结对作业——WordCount进阶版
标签(空格分隔): 软件工程
Task1:Fork仓库的码云地址
- 博客作业要求地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/happyzm/p/9626779.html
- 结对项目码云地址:https://gitee.com/holmec/PairProject-Java/tree/master/
- 结队伙伴:201621123033 姚雯婷
博客地址
Task2:PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | 个人开发流程 | 预估耗费时间(分钟) | 实际耗费时间(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 10 | 20 |
| · Estimate | 明确需求和其他相关因素,估计每个阶段的时间成本 | 20 | 20 |
| Development | 开发 | 420 | 300 |
| · Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 60 | 30 |
| · Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 20 | 25 |
| · Design Review | 设计复审 | 20 | 20 |
| · Coding Standard | 代码规范 | 40 | 10 |
| · Design | 具体设计 | 20 | 26 |
| · Coding | 具体编码 | 120 | 150 |
| · Code Review | 代码复审 | 20 | 25 |
| · Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 100 | 70 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 80 | 110 |
| · | 测试报告 | 20 | 25 |
| · | 计算工作量 | 10 | 15 |
| · | 并提出过程改进计划 | 20 | 15 |
Task3:解题思路描述
题目的需求分析:
WordCount 结对项目在个人项目的基础上,增加新的功能如下:
- 词组统计:能统计文件夹中指定长度的词组的词频
- 自定义输出:能输出用户指定的前n多的单词与其数量
为了实现上述软件,我们首先要在个人项目基础上增量改进,实现一个Core模块,并基于Core模块实现在命令行测试程序中支持下述命令行参数(原有命令行参数不变)
-
-i 参数设定读入的文件路径
wordCount.exe -i [file] -
-m 参数设定统计的词组长度
wordCount.exe -m [number] -
-n参数设定输出的单词数量
wordCount.exe -n [number] -
-o参数设定生成文件的存储路径
wordCount.exe -o output.txt
思路分析:
这道题是继续上次个人作业的,比起之前多了两个功能,同时加上了前端界面的设计。因为是结对编程,首先我们在代码的确定上做了一些交谈。
- 我的代码在功能实现的基础上,对于文件类的读取比较全面,有考虑到打开or写入的文件为空文件,但是在其他特殊符号的处理上没有结对小伙伴的全面。
- 而她的是在特殊符号上做的全面,但是没有考虑到打开空文件的情况
经过一些讨论,我们决定在基础上采用她的代码,进行新功能的添加。她来负责添加新功能,实现用命令行来执行相关操作,我来负责单元测试,用netBean来实现GUI界面。
Task4:设计实现过程
一、相关类的设计
针对这个要求,得到一个主函数,两个类,其中:
- Count类:进行字符数量、行数、单词数、词频的统计。
- File类:进行文件内容的读取,以及处理结果的写入。
- read类:将string类型的字符串转换成ArrayList
类型。 - Main类:结合实际情况,创建以上两种对象,进行方法的调用,实现题目要求。
- CountTest:用于单元测试。
二、相关函数的设计
Count:
- count.CountChars(); //字符数统计
- count.CountWords();//单词数统计
- count.CountLine();//有效行统计
- count.WordTop(n,CountWords);//单词频率统计,统计数量排名前n的单词
- count.CountPhrase(m);//统计长度为m词组
File:
- file.readfile(path);//读出文件内容变成ArrayList
格式类型 - file.writefile(save, CountChars, CountWords, CountLine, wordtop, CountPhrase);//按照要求和给出的路径写入指定文件
read:
- re.readfile(line);//将string类型的字符串转换成ArrayList
类型
三、GUI界面设计
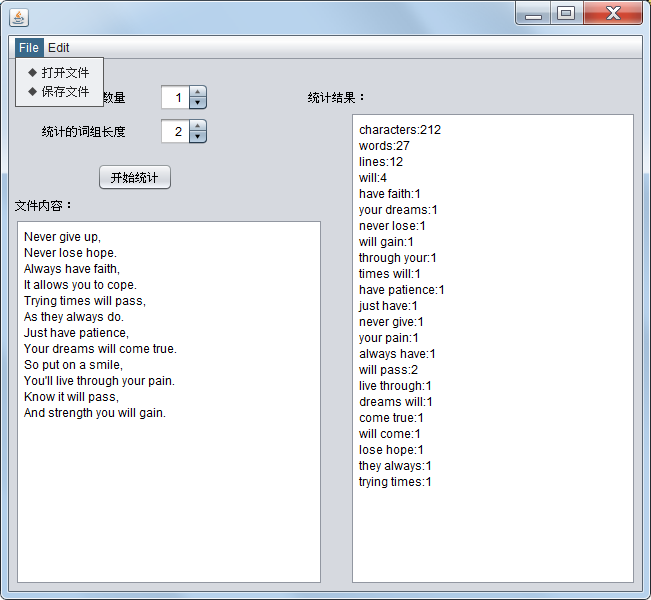
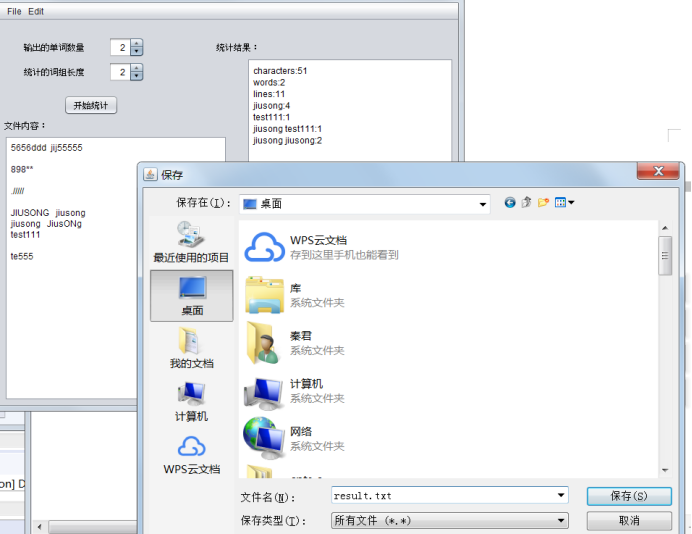
使用netBeans设计其相关界面布局,具有打开指定文件,保存为指定文件,并可以更改参数m和参数n的值进行统计。页面样式如下:
Task5:代码说明
1. Read类中readfile(String line)函数
该函数用于将string类型的字符串转换成ArrayList
public class Read { //将string类型的字符串转换成ArrayList<String>类型
public ArrayList<String> readfile(String line){
ArrayList<String> arrylist=new ArrayList<>();
String[] everyword = line.split("
");//用空格作为分割
System.out.println("everyword.length_"+everyword.length);
String str;
for(int j=0;j<everyword.length;j++){
arrylist.add(everyword[j]);//添加到ArrayList<String>类型数组
}
System.out.println(arrylist);
return arrylist;
}
}
2.GUI界面主要函数
- 触发按钮功能
这一类的方法是,当用户设置好内容点击开始统计按钮后,所绑定的函数进行调用,并在文本框中进行展示
private void jButton2ActionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {//GEN-FIRST:event_jButton2ActionPerformed
// TODO add your handling code here:
int n1 = (int) n.getValue();//获取微调器的内容
int m1 = (int) m.getValue();//获取微调器的内容
System.out.println(n1);
System.out.println(m1);
String line = jTextArea2.getText();//获取文本区域的内容
System.out.println("line_" + line);
// line = line.replace('
',' ');
Read re = new Read();
ArrayList<String> arrylist = new ArrayList<>();
arrylist = re.readfile(line);
System.out.println(arrylist + "!!!!!!!!!!");
Count count = new Count(arrylist);
int CountChars = count.CountChars();
int CountWords = count.CountWords();
int CountLine = count.CountLine();
System.out.println(CountChars);
System.out.println(CountWords);
System.out.println(CountLine);
ArrayList<Entry<String, Integer>> wordtop = count.WordTop(n1, CountWords);
Map<String, Integer> CountPhrase = count.CountPhrase(m1);
String total;
String str1 = "characters:" + CountChars;
String str2 = "words:" + CountWords;
String str3 = "lines:" + CountLine;
total = str1 + "
" + str2 + "
" + str3 + "
";
for (int i = 0; i < wordtop.size(); i++) {//遍历输出
Map.Entry<String, Integer> e = wordtop.get(i);
total = total + e.getKey() + ":" + e.getValue() + "
";
}
for (Entry<String, Integer> Phrase : CountPhrase.entrySet()) {//遍历输出
total = total + Phrase.getKey() + ":" + Phrase.getValue() + "
";
}
jTextArea1.setText(total);//将字符串写入到文本区域中
}//GEN-LAST:event_jButton2ActionPerformed
- 打开文件功能
这个用于设置打开文件时的选择框。
private void jRadioButtonMenuItem1ActionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {//GEN-FIRST:event_jRadioButtonMenuItem1ActionPerformed
// TODO add your handling code here:
f = new Frame("my window");// 创建窗体对象
f.setBounds(300, 100, 650, 600);// 设置窗体位置和大小
open = new FileDialog(f, "打开", FileDialog.LOAD);
open.setVisible(true);//显示打开文件对话框
String dirpath = open.getDirectory();//获取打开文件路径并保存到字符串中。
