判断链表中是否有环
来源:https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle
Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it.
一块一慢两个指针,如果有环,两个指针必定会在某个时刻相同且都不为空
Java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode low = head.next, fast = head.next.next;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null && low != fast) {
low = low.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
if(low == fast && low != null) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
Python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def hasCycle(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: bool
"""
if head == None or head.next == None:
return False
fast = head.next
low = head
while fast != None and fast.next != None:
if fast == low:
return True
fast = fast.next.next
low = low.next
return False
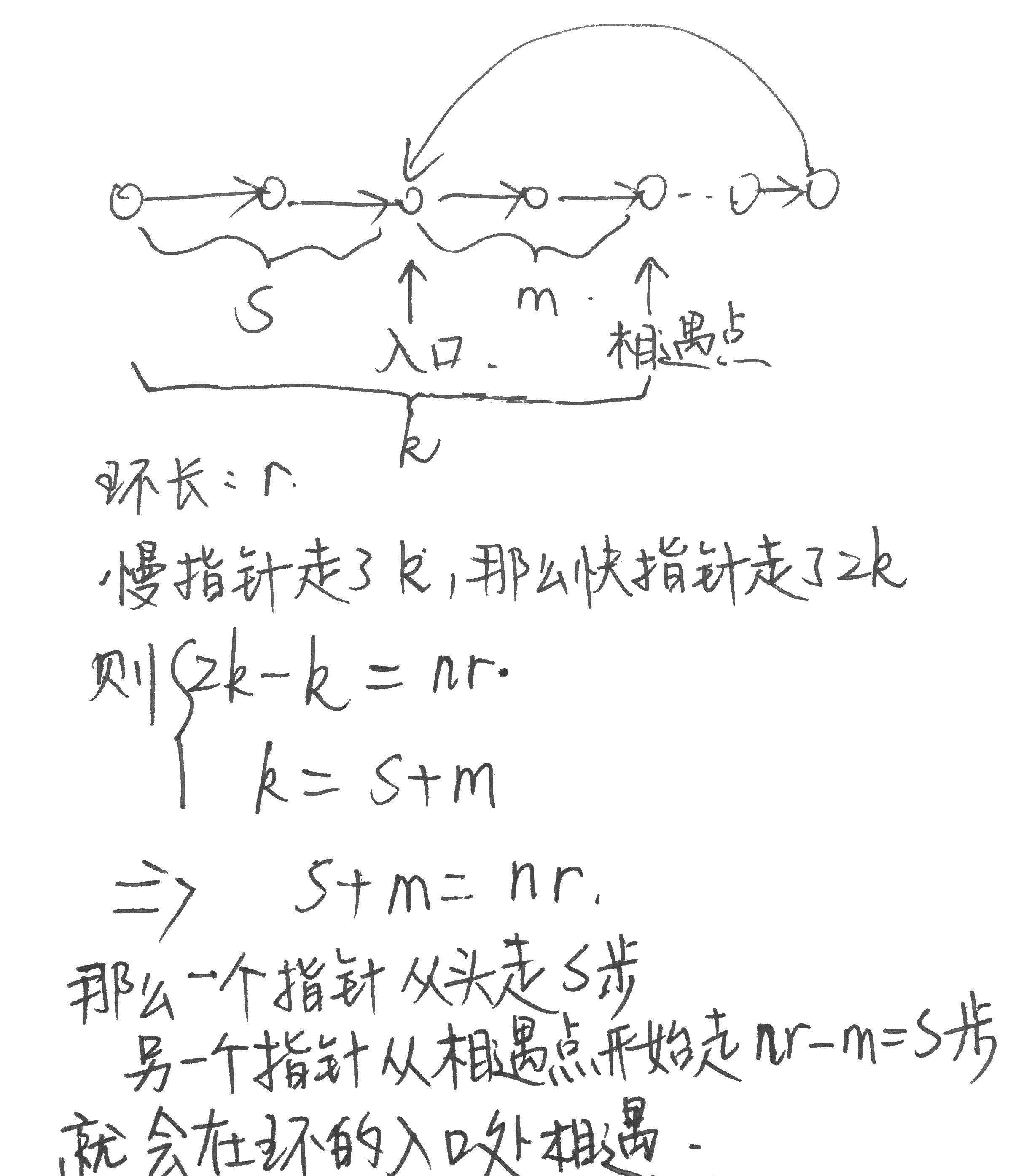
找到链表中环的起点
来源:https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
快慢两个指针相遇时,快指针从头开始一步遍历,慢指针从相遇节点一步遍历,下次相遇的结点就是环的入口节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode low = head.next, fast = head.next.next;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null && low != fast) {
low = low.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
fast = head;
while(low != null && low != fast) {
low = low.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return low;
}
}
Python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def EntryNodeOfLoop(self, pHead):
# write code here
if pHead == None:
return pHead
fast = pHead
slow = pHead
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if fast == slow:
fast = pHead
while fast:
if fast == slow:
return fast
fast = fast.next
slow = slow.next
return None