) = a L(p)
shear
vt. 剪;修剪;剥夺
vi. 剪;剪切;修剪
切力 切变
Affine Transformations
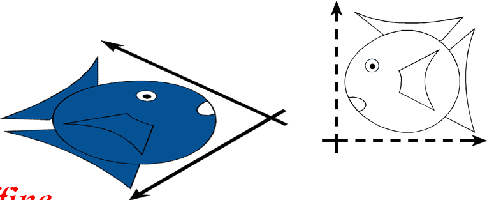
Projective Transformations
preserves lines
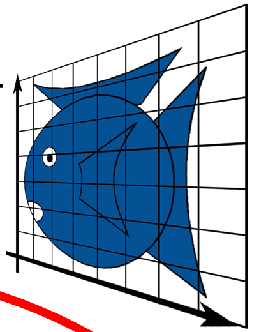

Representing Transformations 变换的表示
Combining Transformations 变换的联合
Change of Orthonormal Basis 改变正交基
How are Transforms Represented?
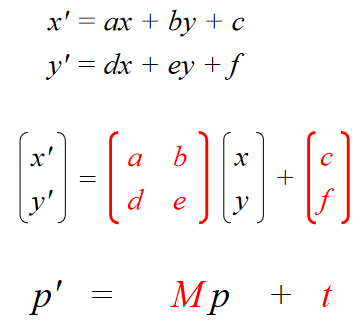
Homogeneous Coordinates 齐次坐标
Add an extra dimension
in 2D, we use 3 x 3 matrices
in 3D, we use 4 x 4 matrices
Each point has an extra value, w

Most of the time w = 1, and we can ignore it
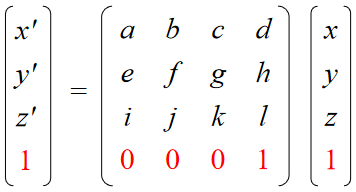
If we multiply a homogeneous coordinate by an affine matrix, w is unchanged
如果通过仿射矩阵来乘齐次坐标系,则w不变
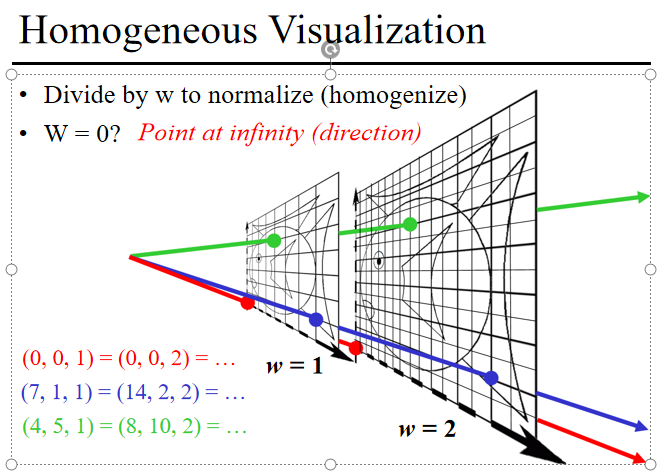
Divide by w to normalize (homogenize)
W = 0? Point at infinity (direction)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Affine_transformation


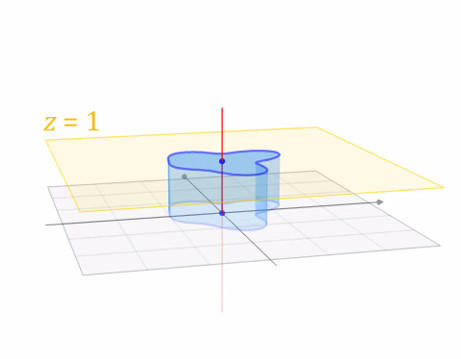
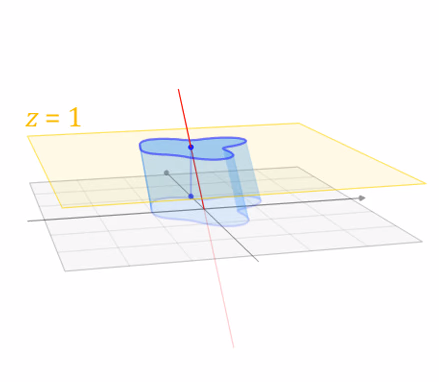
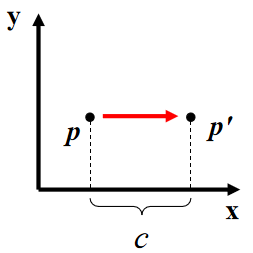
Translate (tx, ty, tz)
Why bother with the extra dimension? Because now translations can be encoded in the matrix!