String fileName = open.getFile();//获取打开文件名称并保存到字符串中
if (dirpath == null || fileName == null)//判断路径和文件是否为空
{
return;
} else {
jTextArea2.setText(null);//文件不为空,清空原来文件内容。
}
java.io.File file = new java.io.File(dirpath, fileName);//创建新的路径和名称
try {
BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));//尝试从文件中读东西
String line = null;//变量字符串初始化为空
while ((line = bufr.readLine()) != null) {
jTextArea2.append(line + "
");//显示每一行内容
}
bufr.close();//关闭文件
} catch (FileNotFoundException e1) {
// 抛出文件路径找不到异常
e1.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e1) {
// 抛出IO异常
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}//GEN-LAST:event_jRadioButtonMenuItem1ActionPerformed
- 保存文件功能
这个用于将运行结果的内容保存到指定地点的指定文件中。
private void jRadioButtonMenuItem2ActionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {//GEN-FIRST:event_jRadioButtonMenuItem2ActionPerformed
// TODO add your handling code here:
save = new FileDialog(f, "保存", FileDialog.SAVE);
if (file == null) {
save.setVisible(true);//显示保存文件对话框
String dirpath = save.getDirectory();//获取保存文件路径并保存到字符串中。
String fileName = save.getFile();////获取打保存文件名称并保存到字符串中
if (dirpath == null || fileName == null)//判断路径和文件是否为空
{
return;//空操作
} else {
file = new java.io.File(dirpath, fileName);//文件不为空,新建一个路径和名称
}
}
try {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));
String text = jTextArea1.getText();//获取文本内容
bw.write(text);//将获取文本内容写入到字符输出流
bw.close();//关闭文件
} catch (IOException e1) {
//抛出IO异常
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}//GEN-LAST:event_jRadioButtonMenuItem2ActionPerformed
Task6:单元测试
根据以上函数,设置了一些测试点,尽可能罗列出各种情况:
- 字符数为空,但有其他换行等符号
- 中文和英文混合文件
- 完全的英文文件
- 完全的英文文件,大小写混合
- 完全的英文文件,无合法单词
对应设置的文件为:
- test1:完全的空文件,但是有回车空格等符号
- test2:中文和英文混合文件
- test3:纯英文文件,完全小写
- test4:纯英文文件,大小写混合
- test5:英文、数字、特殊符号混合
测试代码:
class CountTest {
String file1 = "D:\soft-ware\PersonalProject-Java\201621123037qinyu\WordCount_2\test1.txt";
String file2 = "D:\soft-ware\PersonalProject-Java\201621123037qinyu\WordCount_2\test2.txt";
String file3 = "D:\soft-ware\PersonalProject-Java\201621123037qinyu\WordCount_2\test3.txt";
String file4 = "D:\soft-ware\PersonalProject-Java\201621123037qinyu\WordCount_2\test4.txt";
String file5 = "D:\soft-ware\PersonalProject-Java\201621123037qinyu\WordCount_2\test5.txt";
@BeforeEach
void setUp() throws Exception {
}
@Test
void testCountChars() throws IOException {
File file=new File();
ArrayList<String> line1=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> line2=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> line3=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> line4=new ArrayList<>();
line1=file.readfile(file1);
line2=file.readfile(file2);
line3=file.readfile(file3);
line4=file.readfile(file4);
Count count1=new Count(line1);
Count count2=new Count(line2);
Count count3=new Count(line3);
Count count4=new Count(line4);
int CountChars1=count1.CountChars();
int CountChars2=count2.CountChars();
int CountChars3=count3.CountChars();
int CountChars4=count4.CountChars();
// assertEquals(CountChars1,0);
assertEquals(CountChars2,24);
assertEquals(CountChars3,56);
assertEquals(CountChars4,200);
}
@Test
void testCountWords() throws IOException {
File file=new File();
ArrayList<String> line1=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> line2=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> line3=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> line4=new ArrayList<>();
line1=file.readfile(file1);
line2=file.readfile(file2);
line3=file.readfile(file3);
line4=file.readfile(file4);
Count count1=new Count(line1);
Count count2=new Count(line2);
Count count3=new Count(line3);
Count count4=new Count(line4);
int CountWords1=count1.CountWords();
int CountWords2=count2.CountWords();
int CountWords3=count3.CountWords();
int CountWords4=count4.CountWords();
//assertEquals(CountWords1,5);
assertEquals(CountWords2,1);
assertEquals(CountWords3,9);
assertEquals(CountWords4,27);
}
@Test
void testCountLine() throws IOException {
File file=new File();
ArrayList<String> line1=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> line2=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> line3=new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> line4=new ArrayList<>();
line1=file.readfile(file1);
line2=file.readfile(file2);
line3=file.readfile(file3);
line4=file.readfile(file4);
Count count1=new Count(line1);
Count count2=new Count(line2);
Count count3=new Count(line3);
Count count4=new Count(line4);
int CountLine1=count1.CountLine();
int CountLine2=count2.CountLine();
int CountLine3=count3.CountLine();
int CountLine4=count4.CountLine();
//assertEquals(CountLine1,5);
assertEquals(CountLine2,6);
assertEquals(CountLine3,4);
assertEquals(CountLine4,12);
}
@Test
void testWordTop() throws IOException {
/*File file=new File();
ArrayList<String> line=new ArrayList<>();
