模板语法
一、{{.}}
模板语法都包含在{{和}}中间,其中{{.}}中的点表示当前对象。
当我们传入一个结构体对象时,我们可以根据.来访问结构体的对应字段。例如:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"text/template"
)
// 传入多对象
func grammarFuncMany(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// 1. 编写模板
// 2. 读取模板 解析指定文件生成模板对象
t, err := template.ParseFiles("./grammarTemplate.tmpl")
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("read template faild err: %#v", err)
}
// 3. 渲染模板
// 传入map键值对
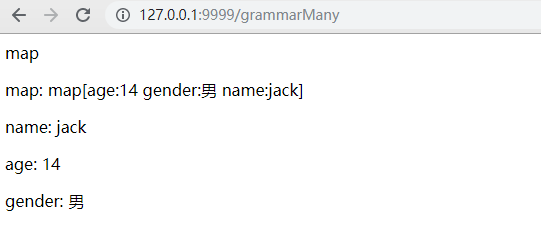
m := map[string]interface{}{}
m["name"] = "jack"
m["age"] = 14
m["gender"] = "男"
t.Execute(w, m)
}
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/grammar", grammarFunc)
http.HandleFunc("/grammarMany", grammarFuncMany)
err := http.ListenAndServe(":9999", nil)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("http server run failed err:%#v", err)
}
}
模板文件grammarTemplate.tmpl内容如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Hello Template</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>userInfo: {{.}}</p>
<p>name: {{.name}}</p>
<p>age: {{.age}}</p>
<p>gender: {{.gender}}</p>
<hr>
</body>
</html>
二、多对象变量传入
当传入的变量是map时,也可以在模板文件中通过.根据key来取值。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"text/template"
)
type UserInfo struct {
Name string
Age int
Gender string
}
// 传入单对象
func grammarFunc(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// 1. 编写模板
// 2. 读取模板 解析指定文件生成模板对象
t, err := template.ParseFiles("./grammarTemplate.tmpl")
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("read template faild err: %#v", err)
}
// 3. 渲染模板
// 利用给定数据渲染模板,并将结果写入w
userInfo := UserInfo{
"RandySun",
18,
"男",
}
t.Execute(w, userInfo)
}
// 传入多对象
func grammarFuncMany(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// 1. 编写模板
// 2. 读取模板 解析指定文件生成模板对象
t, err := template.ParseFiles("./grammarTemplate.tmpl")
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("read template faild err: %#v", err)
}
// 3. 渲染模板
// 传入map键值对
m := map[string]interface{}{}
m["name"] = "jack"
m["age"] = 14
m["gender"] = "男"
//t.Execute(w, userInfo)
t.Execute(w, m)
}
func grammarFuncManyToMany(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// 1. 编写模板
// 2. 读取模板 解析指定文件生成模板对象
t, err := template.ParseFiles("./grammarTemplate.tmpl")
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("read template faild err: %#v", err)
}
// 3. 渲染模板
// 传入map键值对
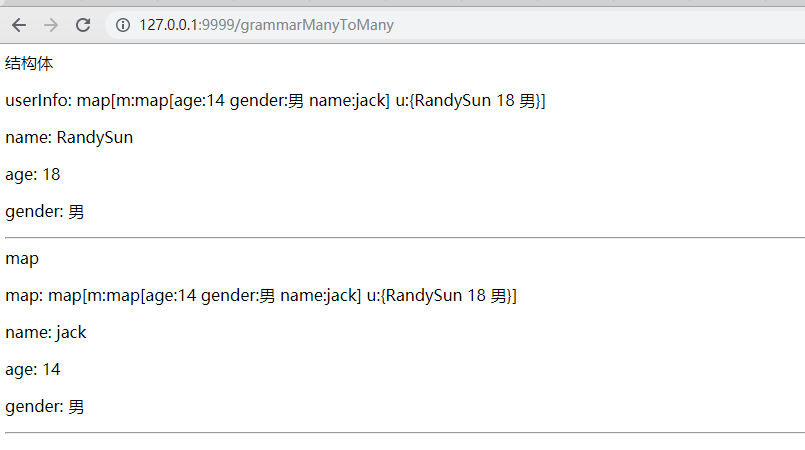
m := map[string]interface{}{}
m["name"] = "jack"
m["age"] = 14
m["gender"] = "男"
userInfo := UserInfo{
"RandySun",
18,
"男",
}
um := map[string]interface{}{
"m":m,
"u": userInfo,
}
t.Execute(w, um)
}
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/grammar", grammarFunc)
http.HandleFunc("/grammarMany", grammarFuncMany)
