实验3:OpenFlow协议分析实践
一、实验目的
1.能够运用 wireshark 对 OpenFlow 协议数据交互过程进行抓包;
2.能够借助包解析工具,分析与解释 OpenFlow协议的数据包交互过程与机制。
二、实验环境
1.下载虚拟机软件Oracle VisualBox;
2.在虚拟机中安装Ubuntu 20.04 Desktop amd64,并完整安装Mininet;
三、实验要求
(一)基本要求
1.搭建下图所示拓扑,完成相关 IP 配置,并实现主机与主机之间的 IP 通信。用抓包软件获取控制器与交换机之间的通信数据包。
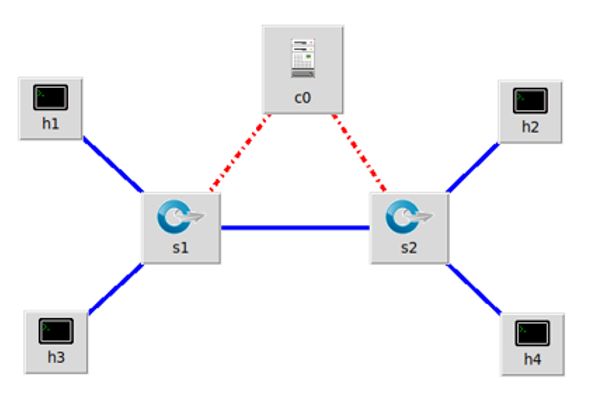
| 主机 | IP地址 |
|---|---|
| h1 | 192.168.0.101/24 |
