(mathcal{Description})
Link.
给定一棵 (n) 个结点的树,每次操作选择三个结点 (a,b,c),满足 ((a,b),(b,c)in E),并令 (a) 的所有邻接点(包括 (b))与 (c) 邻接且不再与 (a) 邻接;再令 (a) 与 (c) 邻接。求至少几次操作使树变为菊花图。
(nle2 imes10^5)。
操作图例:
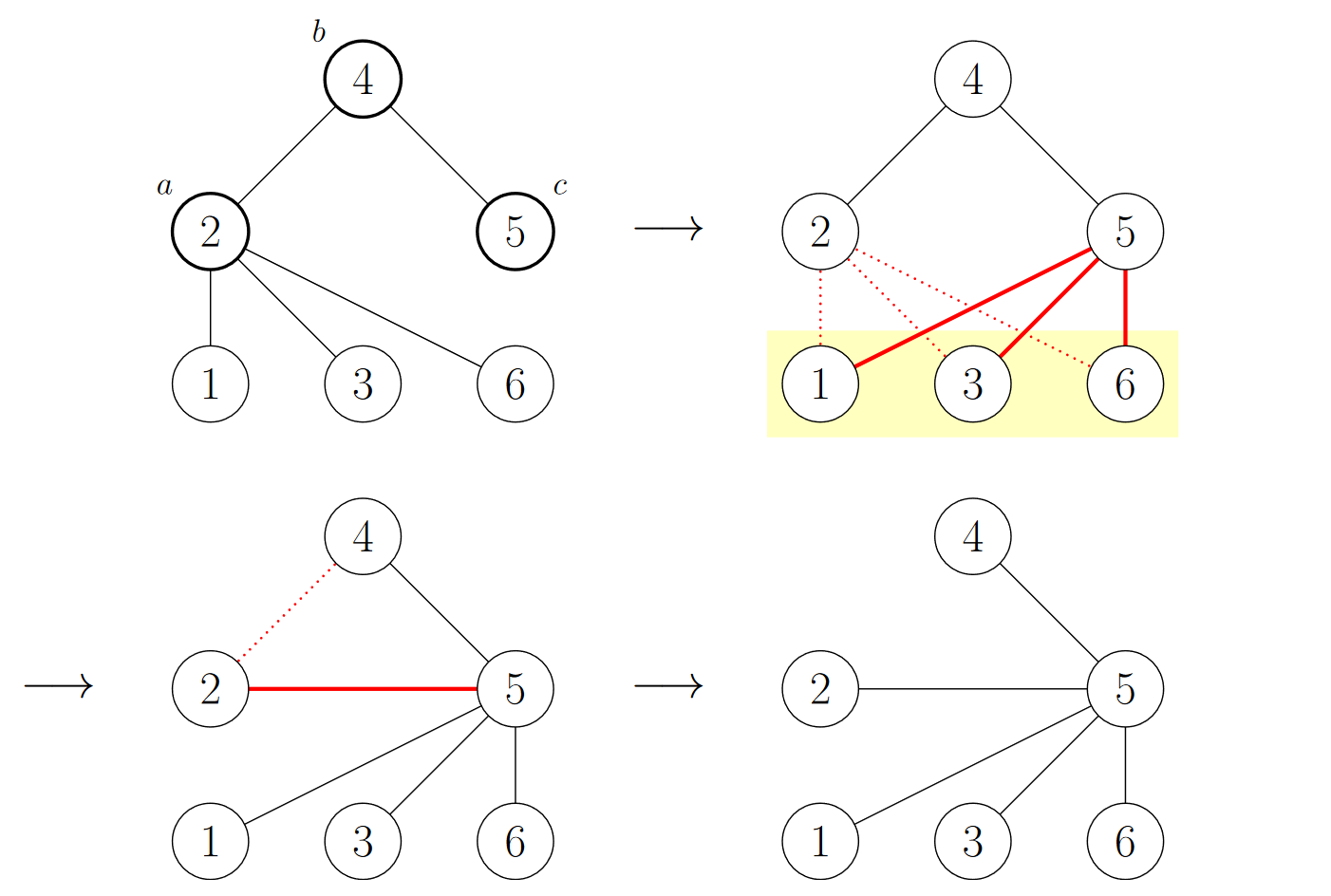
(mathcal{Solution})
和 CF1025G 有点类似。不妨令 (1) 为树的根,结点 (u) 的深度记为 (d(u)),(d(1)=1)。构造势能函数 (Phi:T ightarrowmathbb N_+),有:
[Phi(T)=sum_{uin T}[2|d(u)]
]
先考虑目标状态,菊花图的势能显然为 (1)(根是花瓣)或 (n-1)(根是花蕊)。再观察一次操作带来的势能变化,发现仅有 (a) 结点的深度的奇偶性改变,那么:
[DeltaPhi=pm1
]
记初始时树为 (S),可知答案为:
[min{(n-1)-Phi(S),Phi(S)-1}
]
复杂度 (mathcal O(n))。嗯唔,做完了 www!
(mathcal{Code})
/* Clearink */
#include <cstdio>
inline int rint () {
int x = 0, f = 1; char s = getchar ();
for ( ; s < '0' || '9' < s; s = getchar () ) f = s == '-' ? -f : f;
for ( ; '0' <= s && s <= '9'; s = getchar () ) x = x * 10 + ( s ^ '0' );
return x * f;
}
template<typename Tp>
inline void wint ( Tp x ) {
if ( x < 0 ) putchar ( '-' ), x = ~ x + 1;
if ( 9 < x ) wint ( x / 10 );
putchar ( x % 10 ^ '0' );
}
const int MAXN = 2e5;
int n, ecnt, head[MAXN + 5], cnt[2];
struct Edge { int to, nxt; } graph[MAXN * 2 + 5];
inline void link ( const int s, const int t ) {
graph[++ ecnt] = { t, head[s] };
head[s] = ecnt;
}
inline void solve ( const int u, const int f, const int dep ) {
++ cnt[dep & 1];
for ( int i = head[u], v; i; i = graph[i].nxt ) {
if ( ( v = graph[i].to ) ^ f ) {
solve ( v, u, dep + 1 );
}
}
}
int main () {
n = rint ();
for ( int i = 1, u, v; i < n; ++ i ) {
u = rint (), v = rint ();
link ( u, v ), link ( v, u );
}
solve ( 1, 0, 0 );
printf ( "%d
", ( cnt[0] < cnt[1] ? cnt[0] : cnt[1] ) - 1 );
return 0;
}
(mathcal{Details})
势能分析的方法有点像数学上的特征值法。这种操作题没思路的时候不妨研究一下单次操作,构造出一个变化极为简单的“特征”来快速求解。