2021年7月18日16:11:26:如果有现在看到我这篇文章的朋友
推荐看这篇
写得更好更详细.
我这只能说是跟着阿里云的网课,就着文档的笔记.
远不及这位好兄弟写得透彻.
什么是Servlet
Servlet是Server Applet的缩写.
这是一项时至2020年仍在更新使用的JAVA技术.
它的出现是为了解决服务端为用户提供动态网页的问题.其实这个问题已经有一个解决方案CGI(Common Gateway Interface),但是CGI程序编写困难,响应时间长,以进程方式运行导致性能受限.所以SUN公司推出了Servlet技术来取代它.
Servlet是作为WEB浏览器或者其他HTTP客户端请求和服务器上数据库或者应用程序之间的中间层.使用Servlet,我们可以收集来自网页表单的用户输入,呈现来自数据库或者其他源的记录,或者动态创建页面(比如JSP就是它的一个扩展).
Servlet接口和类
这边就看JAVA EE8.0文档,然后给大家翻译一下吧.
Servlet接口
public interface Servlet
Defines methods that all servlets must implement.
Servlet接口定义了servlets必须实现的方法
A servlet is a small Java program that runs within a Web server. Servlets receive and respond to requests from Web clients, usually across HTTP, the HyperText Transfer Protocol.
一个servlet就是一个运行在Web服务器内的Java小程序.Servlets接收和响应来自Web客户端的请求(一般是通过HTTP)
To implement this interface, you can write a generic servlet that extends javax.servlet.GenericServlet or an HTTP servlet that extends javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet.
要实现这个接口,你可以继承javax.servlet.GenericServlet写一个generic servlet,或者继承javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet写一个HTTP servlet
This interface defines methods to initialize a servlet, to service requests, and to remove a servlet from the server. These are known as life-cycle methods and are called in the following sequence:
1.The servlet is constructed, then initialized with the init method.
2.Any calls from clients to the service method are handled.
3.The servlet is taken out of service, then destroyed with the destroy method, then garbage collected and finalized.
这个接口定义了一些方法,来初始化servlet,服务请求和从服务器中移除servlet.这就是著名的生命周期方法
- servlet被创建,然后通过
init方法进行初始化 - 处理任何来自客户端的服务请求
- servlet停用,然后通过
destory方法进行销毁,接着GC进行垃圾搜集清理
In addition to the life-cycle methods, this interface provides the getServletConfig method, which the servlet can use to get any startup information, and the getServletInfo method, which allows the servlet to return basic information about itself, such as author, version, and copyright.
除了生命周期方法外,这个接口还提供了getServletConfig方法,用于获取启动信息和getServeltInfo方法,获取自身的基本信息(比如作者,版本和版权)
上面这部分就是文档里,Servlet接口的说明部分,但其实还有个很重要的方法没提,这边补充一下.
void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res)
Called by the servlet container to allow the servlet to respond to a request.
由servlet容器调用,使得servlet能够请求和响应.
这边得和参考资料1结合一下,servlet没有main方法,不能独立运行,必须被部署到servlet容器中,由容器来实例化和调用servlet的方法.
GenericServlet
public abstract class GenericServlet extends Object implements Servlet, ServletConfig, Serializable
可以看到这是一个抽象类
Defines a generic, protocol-independent servlet. To write an HTTP servlet for use on the Web, extend HttpServlet instead.
定义了一个泛化,协议独立的servlet.如果要为了写一个HTTP servlet供WEB使用,可以继承HttpServlet作为替代.
换句话说仅用HTTP协议通信就直接用HttpServlet就好了,没必要浪费时间重载GenericServlet的一堆方法.
GenericServlet implements the Servlet and ServletConfig interfaces. GenericServlet may be directly extended by a servlet, although it's more common to extend a protocol-specific subclass such as HttpServlet.
GenericServlet实现了Servlet和ServletConfig接口.
GenericServlet可以被servlet直接继承,但是更常见的是继承一个明确协议的子类,像HttpServlet.
GenericServlet makes writing servlets easier. It provides simple versions of the lifecycle methods init and destroy and of the methods in the ServletConfig interface. GenericServlet also implements the log method, declared in the ServletContext interface.
GenericServlet使得写servlet更简单了.它提供了简化版的生命周期方法和ServletContig接口中的方法.同时,实现了ServletContext接口中声明的log(日志)方法.
To write a generic servlet, you need only override the abstract service method.
要写一个Generic Servlet,你只需要重载特定的抽象服务方法.
HttpServlet
public abstract class HttpServlet extends GenericServlet
继承自GenericServlet的一个抽象类
Provides an abstract class to be subclassed to create an HTTP servlet suitable for a Web site. A subclass of HttpServlet must override at least one method, usually one of these:
doGet, if the servlet supports HTTP GET requests
doPost, for HTTP POST requests
doPut, for HTTP PUT requests
doDelete, for HTTP DELETE requests
init and destroy, to manage resources that are held for the life of the servlet
getServletInfo, which the servlet uses to provide information about itself
There's almost no reason to override the service method. service handles standard HTTP requests by dispatching them to the handler methods for each HTTP request type (the doXXX methods listed above).
提供被子类化的一个抽象类,以创建适用于WEB网站的HTTP servlet.
一个HttpServlet的子类,必须重载至少一个方法,通常是下列之一.
2021年4月29日15:49:14 全翻太累了,直接看吧,重点记一下就好.
- 一般不会去重载
service方法,它是用来处理标准HTTP请求的,把请求按类型分发给对应的处理方法(比如上面的doXXX方法)
Likewise, there's almost no reason to override the doOptions and doTrace methods.
- 同理,一般也不会重载
doOpitons和doTrace方法
Servlets typically run on multithreaded servers, so be aware that a servlet must handle concurrent requests and be careful to synchronize access to shared resources. Shared resources include in-memory data such as instance or class variables and external objects such as files, database connections, and network connections. See the Java Tutorial on Multithreaded Programming for more information on handling multiple threads in a Java program.
- Servelt一般运行在多线程服务器上,所以要注意处理并发请求和对共享资源的同步访问
- 共享资源包括内存里的数据(像实例或类变量和文件,数据库连接,网络连接这些外部对象)
- 看Java Tutorial on Multithreaded Programming了解更多处理多线程的信息
三者关系
- Servlet接口,定义了它的生命周期和服务方法
- GenericServlet类实现了Servlet和其他几个相关接口,使得写servlet更简单了
- HttpServlet是GenericServlet的一个子类,专门用于写处理HTTP的servlet
Servlet生命周期
Servlet接口声明的5个方法中,有3个是生命周期函数
void init(ServletConfig config)- Called by the servlet container to indicate to a servlet that the servlet is being placed into service.
void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res)- Called by the servlet container to allow the servlet to respond to a request.
void destroy()- Called by the servlet container to indicate to a servlet that the servlet is being taken out of service.
这里的Servlet Container一般就是tomcat,可以理解为服务器.
然后,这三个生命周期函数被调用时执行的次数是不同的.
init()和destroy()都只有在类初始化对象和销毁对象时才会执行一次- 但是
service()每次处理请求时都会被调用
并且由于servlet是单例的,也就说一个类只有一个对象,如果多个用户同时访问的话,也是一个对象同时进行服务,所以它是线程不安全的.(这就是文档建议我们了解多线程的原因)
当然这也使得它变得高效(节省了为每个用户单独创建对象的时间,同时节约了内存).
还有一点很值得注意的是,Servlet类虽然是我们写的,但却是由服务器来创建,调用的.
这点文档也反复提及,所以得划下重点.
ServletConfig
先看下文档
public interface ServletConfig
A servlet configuration object used by a servlet container to pass information to a servlet during initialization.
看了简介,可以获得两个信息
- ServletConfig是个接口
- ServletConfig对象被ServletContainer用来在初始化时给servlet传递信息
看下它的方法
String getServletName()- Returns the name of this servlet instance. The name may be provided via server administration, assigned in the web application deployment descriptor, or for an unregistered (and thus unnamed) servlet instance it will be the servlet's class name.
- 获取servlet实例名称
ServletContext getServletContext()- Returns a reference to the ServletContext in which the caller is executing.
- 返回caller正在执行的ServletContext引用
String getInitParameter(String name)- Gets the value of the initialization parameter with the given name.
- 通过名称获取初始化变量值
Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames()- Returns the names of the servlet's initialization parameters as an Enumeration of String objects, or an empty Enumeration if the servlet has no initialization parameters.
- 返回一个包含servlet初始化参数名称的
Enumeration<String>对象.如果servlet没有初始化参数,就返回一个空的enumeration对象
然后看阿里云大学的教程
- 一个ServletConfig对象对应一段
web.xml中的Servlet配置信息getServletName方法获取的就是web.xml中的servlet-name标签值getInitParameter方法就是根据字符串name,获取在web.xml中的init-param标签值getInitParameterNames方法则是直接获得所有iniit-param的name
- ServletConfig是接口,它的实现类由Tomcat提供
ServletRequest & ServletResponse
void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException
在servlet接口的service方法中,包含两个相关接口ServletRequest和ServletResponse
看名字就知道,这是让我们在实现servlet时,传入请求,传出响应用的,看了下文档中的方法,也确实如此
由于之后我们主要继承HttpServlet进行开发,这里大致了解一下就好了
稍微看下overview吧
public interface ServletRequest
Defines an object to provide client request information to a servlet. The servlet container creates a ServletRequest object and passes it as an argument to the servlet's service method.
A ServletRequest object provides data including parameter name and values, attributes, and an input stream. Interfaces that extend ServletRequest can provide additional protocol-specific data (for example, HTTP data is provided by HttpServletRequest.
public interface ServletResponse
Defines an object to assist a servlet in sending a response to the client. The servlet container creates a ServletResponse object and passes it as an argument to the servlet's service method.
To send binary data in a MIME body response, use the ServletOutputStream returned by getOutputStream(). To send character data, use the PrintWriter object returned by getWriter(). To mix binary and text data, for example, to create a multipart response, use a ServletOutputStream and manage the character sections manually.
The charset for the MIME body response can be specified explicitly using any of the following techniques: per request, per web-app (using ServletContext.setRequestCharacterEncoding(java.lang.String), deployment descriptor), and per container (for all web applications deployed in that container, using vendor specific configuration). If multiple of the preceding techniques have been employed, the priority is the order listed. For per request, the charset for the response can be specified explicitly using the setCharacterEncoding(java.lang.String) and setContentType(java.lang.String) methods, or implicitly using the setLocale(java.util.Locale) method. Explicit specifications take precedence over implicit specifications. If no charset is explicitly specified, ISO-8859-1 will be used. The setCharacterEncoding, setContentType, or setLocale method must be called before getWriter and before committing the response for the character encoding to be used.
GenericServlet
在一开始看文档的时候,已经基本介绍了GenericServlet类的概述和方法
阿里云大学的教程又结合Tomcat源码,深入剖析了GenericServlet类是如何实现的
- 通过
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException中的this.config=config保存了Servlet Container/Tomcat传入的ServletConfig配置信息 - 然后基于
init()函数保存的config,实现其他的方法比如getServletContext(),getServletName()
结合起来看,文档中说的GenericServlet实现了Servlet,ServletConfig接口,使得更易于创建Servlet,就很好理解了
可以调用方法直接获取配置信息肯定是比手动再实现一遍方法来得简单快捷的
HttpServlet
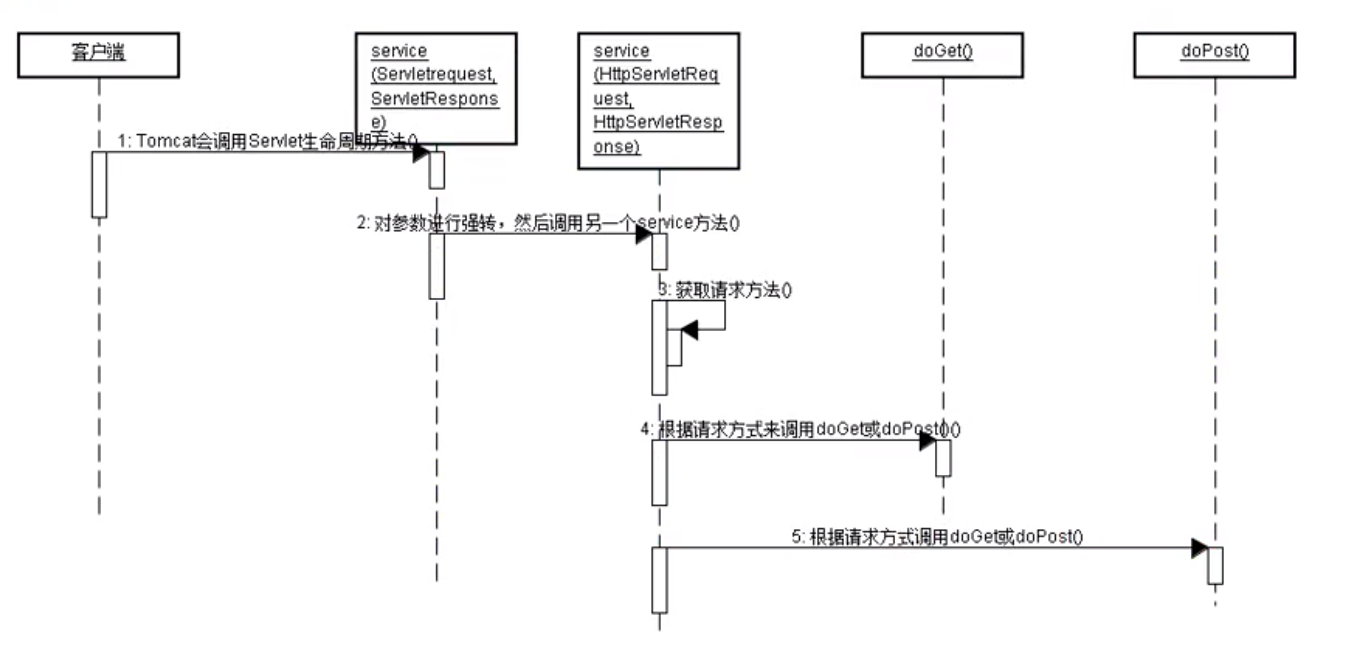
我们只需要实现HttpServlet的doPost/doGet之类的方法
Tomcat接收到请求后,会依据上图逐层进行函数调用
- 重定向
request.getRequestDispatcher("/xxx").forward(request,response);response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/xxx.jsp")
Servlet的细节
- Servlet与线程安全
- 一个类型的Servlet只有一个实例对象=>一个Servlet同时处理多个请求=>效率高+线程不安全
- 解决方法:
- 不在Servlet中创建成员,仅创建局部变量
- 创建无状态成员
- 创建有状态成员,但是状态必须为只读
- 让服务器启动时就创建Servlet
- 避免第一次惩罚(第一次访问时才创建,那么第一次访问的响应会很缓慢)
- 解决方法:
- 在
web.xml中的<servlet>标签内添加<load-on-startup><load-on-startup>值给一个非负整数,标记各个servlet的启动顺序
- 在
<url-pattern><servlet-mapping>中可以有多个<url-pattern>- 可以在路径中使用通配符
*
web.xmltomcat/conf/web.xml是每个web.xml的模板<session-timeout>mime-mapping
Servlet和反射
- tomcat如何通过
web.xml配置文件,为客户端请求创建Servlet实例?
- 通过
<servlet-mapping>找到url对应的servlet-name - 通过
<servlet>找到servlet-name对应的servlet-class - 通过反射,具体说是
Class.forName(),将servlet-class标签的值(字符串),找到对应的类,再通过.newInstance()创建该类实例- 注意该类必须有无参构造器
- 之后可以通过
getMethod(),获得方法,再通过invoke()对method进行调用
ServletContext
概述
- 一个项目只有一个ServletContext对象=>一般起名叫application
- 多个Servlet间通过它来进行数据传输
- Tomcat启动时创建,关闭时销毁
获取ServletContext对象
- 只要实现了
ServletConfig接口,就能够调用getServletContext方法,来获取该对象- 或者
GenericServlet,HTTPServlet类可以先调用getServletConfig方法获得ServletConfig,再调用getServletContext方法来获取该对象
- 或者
- 未实现该接口的其他接口,也可能实现了
getServletContext方法,可以调用该方法来获取上下文- 如
HttpSession,ServletContextEvent
- 如
域对象的功能
- ServletContext是JAVA 4大域对象之一
- 域对象:可用于在多个Servlet间传递数据
- 4大域对象:
PageContext,ServletRequest,HttpSession,ServletContext
- 所有域对象都有存取数据的功能
- 因为内部有一个Map,用于存储数据
ServletContext操作数据的方法:setAttribute(String name, Object object)- Binds an object to a given attribute name in this ServletContext.
Object getAttribute(String name)- Returns the servlet container attribute with the given name, or null if there is no attribute by that name.
removeAttribute(String name)- Removes the attribute with the given name from this ServletContext.
getAttributeNames()- Returns an Enumeration containing the attribute names available within this ServletContext.
- HttpServlet存取ServletContext
- 存储数据
ServletContext application = this.getServletContext(); application.setAttribute("name","Crystal");- 获取数据
ServletContext application = this.getServletContext(); String name = (String)application.getAttribute("name"); System.out.println(name);
获取公共初始化参数
- 可以通过
<context-param>配置初始化参数,供所有servlet使用- servlet也可以获取初始化参数,但是只能获取自身的,而Context获取的是公共的
- 在HttpServlet中获取context配置的初始化参数
- 得到ServletContext
ServletContext app = this.getServletContext(); - 调用
getInitParameter()
String value = app.getInitParameter("context-param");
- 得到ServletContext
获取资源的方法
- 获取真实路径
String path = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/fileName");- 得到有盘符的真实路径
- 获取资源流
InputStream input = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream('/fileName');- 相当于获取真实路径后,用文件输入流打开
InputStream input = new FileInputStream(path);
- 相当于获取真实路径后,用文件输入流打开
- 获取指定目录下所有资源的路径
Set<String> path = this.getServletContext().getResoucePaths("/dictionary");
访问量统计
- 创建一个int类型变量,记录访问量,存到
ServletContext的域中=>这样所有的Servlet就都能访问到
ServletContext application = this.getServletContext();
Integer count = (Integer)application.getAttribute("count");
if(count == null){
count = 1;
} else {
count++;
}
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().print("<h1>This website has been visited " + count + " times."</h1>);
application.setAttribute("count",count);
获取类路径下的资源
- 类路径下的资源
/WEB-INF/classes和/WEB-INF/lib/下的每个jar包- 开发环境中
/src/目录下的.java文件,之后会被编译后放到/WEB-INF/classes路径 /WEB-INF/lib/存放的则是程序需要/依赖的JAR包,可以是包管理工具导入或者手动导入
- 开发环境中
- 可用Class/ClassLoader获取类路径下的资源
InputStream ClassLoader.getResourceAsStream(PathAndFileName)InputStream Class.getResourceAsStream(PathAndFileName)- 不以
/开头,在源码编译后.class文件所在目录 - 以
/开头,相对/classes/路径
- 不以
ServletContextgetRealPath(String path)方法,获取WEB-ROOT下资源的绝对路径getResourceAsStream(String path)方法,获取WEB-ROOT路径下资源的流对象
HttpServlet优化
我们可还以对HttpServlet再进行封装,使得开发更加高效
- 一个Servlet处理多种请求处理方法=>避免Servlet暴增
- 用户传入的url必须带method参数,指定要调用的功能
- 实现service方法,根据传入method来调用method指定的方法(通过反射调用)
- 具体的方法函数原型要和service一样=>才能够收发请求响应,适当抛出异常
- 令具体method返回string,然后根据返回字符串判断行为(转发,重定向,不操作),和相关地址
参考资料
- 几个概念:Servlet、Servlet容器、Tomcat - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
- Java Servlet Technology Overview (oracle.com)
- Servlet 简介 | 菜鸟教程 (runoob.com)
- Java Servlet - 维基百科,自由的百科全书 (wikipedia.org)
- 聊聊Tomcat的架构设计 (objcoding.com)
- Apache Tomcat - 维基百科,自由的百科全书 (wikipedia.org)
- Overview (Java Platform SE 8 ) (oracle.com)
- Servlet入门 - 阿里云大学 - 官方网站,云生态下的创新人才工场 (aliyun.com)
- servlets - What is WEB-INF used for in a Java EE web application? - Stack Overflow
- Servlet--Context - 华为云 (huaweicloud.com)