Translate(c,0,0)
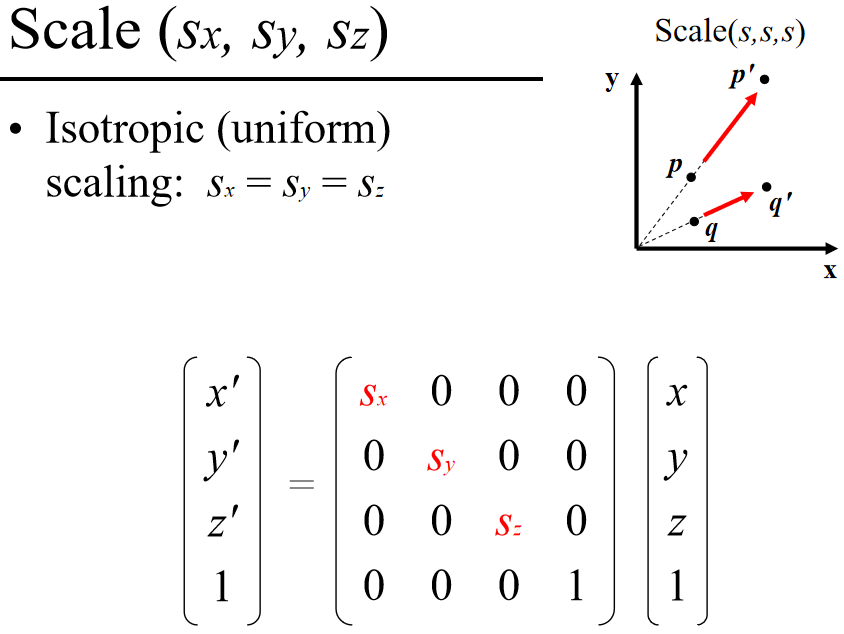
Scale (sx, sy, sz)
Isotropic (uniform) scaling: sx = sy = sz
扩展
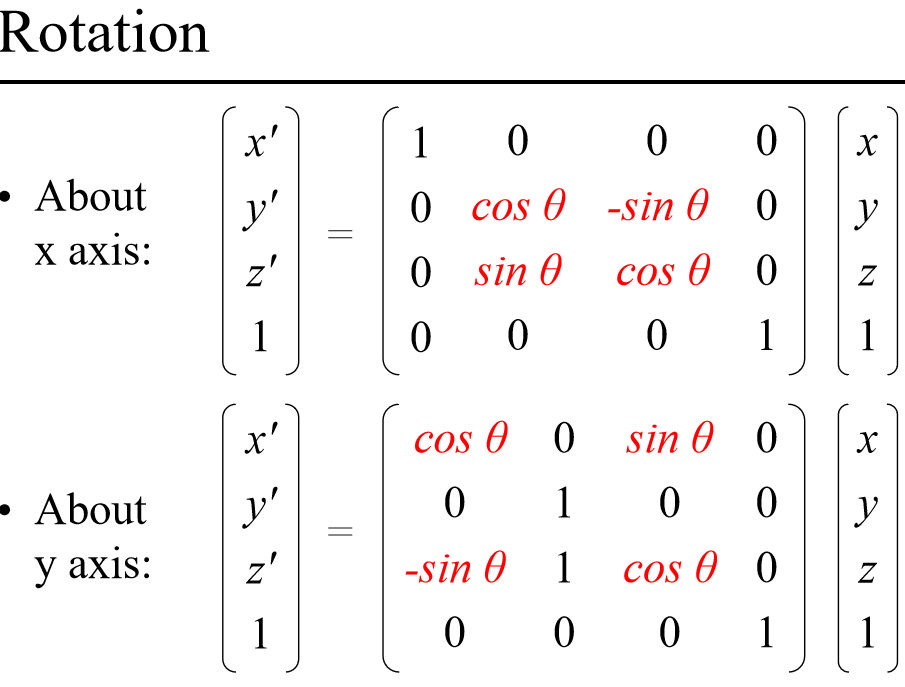
旋转
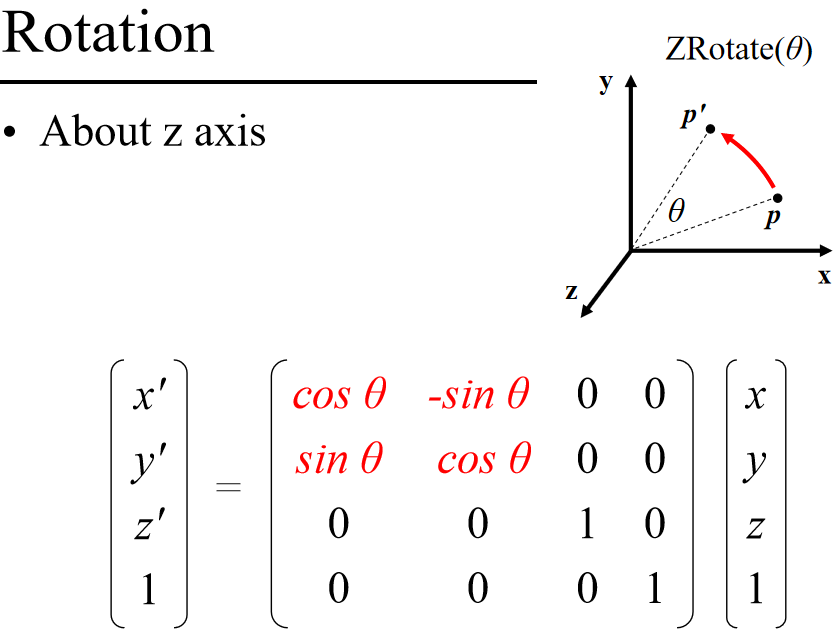
关于不同坐标轴旋转
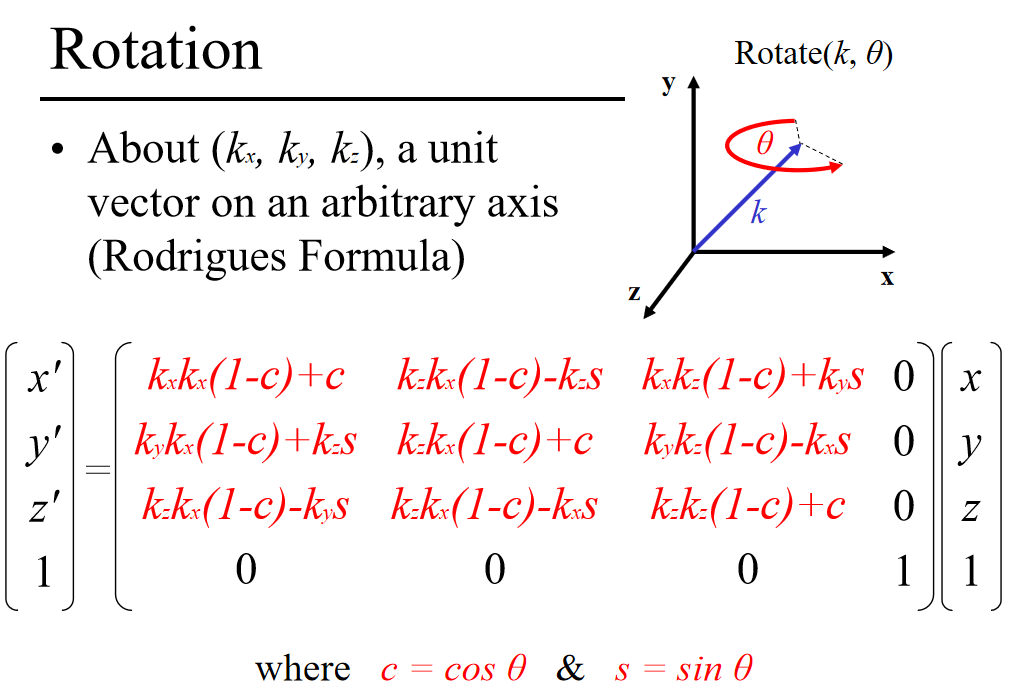
About (kx, ky, kz), a unit vector on an arbitrary axis (Rodrigues Formula)
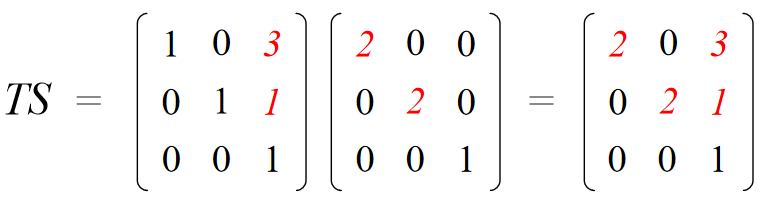
How are transforms combined?
Scale then Translate

Use matrix multiplication: p' = T ( S p ) = TS p
Caution: matrix multiplication is NOT commutative!
矩阵相乘不可以交换
Non-commutative Composition
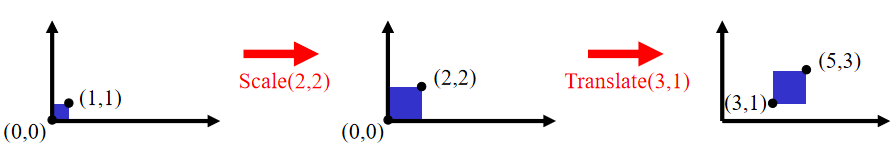
Scale then Translate: p' = T ( S p ) = TS p
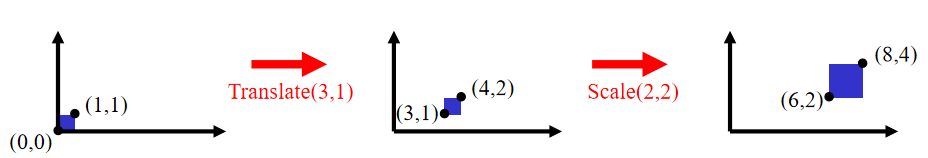
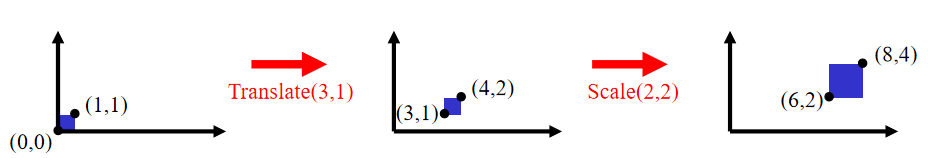
Translate then Scale: p' = S ( T p ) = ST p

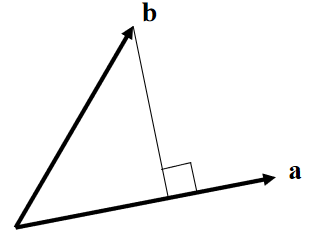
Review of Dot Product
点乘
Change of Orthonormal Basis
Given: coordinate frames
xyz and uvn
point p = (x,y,z)
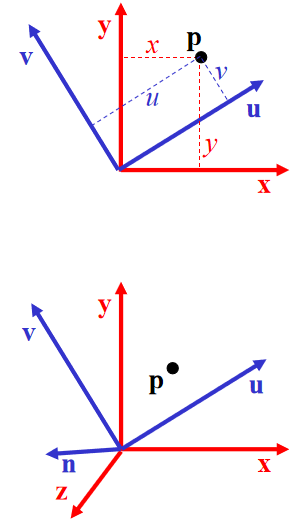
Find: p = (u,v,n)
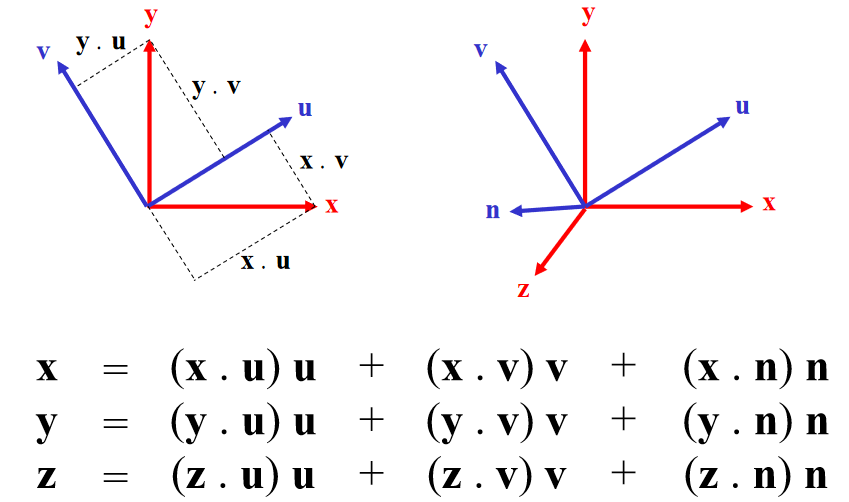
Substitute into equation for p:
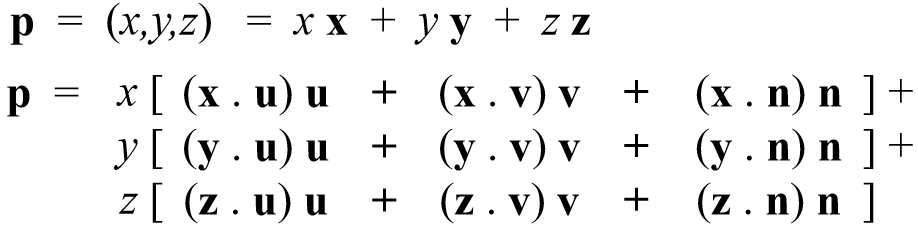
Rewrite:
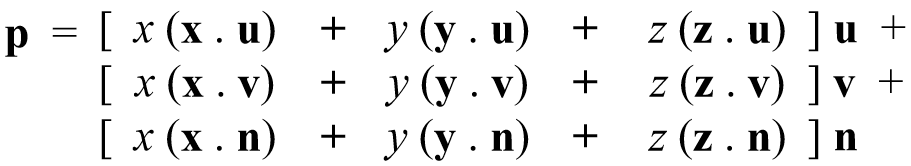
p = (u,v,n) = u u + v v + n n
Expressed in uvn basis:

In matrix form: