一.Ajax了解
AJAX(Asynchronous Javascript And XML)优点是在不重新加载整个页面的情况下,可以与服务器交换数据并更新部分网页内容
优点:
1.ajax使用JavaScript技术向服务器发送异步请求
2.ajax请求无需刷新整个页面(浏览器局部刷新)
3.服务器响应内容不再是整个页面,而是页面中的部分内容,所以ajax性能高
二.Ajax使用
基本格式
//基于按钮点击事件实现的
<script src="{% static 'js/jquery.js' %}"></script>
<script>
$('#sub').click(function () {
//$.ajax({键值对参数})
$.ajax({
url:"{% url 'login' %}",
type:'post',
data:{'username':uname,'pwd':pwd,'csrfmiddlewaretoken':csrf_token},
success:function (response) { // response这个参数名字是自定义的
}
})
})
</script>
1.jQuery的实现
<button class="send_Ajax">send_Ajax</button>
<script>
$(".send_Ajax").click(function(){
$.ajax({
url:"/handle_Ajax/",
type:"POST",
data:{username:"tom",password:123},
success:function(data){
console.log(data)
},
error: function (jqXHR, textStatus, err) {
console.log(arguments);
},
complete: function (jqXHR, textStatus) {
console.log(textStatus);
},
statusCode: {
'403': function (jqXHR, textStatus, err) {
console.log(arguments);
},
'400': function (jqXHR, textStatus, err) {
console.log(arguments);
}
}
})
})
</script>
2.原生Js实现
var bt2 = document.getElementById("bt2");
bt2.onclick = function () {
// 原生JS
var xmlHttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xmlHttp.open("POST", "/ajax_test/", true);
xmlHttp.setRequestHeader("Content-type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
xmlHttp.send("username=tom&password=123");
xmlHttp.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xmlHttp.readyState === 4 && xmlHttp.status === 200) {
alert(xmlHttp.responseText);
}
};
};
三.使用ajax传送数据
用一个简单的登录验证实例来说明,用户名和密码正确提示成功.否则显示失败
发送的数据如果是字典时,其中的引号必须是双引号,否则传到前端使用会报错,
如{ “data”: data } , 不要用{‘data’: data}
1.使用 JsonResponse 来发送数据(最好)
这样发送的数据,前端就不用解析了,可以直接当作对象来使用
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render,redirect,HttpResponse
from django.http import JsonResponse
from app01 import models
# Create your views here.
def login(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
username = request.POST.get("username")
password = request.POST.get("password")
print(username, password)
ret = models.Userinfo.objects.filter(username=username,password=password)
print(ret)
a = {"status":None}
if ret:
a["status"] = True
print(a)
return JsonResponse(a)
else:
return HttpResponse("fail")
else:
return render(request,"login.html")
login.html
{% load static %}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
{% csrf_token %}
用户名: <input type="text" id="username">
密码: <input type="password" id="password">
<button id="sub">登陆</button>
<span id="mag" style="color: red;font-size: 12px;"></span>
<script src="{% static 'js/jquery.min.js' %}"></script>
<script>
$("#sub").click(function () {
var uname = $("#username").val();
var pwd = $("#password").val();
var csrf_token = $("input[name=csrfmiddlewaretoken]").val();
$.ajax({
url:"{% url 'login' %}",
type:"post",
data:{"username":uname,"password":pwd,"csrfmiddlewaretoken":csrf_token},
success:function (response) {
console.log(response, typeof response);
if (response.status){
$("span").text("登陆成功");
}else{
$("span").text("失败");
}
}
}
)
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
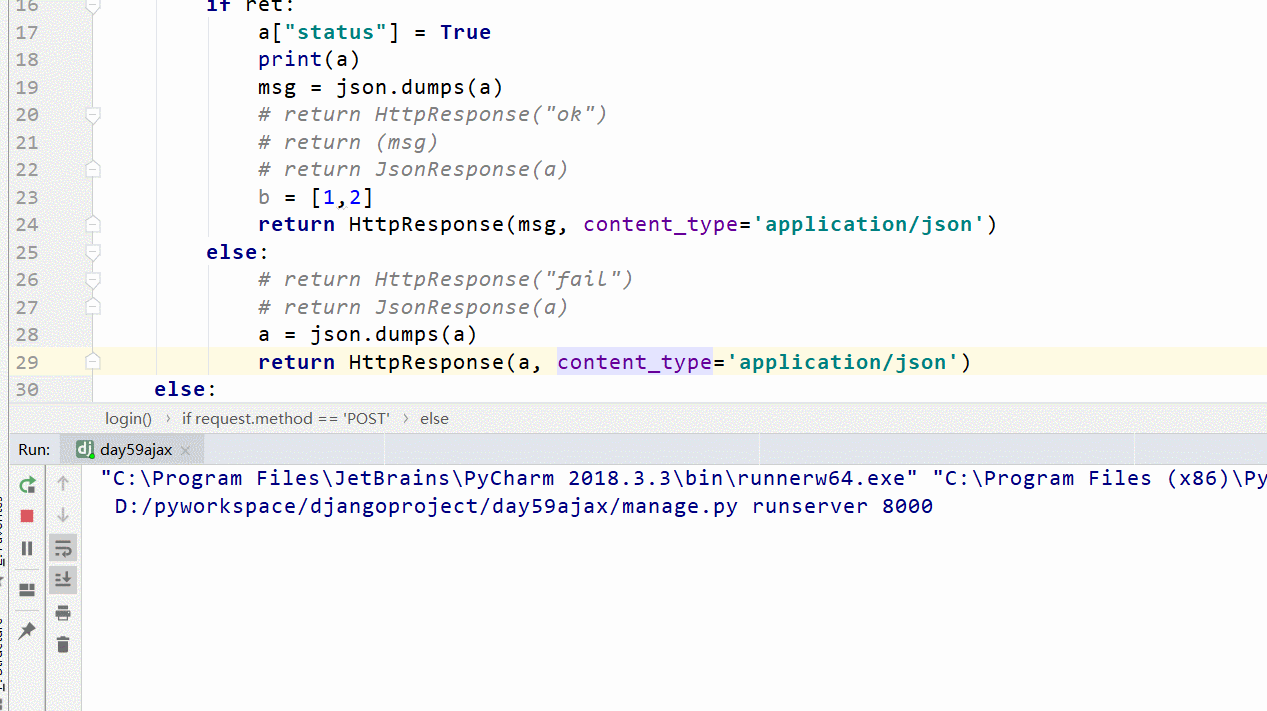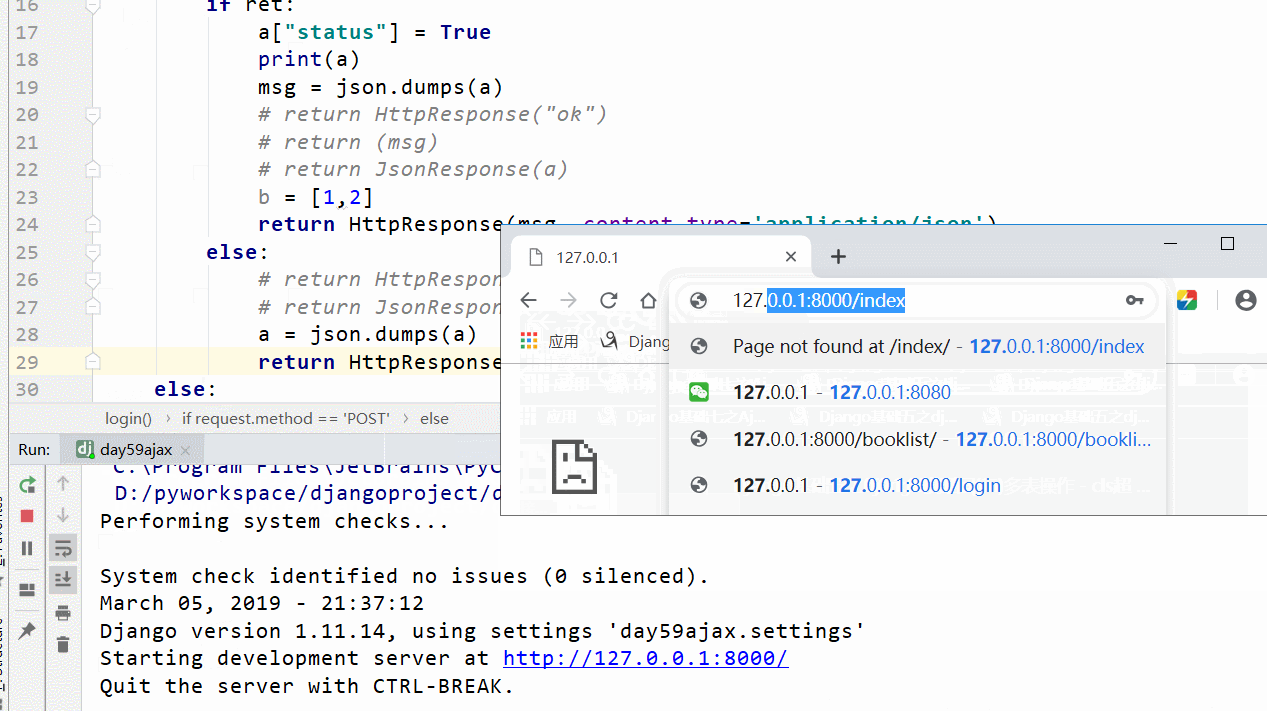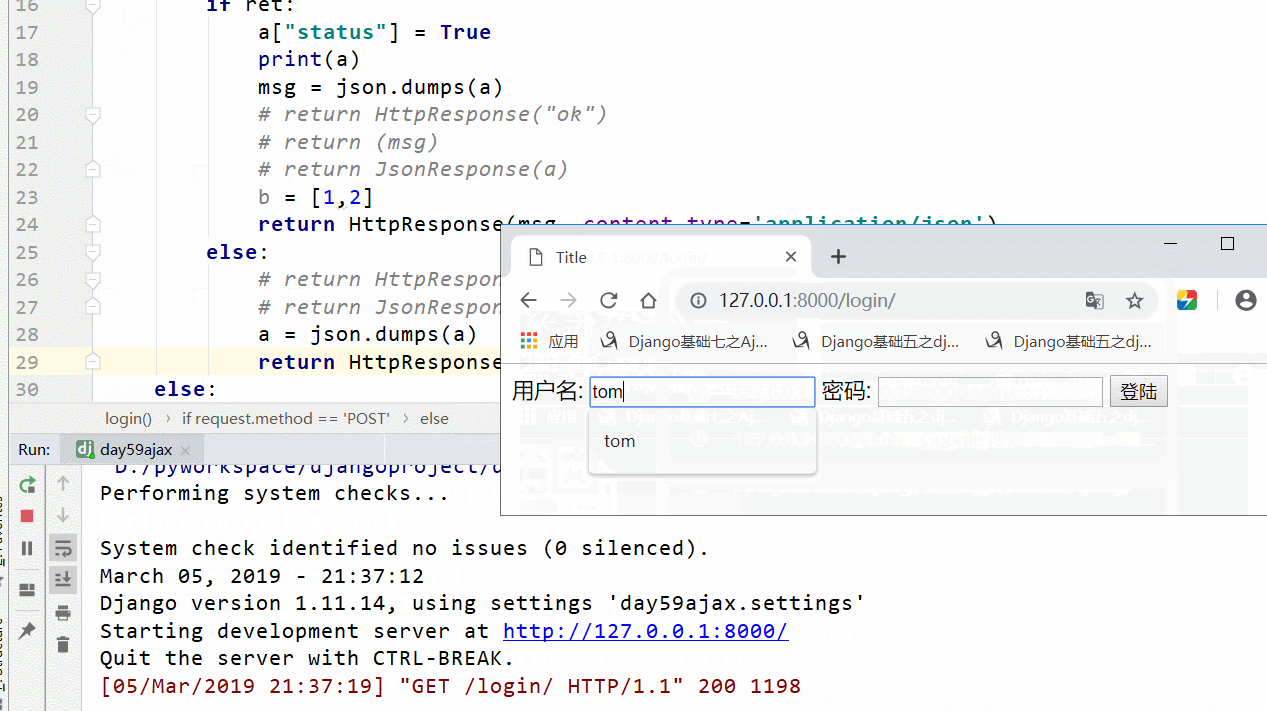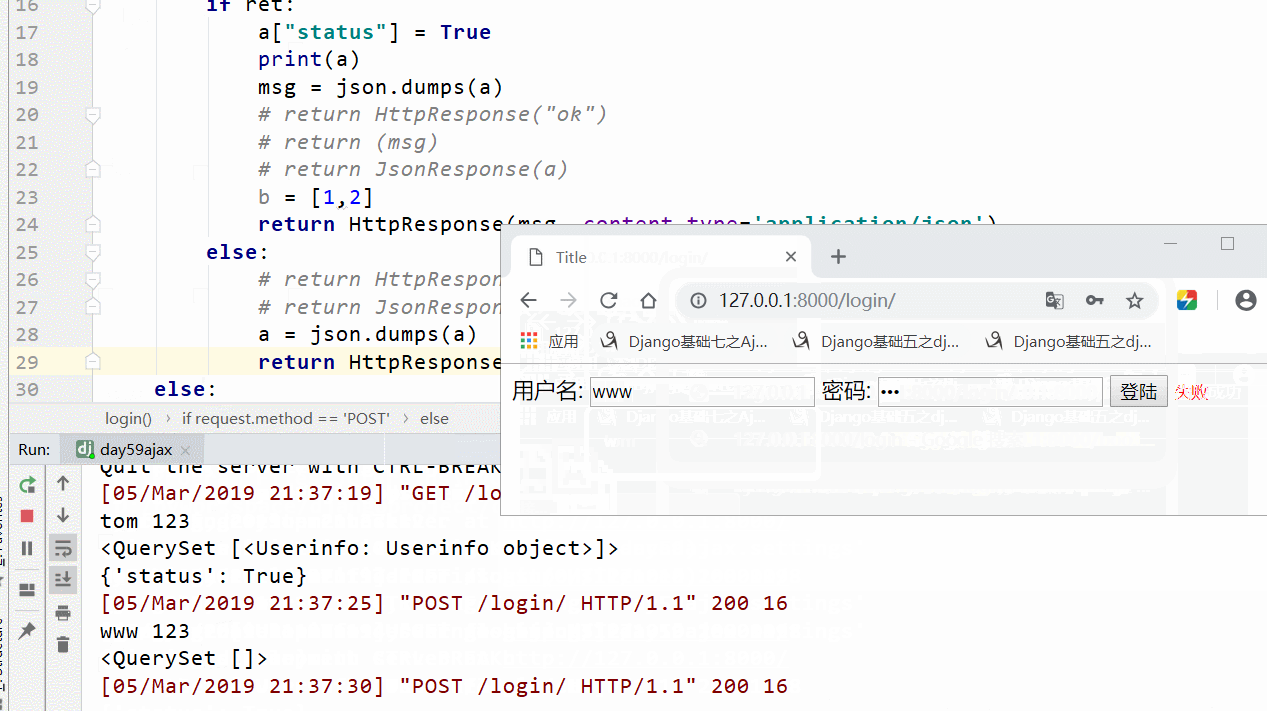
2.使用HttpResponse来向前端发送消息
HttpResponse加一个头就可以了,这样使用HttpResponse(data, content_type=content_type='application/json')
这样在前端html页面就不用解析json格式了,可以直接作为对象调用数据
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render,redirect,HttpResponse
from django.http import JsonResponse
from app01 import models
import json
# Create your views here.
def login(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
username = request.POST.get("username")
password = request.POST.get("password")
print(username, password)
ret = models.Userinfo.objects.filter(username=username,password=password)
print(ret)
a = {"status":None}
if ret:
a["status"] = True
print(a)
msg = json.dumps(a)
return HttpResponse(msg, content_type='application/json')
else:
msg = json.dumps(a)
return HttpResponse(msg, content_type='application/json')
else:
return render(request,"login.html")
login.html
{% load static %}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
{% csrf_token %}
用户名: <input type="text" id="username">
密码: <input type="password" id="password">
<button id="sub">登陆</button>
<span id="mag" style="color: red;font-size: 12px;"></span>
<script src="{% static 'js/jquery.min.js' %}"></script> # 通过别名引入静态文件
<script>
$("#sub").click(function () {
var uname = $("#username").val();
var pwd = $("#password").val();
var csrf_token = $("input[name=csrfmiddlewaretoken]").val();
$.ajax({
url:"{% url 'login' %}",
type:"post",
data:{"username":uname,"password":pwd,"csrfmiddlewaretoken":csrf_token},
success:function (response) {
console.log(response, typeof response);
if (response.status){
$("span").text("登陆成功");
}else{
$("span").text("失败");
}
}
}
)
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
3.引入json模块,发送json格式的消息
向前端发送的是json格式的消息,所以在前端要用JSON.parse()来反序列化字符串为JSON对象之后才能使用
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render,redirect,HttpResponse
from app01 import models
import json
# Create your views here.
def login(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
username = request.POST.get("username")
password = request.POST.get("password")
print(username, password)
ret = models.Userinfo.objects.filter(username=username,password=password)
print(ret)
a = {"status":None}
if ret:
a["status"] = True
print(a) # {'status': True}
msg = json.dumps(a)
return HttpResponse(msg)
else:
return HttpResponse(a)
else:
return render(request,"login.html")
login.html
{% load static %}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
{% csrf_token %}
用户名: <input type="text" id="username">
密码: <input type="password" id="password">
<button id="sub">登陆</button>
<span id="mag" style="color: red;font-size: 12px;"></span>
<script src="{% static 'js/jquery.min.js' %}"></script>
<script>
$("#sub").click(function () {
var uname = $("#username").val();
var pwd = $("#password").val();
var csrf_token = $("input[name=csrfmiddlewaretoken]").val();
$.ajax({
url:"{% url 'login' %}",
type:"post",
data:{"username":uname,"password":pwd,"csrfmiddlewaretoken":csrf_token},
success:function (response) {
console.log(response, typeof response);
msg = JSON.parse(response);
if (msg.status){
$("span").text("登陆成功");
}else{
$("span").text("失败");
}
}
}
)
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
实现结果: