一、循环嵌套
1、格式
for()
{
for()
{
}
}
2、执行顺序
先执行外边循环进到循环体发现里面的循环,开始执行里面的循环。等到里面的循环执行完毕,再执行外边的循环。
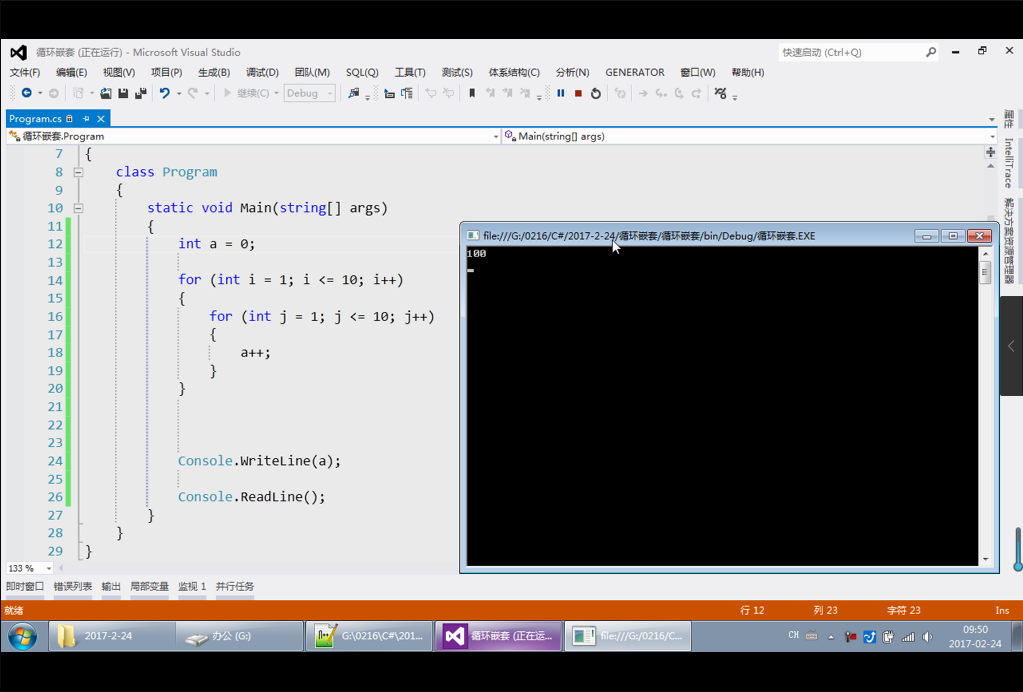
在外面循环第一次,进到里面循环十次,再出去循环第二次,再进到里面循环十次。一共循环了100次。
3、练习题:打印九九乘法表
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace _9x9乘法表 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) { Console.Write(i+"x"+j+"="+i*j+" "); } Console.WriteLine(); } Console.ReadLine(); } } }
二、跳转语句
1、 break; 跳出循环,终止接下来所有的循环次数。
2、 continue; 终止当前这一次的循环,继续下一次循环。
三、迭代穷举
1、迭代: 不断在自身上增加新的功能
例如:
int a =0;
for(int i =1; i<10; i++)
{
a++;
}
console.write(a);
2、穷举法
代表题目:百鸡百钱。将所有的可能性全部列举出来。
有100文钱,小鸡0.5文钱 ,母鸡1文钱,公鸡2文钱
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace 下午内容 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int count = 0; for (int i = 0; i <= 200; i++) { for (int m = 0; m <= 100; m++) { for (int g = 0; g <= 50; g++) { if ((i * 0.5) + (m * 1) + (g * 2) == 100 && i + m + g == 100) { Console.WriteLine("小鸡" + i + "只,花费" + (i * 0.5) + "元,母鸡" + m + "只,花费" + m + "元,公鸡" + g + "只,花费" + (g * 2) + "元"); count++; } } } } Console.WriteLine("总共有["+count+"]种可能性"); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
四、异常语句
作用:捕获异常,并作出相应的处理
格式:
try
{
可能会出错的代码语句
如果这里出错了,那么不会在继续下面的代码,而是直接进入catch中处理异常
}
catch
{
如果上面出错了,这里是对这个异常的处理方式;
}
finally //可写可不写
{
不管上面有没有错,这里都会走,
}
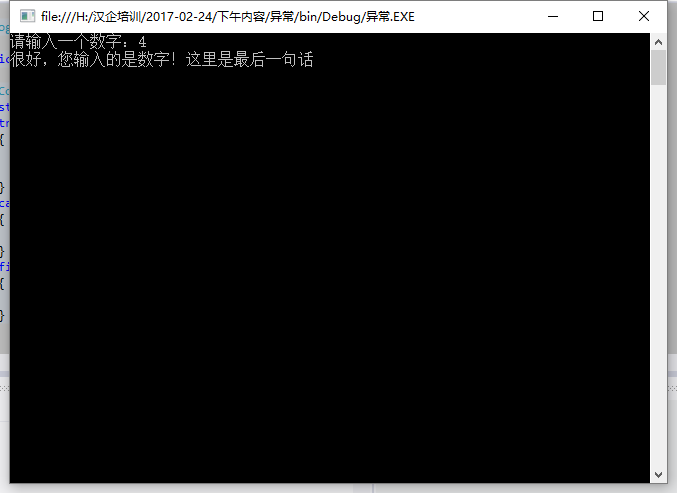
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace 异常 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.Write("请输入一个数字:"); string a = Console.ReadLine(); try { int b = Convert.ToInt32(a); Console.Write("很好,您输入的是数字!"); } catch { Console.Write("您输入的不是数字!"); } finally { Console.Write("这里是最后一句话"); } Console.ReadLine(); } } }

五、while循环
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace while循环 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int sum = 0; int a = 1;//初始条件 while (a <= 10)//循环条件 { sum++;//循环体 a++;//状态改变 } Console.WriteLine(sum); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
注:while 常用于设定一个死循环。
while (true)
{
}