http.HandleFunc("/grammarManyToMany", grammarFuncManyToMany)
err := http.ListenAndServe(":9999", nil)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("http server run failed err:%#v", err)
}
}
模板文件grammarManyToMany.tmpl内容如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Hello Template</title>
</head>
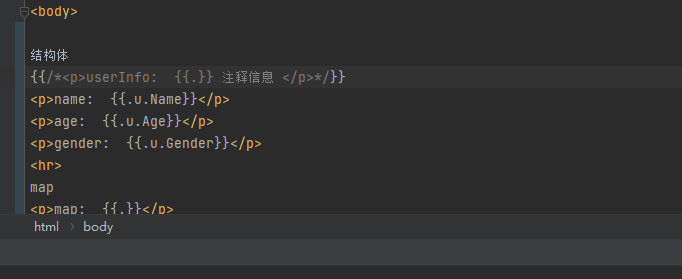
<body>
结构体
<p>userInfo: {{.}}</p>
<p>name: {{.u.Name}}</p>
<p>age: {{.u.Age}}</p>
<p>gender: {{.u.Gender}}</p>
<hr>
map
<p>map: {{.}}</p>
<p>name: {{.m.name}}</p>
<p>age: {{.m.age}}</p>
<p>gender: {{.m.gender}}</p>
<hr>
</body>
</html>
三、注释
{{/* a comment */}}
注释,执行时会忽略。可以多行。注释不能嵌套,并且必须紧贴分界符始止。
四、pipeline
pipeline是指产生数据的操作。比如{{.}}、{{.Name}}等。Go的模板语法中支持使用管道符号|链接多个命令,用法和unix下的管道类似:|前面的命令会将运算结果(或返回值)传递给后一个命令的最后一个位置。
注意:并不是只有使用了|才是pipeline。Go的模板语法中,pipeline的概念是传递数据,只要能产生数据的,都是pipeline。
五、变量
我们还可以在模板中声明变量,用来保存传入模板的数据或其他语句生成的结果。具体语法如下:
$obj := {{.}}
其中$obj是变量的名字,在后续的代码中就可以使用该变量了。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"text/template"
)
type UserInfo struct {
Name string
Age int
Gender string
}
func grammarFuncManyToMany(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// 1. 编写模板
// 2. 读取模板 解析指定文件生成模板对象
t, err := template.ParseFiles("./grammarTemplate.tmpl")
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("read template faild err: %#v", err)
}
// 3. 渲染模板
// 传入map键值对
m := map[string]interface{}{}
m["name"] = "jack"
m["age"] = 14
m["gender"] = "男"
userInfo := UserInfo{
"RandySun",
18,
"男",
}
um := map[string]interface{}{
"m":m,
"u": userInfo,
}
t.Execute(w, um)
}
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/grammarManyToMany", grammarFuncManyToMany)
err := http.ListenAndServe(":9999", nil)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("http server run failed err:%#v", err)
}
}
模板
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Hello Template</title>
</head>
<body>
{{$varObj :=.m.age}}
<p>变量赋值varObj:{{$varObj}}</p>
</body>
</html>
六、移除空格
有时候我们在使用模板语法的时候会不可避免的引入一下空格或者换行符,这样模板最终渲染出来的内容可能就和我们想的不一样,这个时候可以使用{{-语法去除模板内容左侧的所有空白符号, 使用-}}去除模板内容右侧的所有空白符号。
例如:
{{- .Name -}}
注意:-要紧挨{{和}},同时与模板值之间需要使用空格分隔。
七、条件判断和比较函数
Go模板语法中的条件判断有以下几种:
{{if pipeline}} T1 {{end}}
{{if pipeline}} T1 {{else}} T0 {{end}}
{{if pipeline}} T1 {{else if pipeline}} T0 {{end}}
布尔函数会将任何类型的零值视为假,其余视为真。
下面是定义为函数的二元比较运算的集合:
eq 如果arg1 == arg2则返回真
ne 如果arg1 != arg2则返回真
lt 如果arg1 < arg2则返回真
le 如果arg1 <= arg2则返回真
gt 如果arg1 > arg2则返回真
ge 如果arg1 >= arg2则返回真
为了简化多参数相等检测,eq(只有eq)可以接受2个或更多个参数,它会将第一个参数和其余参数依次比较,返回下式的结果:
{{eq arg1 arg2 arg3}}
比较函数只适用于基本类型(或重定义的基本类型,如”type Celsius float32”)。但是,整数和浮点数不能互相比较。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"text/template"
)
type UserInfo struct {
Name string
Age int
Gender string
}
func grammarFuncManyToMany(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// 1. 编写模板
// 2. 读取模板 解析指定文件生成模板对象
t, err := template.ParseFiles("./grammarTemplate.tmpl")
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("read template faild err: %#v", err)
}
// 3. 渲染模板
// 传入map键值对
m := map[string]interface{}{}
m["name"] = "jack"
m["age"] = 14
m["gender"] = "男"
userInfo := UserInfo{
"RandySun",
18,
"男",
}
um := map[string]interface{}{
"m":m,
"u": userInfo,
}
t.Execute(w, um)
}
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/grammarManyToMany", grammarFuncManyToMany)
err := http.ListenAndServe(":9999", nil)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("http server run failed err:%#v", err)
}
}
模板:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Hello Template</title>
</head>
条件判断和比较函数 <br>
{{if lt .m.age 23}}
<span style="color: #d21414">去上学吧,你不配打工人</span>
{{else if gt 23}}
打工人
{{end}}
</body>
</html>

八、range
Go的模板语法中使用range关键字进行遍历,有以下两种写法,其中pipeline的值必须是数组、切片、字典或者通道。
{{range pipeline}} T1 {{end}}
如果pipeline的值其长度为0,不会有任何输出
{{range pipeline}} T1 {{else}} T0 {{end}}
如果pipeline的值其长度为0,则会执行T0。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"text/template"
)
type UserInfo struct {
Name string
Age int
Gender string
}
func grammarFuncManyToMany(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// 1. 编写模板
// 2. 读取模板 解析指定文件生成模板对象
t, err := template.ParseFiles("./grammarTemplate.tmpl")
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("read template faild err: %#v", err)
}
// 3. 渲染模板
// 传入map键值对
m := map[string]interface{}{}
m["name"] = "jack"
m["age"] = 14
m["gender"] = "男"
userInfo := UserInfo{
"RandySun",
18,
"男",
}
um := map[string]interface{}{
"m":m,
"u": userInfo,
}
t.Execute(w, um)
}
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/grammarManyToMany", grammarFuncManyToMany)
err := http.ListenAndServe(":9999", nil)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("http server run failed err:%#v", err)
}
}
模板
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Hello Template</title>
</head>
range使用 <br>
{{range $k, $v := .}}
key:  {{$k}}    value:  {{$v}} <br>
{{else}}
空空如也,真穷啥也不给我
{{end}}
</body>
</html>

九、with局部作用域
{{with pipeline}} T1 {{end}}
如果pipeline为empty不产生输出,否则将dot设为pipeline的值并执行T1。不修改外面的dot。
{{with pipeline}} T1 {{else}} T0 {{end}}
如果pipeline为empty,不改变dot并执行T0,否则dot设为pipeline的值并执行T1。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"text/template"
)
type UserInfo struct {
Name string
Age int
Gender string
}
func grammarFuncManyToMany(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// 1. 编写模板
// 2. 读取模板 解析指定文件生成模板对象
t, err := template.ParseFiles("./grammarTemplate.tmpl")
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("read template faild err: %#v", err)
}
// 3. 渲染模板
// 传入map键值对
m := map[string]interface{}{}
m["name"] = "jack"
m["age"] = 14
m["gender"] = "男"
userInfo := UserInfo{
"RandySun",
18,
"男",
}
um := map[string]interface{}{
"m":m,
"u": userInfo,
}
t.Execute(w, um)
}
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/grammarManyToMany", grammarFuncManyToMany)
err := http.ListenAndServe(":9999", nil)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("http server run failed err:%#v", err)
}
}
模板
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Hello Template</title>
</head>
<hr>
with局部作用域 <br>
{{with .m}}
<p>name: {{.name}}</p>
<p>age: {{.age}}</p>
<p>gender: {{.gender}}</p>
{{else}}
空空如也,真穷啥也不给我
{{end}}
<hr>
</body>
</html>

十、预定义函数
执行模板时,函数从两个函数字典中查找:首先是模板函数字典,然后是全局函数字典。一般不在模板内定义函数,而是使用Funcs方法添加函数到模板里。
预定义的全局函数如下:
and
函数返回它的第一个empty参数或者最后一个参数;
就是说"and x y"等价于"if x then y else x";所有参数都会执行;
or
返回第一个非empty参数或者最后一个参数;
亦即"or x y"等价于"if x then x else y";所有参数都会执行;
not
返回它的单个参数的布尔值的否定
len
返回它的参数的整数类型长度
index
执行结果为第一个参数以剩下的参数为索引/键指向的值;
如"index x 1 2 3"返回x[1][2][3]的值;每个被索引的主体必须是数组、切片或者字典。
print
即fmt.Sprint
printf
即fmt.Sprintf
println
即fmt.Sprintln
html
返回与其参数的文本表示形式等效的转义HTML。
这个函数在html/template中不可用。
urlquery
以适合嵌入到网址查询中的形式返回其参数的文本表示的转义值。
这个函数在html/template中不可用。
js
返回与其参数的文本表示形式等效的转义JavaScript。
call
执行结果是调用第一个参数的返回值,该参数必须是函数类型,其余参数作为调用该函数的参数;
如"call .X.Y 1 2"等价于go语言里的dot.X.Y(1, 2);
其中Y是函数类型的字段或者字典的值,或者其他类似情况;
call的第一个参数的执行结果必须是函数类型的值(和预定义函数如print明显不同);
该函数类型值必须有1到2个返回值,如果有2个则后一个必须是error接口类型;
如果有2个返回值的方法返回的error非nil,模板执行会中断并返回给调用模板执行者该错误;
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"text/template"
)
type UserInfo struct {
Name string
Age int
Gender string
}
func grammarFuncManyToMany(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// 1. 编写模板
// 2. 读取模板 解析指定文件生成模板对象
t, err := template.ParseFiles("./grammarTemplate.tmpl")
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("read template faild err: %#v", err)
}
// 3. 渲染模板
// 传入map键值对
m := map[string]interface{}{}
m["name"] = "jack"
m["age"] = 14
m["gender"] = "男"
userInfo := UserInfo{
"RandySun",
18,
"男",
}
um := map[string]interface{}{
"m": m,
"u": userInfo,
"s": []int{1, 3, 4},
}
t.Execute(w, um)
}
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/grammar", grammarFunc)
http.HandleFunc("/grammarMany", grammarFuncMany)
http.HandleFunc("/grammarManyToMany", grammarFuncManyToMany)
err := http.ListenAndServe(":9999", nil)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("http server run failed err:%#v", err)
}
}
模板
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Hello Template</title>
</head>
{{len .m}} <br>
{{index .s 2}} <br>
</html>
