转载自:IT学习者-螃蟹
一个方法A使用了Scanner,在里面把它关闭了。然后又在方法B里调用方法A之后就不能再用Scanner了Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
测试代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner; /** * * @author IT学习者-螃蟹 * * */ public class ItxxzScanner { //第一次输入 public void FistTime (){ Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in); int first = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("first:"+first); sc.close(); } //第二次输入 public void SecondTime(){ Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in); int second = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("second:"+second); sc.close(); } //测试入口 public static void main(String arg[]){ ItxxzScanner t = new ItxxzScanner(); t.FistTime(); t.SecondTime(); } }
运行后便抛出如下异常:
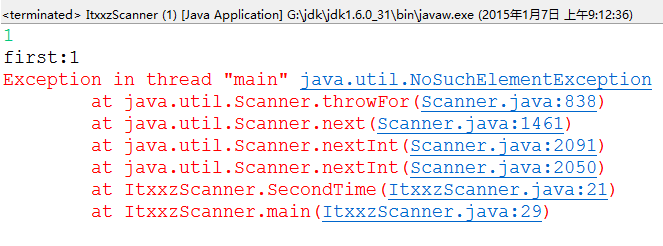
可以看出,在代码第29行的时候报错,抛出了 java.util.NoSuchElementException 异常,
下面我们来分析一下报错的原因:
1、在 FistTime(){...} 使用sc.close();进行关闭处理,会把System.in也关闭了
2、当下次在SecondTime(){...}方法中再进行new Scanner (System.in)操作读取的时候,因为输入流已经关闭,所以读取的值就是-1;
3、在Scanner 的readinput方法里面有以下代码:
try { n = source.read(buf); } catch (IOException ioe) { lastException = ioe; n = -1; } if (n == -1) { sourceClosed = true; needInput = false; }
4、因为读到了-1就设置sourceClosed =true;neepinput=false;
5、在next方法里面有以下代码:
if (needInput) readInput(); else throwFor();
6、当needinput为false,就执行throwFor,因此再看throwFor
skipped = false; if ((sourceClosed) && (position == buf.limit())) throw new NoSuchElementException(); else throw new InputMismatchException();
7、position 是当前读取的内容在缓冲区中位置,因为读取的是-1,因此position =0,而buf.limit()也等于0,因此就执行了throw new NoSuchElementException();