| h2 | 192.168.0.102/24 |
| h3 | 192.168.0.103/24 |
| h4 | 192.168.0.104/24 |
- 构建拓扑,并按要求配置IP地址
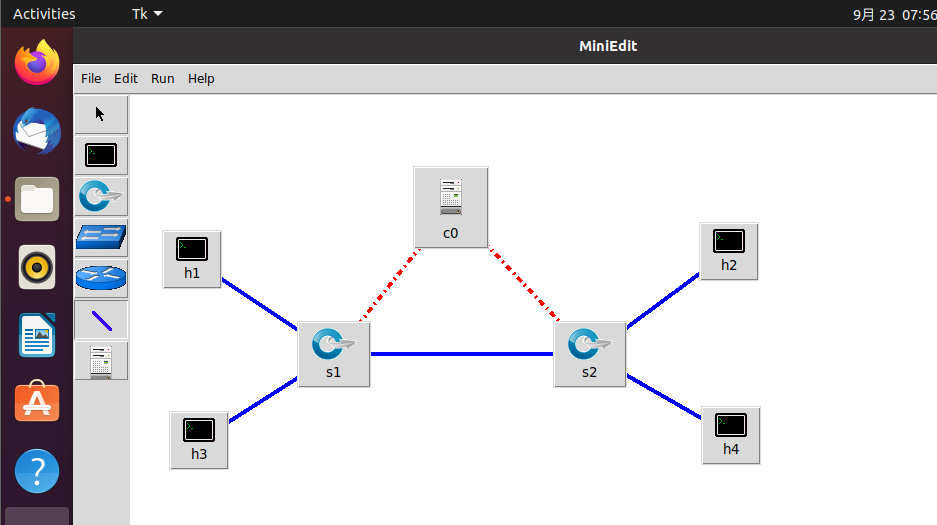
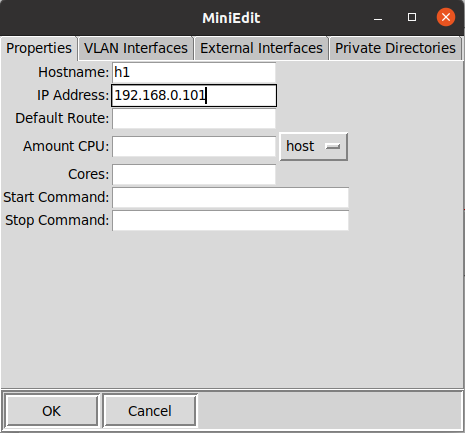
- 配置完毕后将文件保存至031902113/lab3
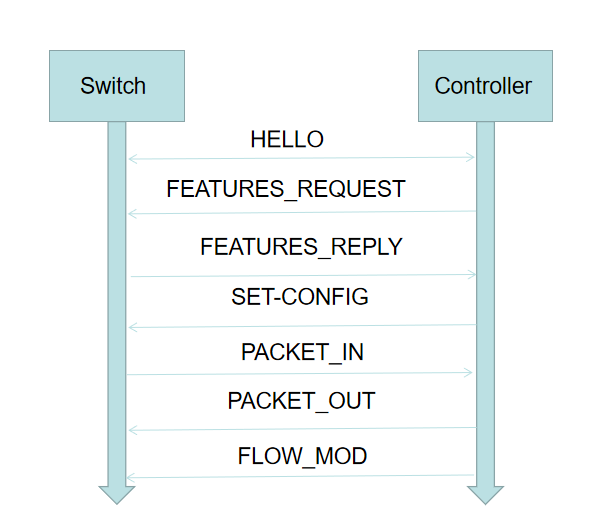
2.查看抓包结果,分析OpenFlow协议中交换机与控制器的消息交互过程,画出相关交互图或流程图。
sudo wireshark启动wireshark,选择any模式进行抓包
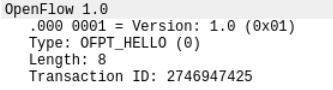
Type:OFPT_HELLO 控制器6633端口-->交换机35850端口,协议为openflow1.0
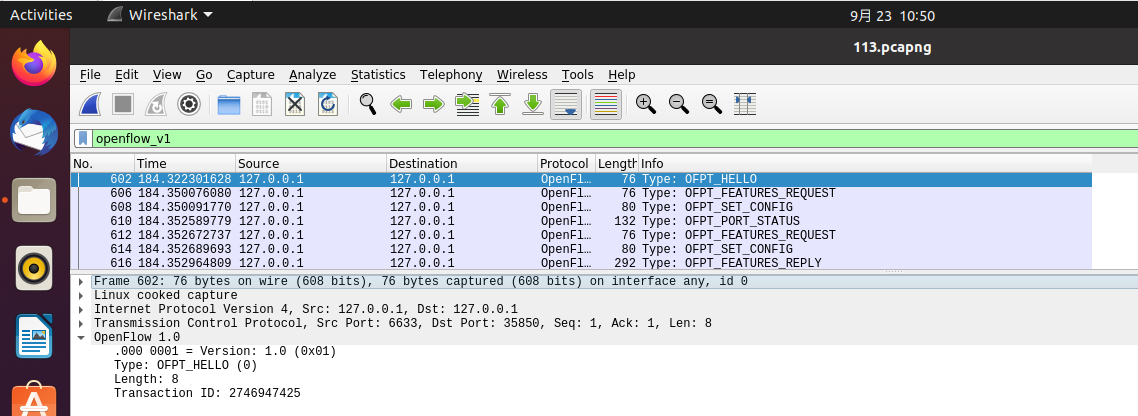
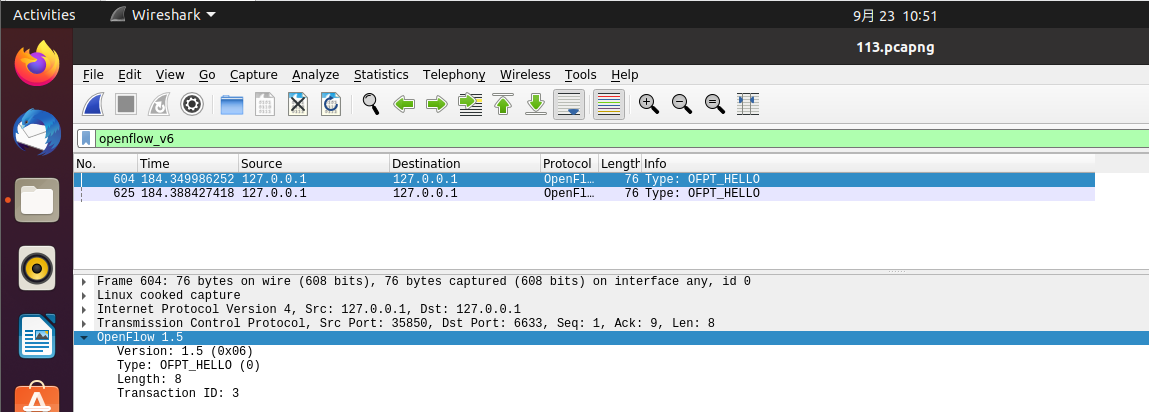
交换机35850端口-->控制器6633端口,协议为openflow1.5
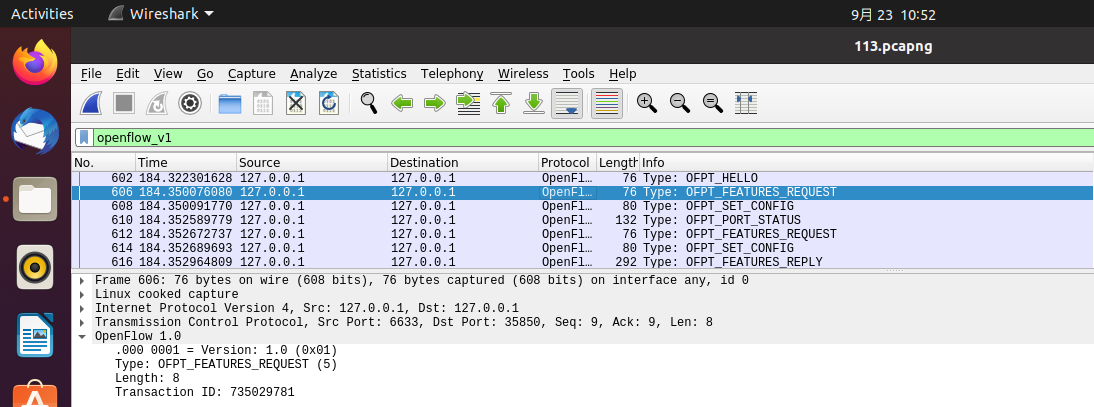
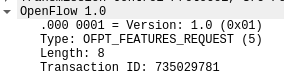
Type:OFPT_FEATURES_REQUEST控制器6633端口-->交换机35850端口,协议为openflow1.0
Type:OFPT_SET_CONFIG控制器6633端口-->交换机35850端口,协议为openflow1.0
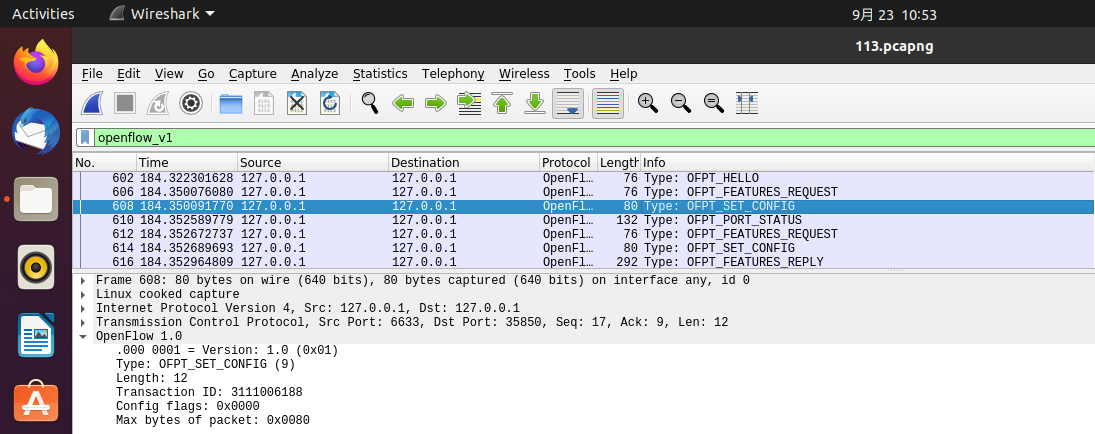
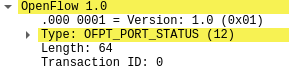
Type:OFPT_PORT_STATUS交换机35850端口-->控制器6633端口,协议为openflow1.0
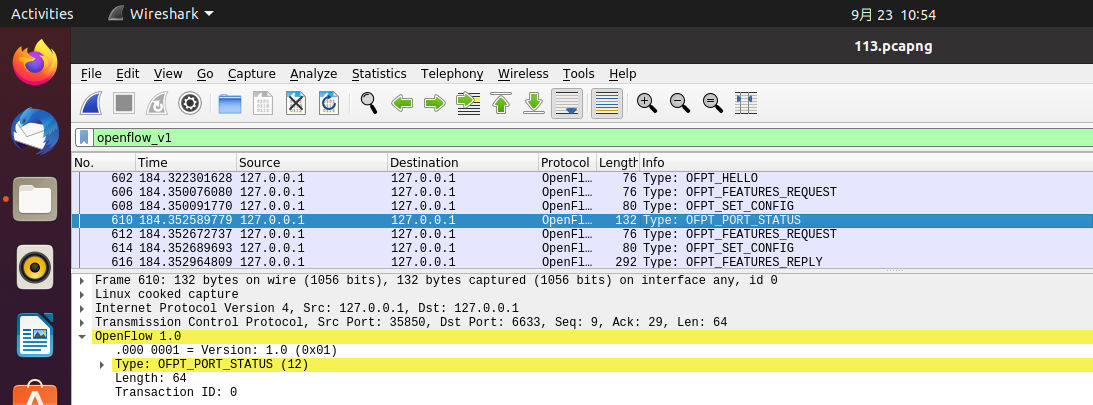
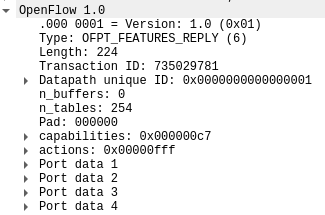
OFPT_FEATURES_REPLY交换机35850端口-->控制器6633端口,协议为openflow1.0
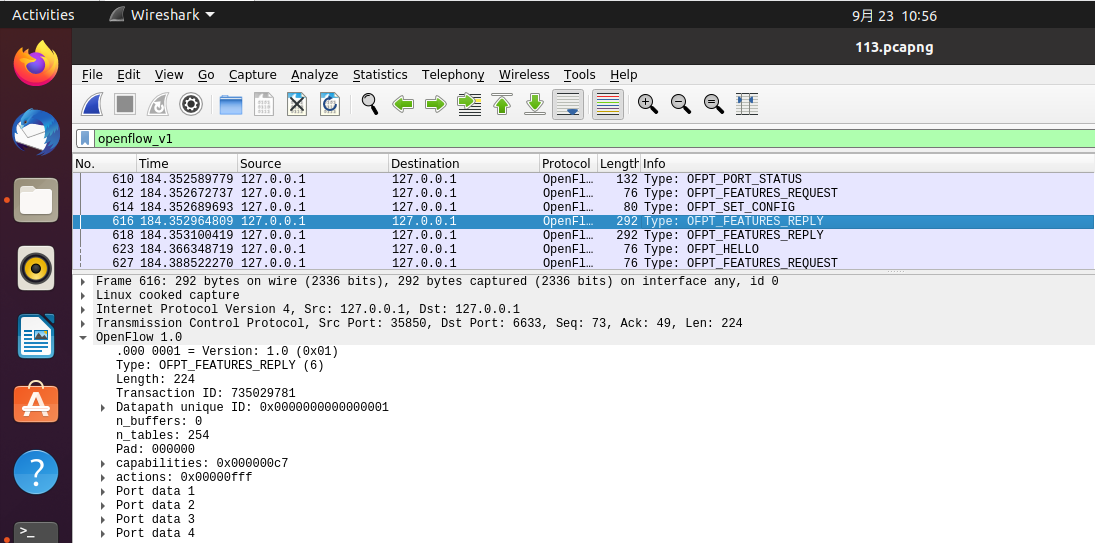
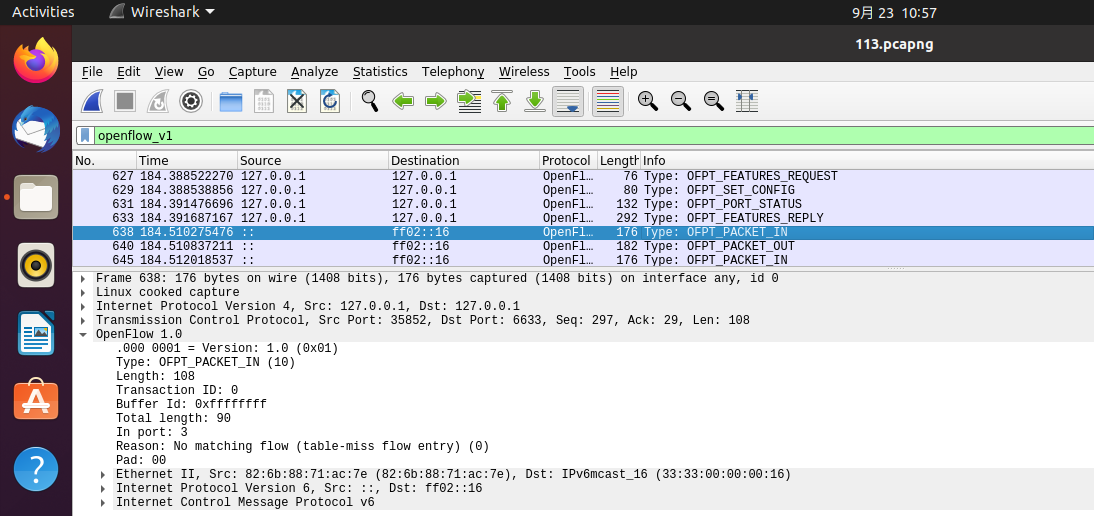
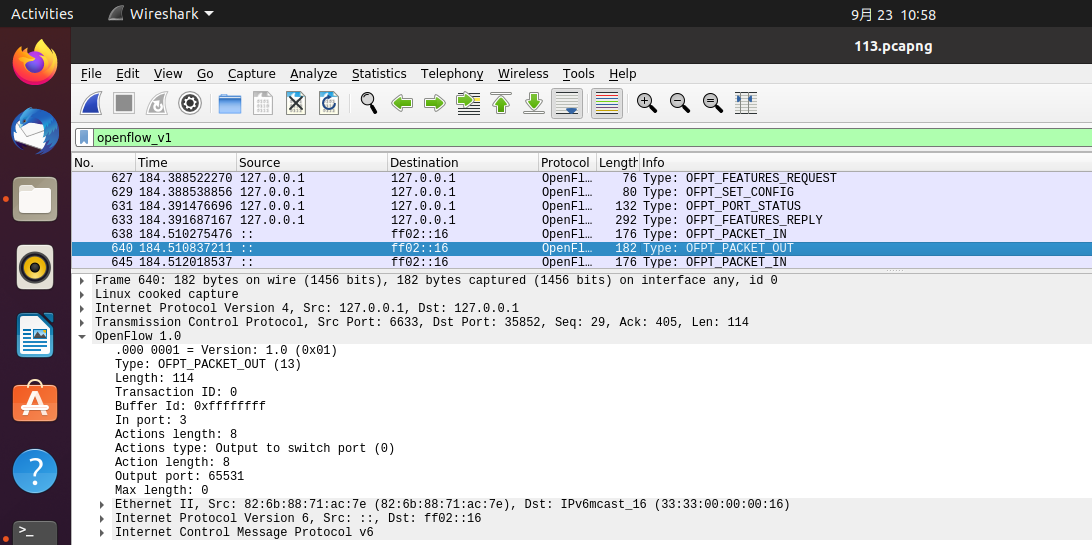
OFPT_PACKET_IN交换机35852端口-->控制器6633端口,协议为openflow1.0
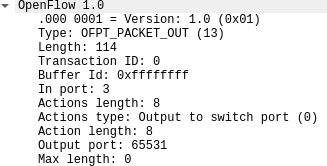
OFPT_PACKET_OUT控制器6633端口-->交换机35852端口,协议为openflow1.0
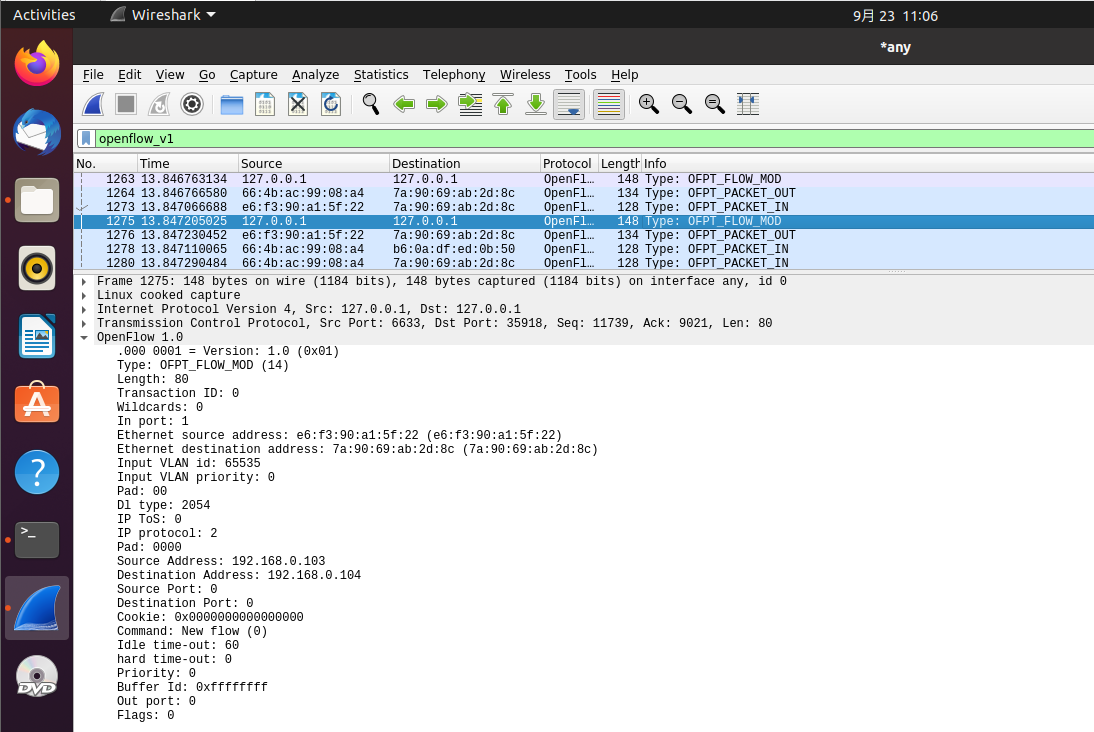
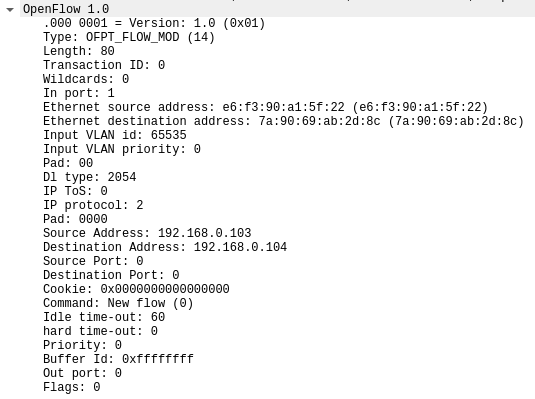
OFPT_FLOW_MOD控制器6633端口-->交换机35918端口,协议为openflow1.0
- 本实验中交换机和控制器之间消息交互图
3.回答问题:交换机与控制器建立通信时是使用TCP协议还是UDP协议?
答:交换机与控制器建立通信时使用Transmission Control Protocol为TCP协议。
(二)进阶要求
1.将抓包结果对照OpenFlow源码,了解OpenFlow主要消息类型对应的数据结构定义。
1.HELLO源码与对应抓包结果
struct ofp_header {
uint8_t version; /* OFP_VERSION. */
uint8_t type; /* One of the OFPT_ constants. */
uint16_t length; /* Length including this ofp_header. */
uint32_t xid; /* Transaction id associated with this packet.
Replies use the same id as was in the request
to facilitate pairing. */
};
struct ofp_hello {
struct ofp_header header;
};
2.FEATURES_REQUEST源码参数格式与HELLO相同,对应抓包结果
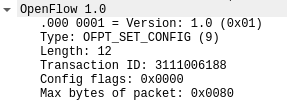
3.SET_CONFIG源码与对应抓包结果
/* Switch configuration. */
struct ofp_switch_config {
struct ofp_header header;
uint16_t flags; /* OFPC_* flags. */
uint16_t miss_send_len; /* Max bytes of new flow that datapath should
send to the controller. */
};
4.PORT_STATUS源码与对应抓包结果
/* A physical port has changed in the datapath */
struct ofp_port_status {
struct ofp_header header;
uint8_t reason; /* One of OFPPR_*. */
uint8_t pad[7]; /* Align to 64-bits. */
struct ofp_phy_port desc;
};
5.FEATUERS_REPLY源码与对应抓包结果
struct ofp_switch_features {
struct ofp_header header;
uint64_t datapath_id; /* Datapath unique ID. The lower 48-bits are for
a MAC address, while the upper 16-bits are
implementer-defined. */
uint32_t n_buffers; /* Max packets buffered at once. */
uint8_t n_tables; /* Number of tables supported by datapath. */
uint8_t pad[3]; /* Align to 64-bits. */
/* Features. */
uint32_t capabilities; /* Bitmap of support "ofp_capabilities". */
uint32_t actions; /* Bitmap of supported "ofp_action_type"s. */
/* Port info.*/
struct ofp_phy_port ports[0]; /* Port definitions. The number of ports
is inferred from the length field in
the header. */
};
/* Description of a physical port */
struct ofp_phy_port {
uint16_t port_no;
uint8_t hw_addr[OFP_ETH_ALEN];
char name[OFP_MAX_PORT_NAME_LEN]; /* Null-terminated */
uint32_t config; /* Bitmap of OFPPC_* flags. */
uint32_t state; /* Bitmap of OFPPS_* flags. */
/* Bitmaps of OFPPF_* that describe features. All bits zeroed if
* unsupported or unavailable. */
uint32_t curr; /* Current features. */
uint32_t advertised; /* Features being advertised by the port. */
uint32_t supported; /* Features supported by the port. */
uint32_t peer; /* Features advertised by peer. */
};
6.PACKET_IN源码与对应抓包结果
struct ofp_packet_in {
struct ofp_header header;
uint32_t buffer_id; /* ID assigned by datapath. */
uint16_t total_len; /* Full length of frame. */
uint16_t in_port; /* Port on which frame was received. */
uint8_t reason; /* Reason packet is being sent (one of OFPR_*) */
uint8_t pad;
uint8_t data[0]; /* Ethernet frame, halfway through 32-bit word,
so the IP header is 32-bit aligned. The
amount of data is inferred from the length
field in the header. Because of padding,
offsetof(struct ofp_packet_in, data) ==
sizeof(struct ofp_packet_in) - 2. */
};
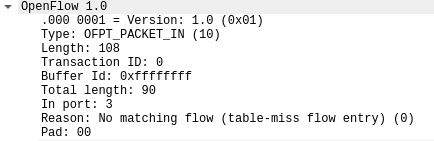
7.PACKET_OUT源码与对应抓包结果
struct ofp_packet_out {
struct ofp_header header;
uint32_t buffer_id; /* ID assigned by datapath (-1 if none). */
uint16_t in_port; /* Packet's input port (OFPP_NONE if none). */
uint16_t actions_len; /* Size of action array in bytes. */
struct ofp_action_header actions[0]; /* Actions. */
/* uint8_t data[0]; */ /* Packet data. The length is inferred
from the length field in the header.
(Only meaningful if buffer_id == -1.) */
};
8.FLOW_MOD源码与对应抓包结果
struct ofp_flow_mod {
struct ofp_header header;
struct ofp_match match; /* Fields to match */
uint64_t cookie; /* Opaque controller-issued identifier. */
/* Flow actions. */
uint16_t command; /* One of OFPFC_*. */
uint16_t idle_timeout; /* Idle time before discarding (seconds). */
uint16_t hard_timeout; /* Max time before discarding (seconds). */
uint16_t priority; /* Priority level of flow entry. */
uint32_t buffer_id; /* Buffered packet to apply to (or -1).
Not meaningful for OFPFC_DELETE*. */
uint16_t out_port; /* For OFPFC_DELETE* commands, require
matching entries to include this as an
output port. A value of OFPP_NONE
indicates no restriction. */
uint16_t flags; /* One of OFPFF_*. */
struct ofp_action_header actions[0]; /* The action length is inferred
from the length field in the
header. */
};
struct ofp_action_header {
uint16_t type; /* One of OFPAT_*. */
uint16_t len; /* Length of action, including this
header. This is the length of action,
including any padding to make it
64-bit aligned. */
uint8_t pad[4];
};
个人总结
遇到的问题一:抓包时只找到了REQUEST和REPLY的包
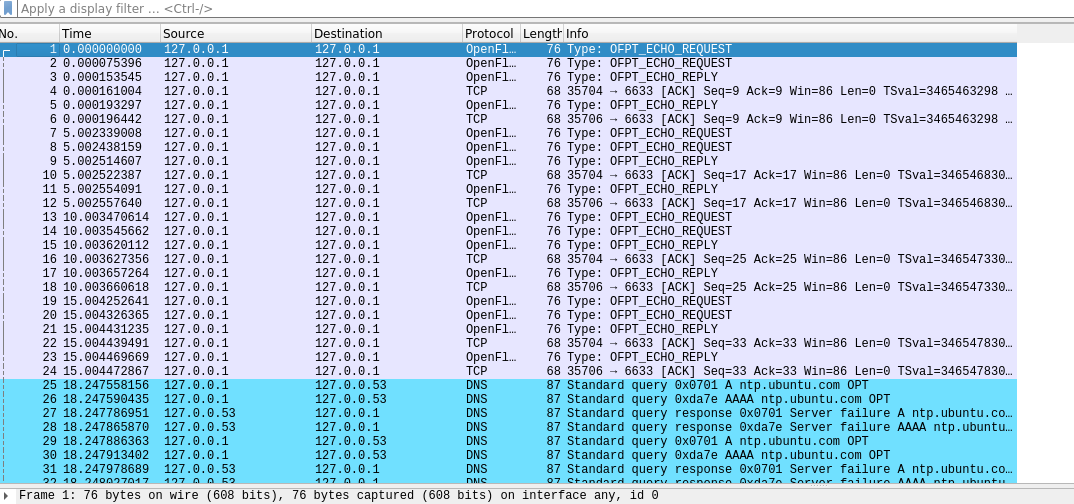
解决:原因是在运行mininet后才打开wireshark进行抓包,实际上要先打开wireshark进行监测,再运行mininet。
遇到的问题二:抓取的包括DNS协议的包,如何进行筛选?
解决:在wireshark中Apply a display filte中输入openflow_v1或着其他进行筛选。
遇到的问题三:找不到交换机给控制器发送的HELLO报文
解决:当选择openflow_v6时会出现两个交换机给控制器发送的HELLO报文,协议为OpenFlow1.5。
遇到的问题四:为什么最后三种报文的交换机端口都改变了?
解决:这次实验拓扑里有两个交换机,端口会变是因为选的不是同一个交换机的数据包,而FLOW_MOD交换机端口号的改变是因为第一次没找到该报文,而重新做的时候重新给交换机分配了端口号。
实验心得
本次实验在命令输入上较于前两次实验的难度有降低,主要是考验如何使用wireshark进行数据抓包的操作以及需要将openflow源码与抓包结果对应起来。在更加熟悉使用wireshark进行抓包操作的同时,让我更进一步理解交换机和控制器之间消息交互过程,在进阶部分找到的源码可以作进一步的分析,这样可以对OpenFlow协议有更深刻的认识。