什么是异常?
不正常的,会影响程序的正常执行流程。
例如下面的程序
public static void main(String[] args) { TestDemo1 t = new TestDemo1(); t.a(); System.out.println("其它程序代码"); } public void a() { b(); } public void b() { int x =5; int y = 0; int z = x / y; System.out.println("结果是:"+z); }
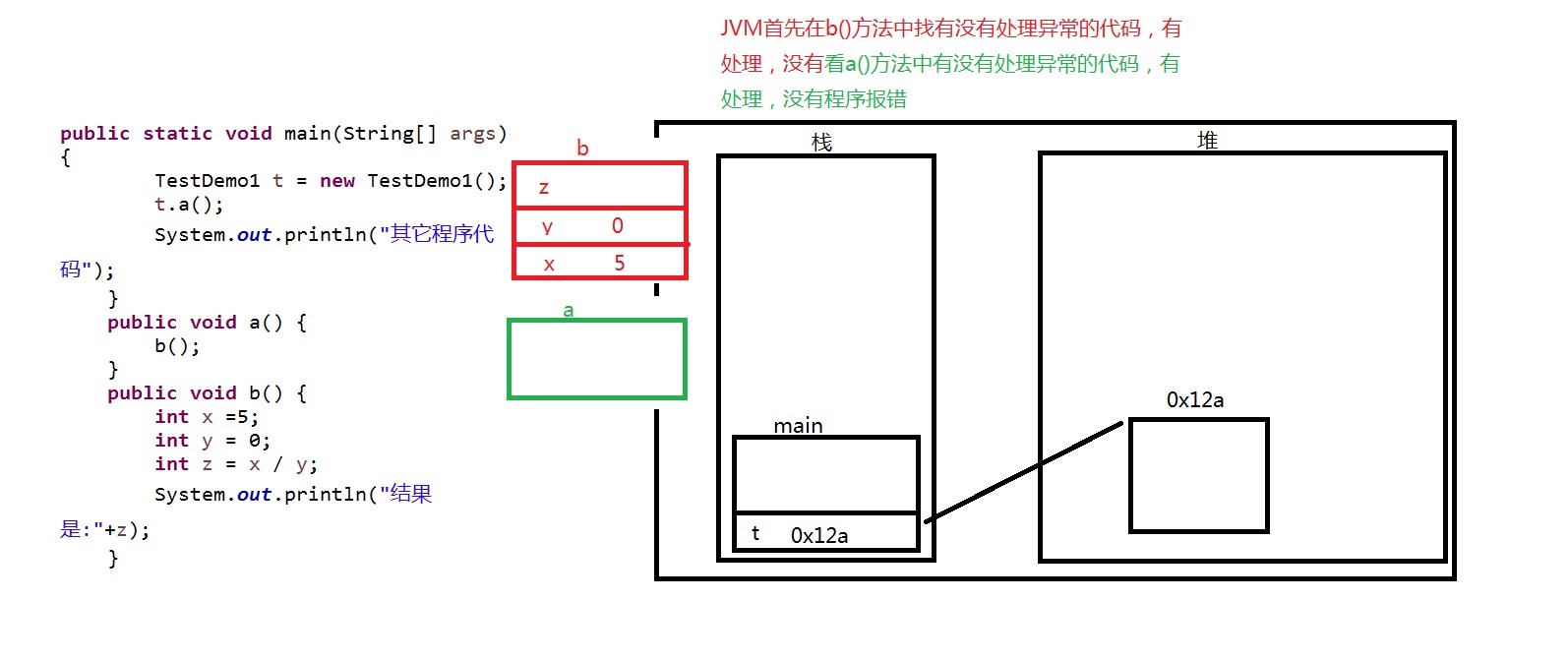
Error:错误
JVM自身的错误,程序员不能处理。
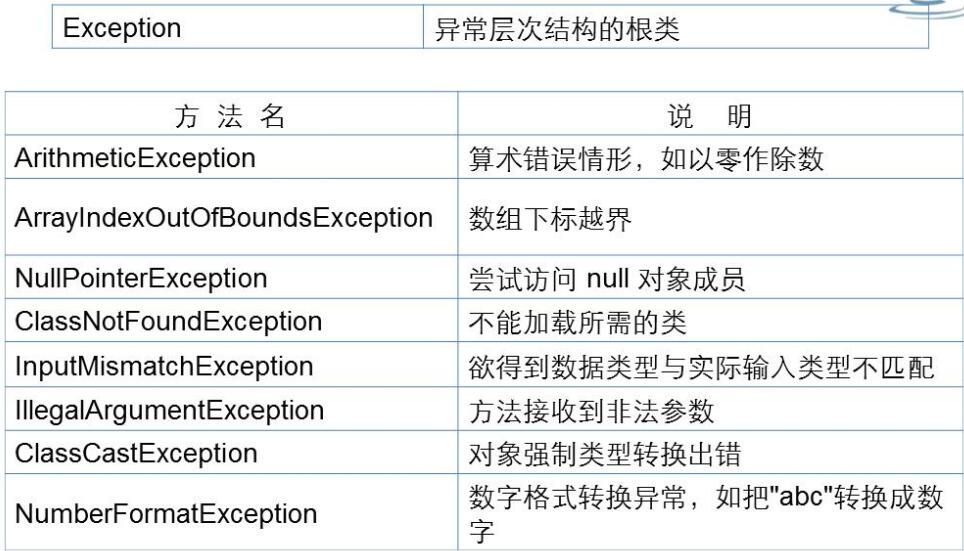
Exception:异常
受检异常(非运行时异常)
程序员必须进行异常处理,否则编译通不过
运行时异常
程序员可以不做处理。改代码。
也可以处理,处理了程序可以不中断。
Java的异常处理是通过5个关键字来实现的:try、catch、finally、throw和throws。
可以添加多个catch
public void method() { try { //代码段(此处可能会产生异常) }catch(异常类型 ex) { //对异常进行处理的代码段 } //代码段 }
try...catch三种情况
2.异常类型匹配,可以处理,程序不会中断,执行catch块,其他代码正常执行
3.异常类型不匹配,程序中断,不执行catch块
public void method() { try { //代码段(此处可能会产生异常) }catch(异常类型 ex1) { //对异常进行处理的代码段 }catch(异常类型 ex2) { //对异常进行处理的代码段 } //代码段 }
多重catch块的好处
对不同的异常,进行不同的处理
但是,遵循规则:
2.先普通后特殊。
保证一些资源释放的代码一定会执行
public void method() { try { //代码段(此处可能会产生异常) }catch(异常类型 ex1) { //对异常进行处理的代码段 }catch(异常类型 ex2) { //对异常进行处理的代码段 }finally{ //此代码块一定会执行,无论是否引发异常 System.out.println("此代码块一定会执行"); } //代码段 }

1 public class TestException2 { 2 3 public void showArr() { 4 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 5 int [] arr = new int[5]; 6 System.out.println("赋值:"); 7 try { 8 for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { 9 arr[i] = input.nextInt(); 10 } 11 Arrays.stream(arr).forEach(System.out::println); 12 } catch (InputMismatchException e) { 13 System.out.println("赋值出错了"); 14 e.printStackTrace(); 15 } catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { 16 System.out.println("赋值出错了"); 17 e.printStackTrace(); 18 } catch (Exception e) { 19 System.out.println("赋值出错了"); 20 e.printStackTrace(); 21 } finally { 22 input.close();//释放资源 23 System.out.println("程序运行结束"); 24 } 25 } 26 public static void main(String[] args) { 27 new TestException2().showArr(); 28 29 } 30 31 }
调用者处理方式
2.throws
throws 运行时异常:调用者可不做处理。

1 class Demo{ 2 public void div() throws RuntimeException{ 3 //我不想处理 4 //处理不了 5 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 6 System.out.println("输入数字"); 7 int n1 = input.nextInt(); 8 int n2 = input.nextInt(); 9 int n3 = n1 / n2; 10 System.out.println(n3); 11 } 12 } 13 public class TestException3 { 14 // 2.继续 throws 向上抛出 throws Exception 15 public static void main(String[] args){ 16 Demo demo = new Demo(); 17 //调用者 18 //(1)处理了 用try - catch 19 /* try { 20 demo.div(); 21 } catch (Exception e) { 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 }*/ 24 demo.div(); 25 26 } 27 28 }
自定义异常
定义类继承自系统异常父类

1 class AgeException extends Exception{ 2 String str; 3 AgeException(String str){ 4 // this.str = str; 5 super(str); 6 } 7 @Override 8 public String getMessage() { 9 return "Message:年龄必须是 0 - 150"; 10 } 11 @Override 12 public String toString() { 13 return "String:年龄必须是 0 - 150"; 14 } 15 @Override 16 public void printStackTrace() { 17 System.out.println("stack:年龄必须是 0 - 150"); 18 } 19 } 20 class Employee{ 21 private int age; 22 private String sex;//男 和 女 Gender 23 24 public String getSex() { 25 return sex; 26 } 27 public void setSex(String sex) throws Exception{ 28 if(sex.equals("男") || sex.equals("女")) { 29 this.sex = sex; 30 }else { 31 throw new Exception("性别必须是男 和女"); 32 } 33 34 } 35 public int getAge() { 36 return age; 37 } 38 /* public void setAge(int age) throws Exception{ 39 if(age >= 0 && age <= 150) { 40 this.age = age; 41 }else { 42 //抛异常 43 throw new Exception("年龄必须在 0 - 150之间"); 44 } 45 }*/ 46 public void setAge(int age) throws AgeException{ 47 if(age >= 0 && age <= 150) { 48 this.age = age; 49 }else { 50 //抛异常 运行时异常 51 throw new AgeException("年龄必须在 0 - 150之间"); 52 } 53 } 54 } 55 public class TestEmployee { 56 57 public static void main(String[] args) { 58 59 try { 60 new Employee().setAge(245); 61 62 } catch (AgeException e) { 63 64 // e.printStackTrace(); 65 // System.out.println(e); 66 System.out.println(e.getMessage()); 67 } 68 } 69 70 }
异常处理的原则
2.尽量避免用过大的try块
3.尽量用多重catch块,对不同的异常进行不同的处理
4.尽量处理异常,不要避免异常
5.最好在@throws中标出异常类型