int n = 10;//-n参数设定输出的单词数量
line=file.readfile(file1);
Count count=new Count(line);
int CountWords=count.CountWords();
int WordTop=count.WordTop(n,CountWords).size();
assertEquals(WordTop,10);*/
}
@Test
void testCountPhrase() throws IOException {
/*
File file=new File();
ArrayList<String> line=new ArrayList<>();
line=file.readfile(file4);
//System.out.println(line);
Count count=new Count(line);
Map<String,Integer> CountPhrase=count.CountPhrase(4);*/
File file=new File();
ArrayList<String> line=new ArrayList<>();
line=file.readfile(file4);
Count count=new Count(line);
int CountChars=count.CountChars();
int CountWords=count.CountWords();
int CountLine=count.CountLine();
//ArrayList<Entry<String, Integer>> wordtop=count.WordTop(n,CountWords);
Map<String,Integer> CountPhrase=count.CountPhrase(4);
/*Map<String,Integer> w1 = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
Map<String,Integer> w2 = new HashMap<String,Integer>();*/
Map<String,Integer> w3 = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
// Map<String,Integer> w4 = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
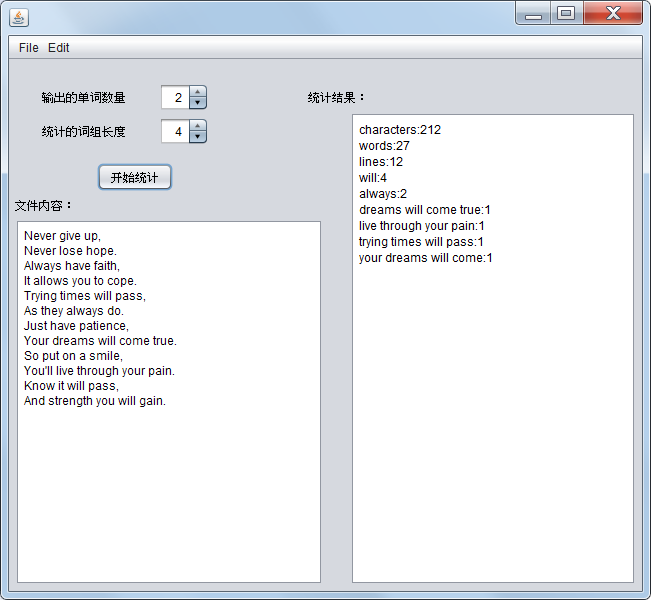
w3.put("dreams will come true", 1);
w3.put("live through your pain", 1);
w3.put("trying times will pass", 1);
w3.put("your dreams will come", 1);
System.out.println("CountPhrase");
System.out.println(CountPhrase);
System.out.println("w3");
System.out.println(w3);
assertEquals(CountPhrase, w3);
}
}
测试结果:
错误问题:

在测试testCountPhrase()中,运用如下代码测试结果一直出错,输出的部分也可以看出CountPhrase中的内容一直为空,但是在之前写好的main函数中同样调用却不会出问题。
测试代码:
File file=new File();
ArrayList<String> line=new ArrayList<>();
line=file.readfile(file4);
//System.out.println(line);
Count count=new Count(line);
Map<String,Integer> CountPhrase=count.CountPhrase(4);
输出结果:
CountPhrase
{}
w3
{dreams will come true=1, live through your pain=1, trying times will pass=1, your dreams will come=1}
解决过程:
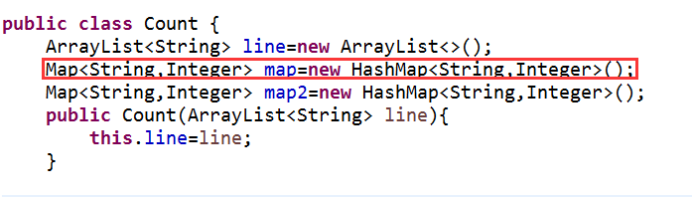
经过反复输出核对代码,发现在count类中有设置一个Map<String,Integer> map=new HashMap<String,Integer>();,并且这个参数在以下两个方法中都有被调用。


故,测试代码:
File file=new File();
ArrayList<String> line=new ArrayList<>();
line=file.readfile(file4);
Count count=new Count(line);
int CountChars=count.CountChars();
int CountWords=count.CountWords();
int CountLine=count.CountLine();
Map<String,Integer> CountPhrase=count.CountPhrase(4);
测试结果:

分值覆盖率截图:

Task7:对netBeans进行文件内容测试截图
运行结果:
test1.txt
test2.txt
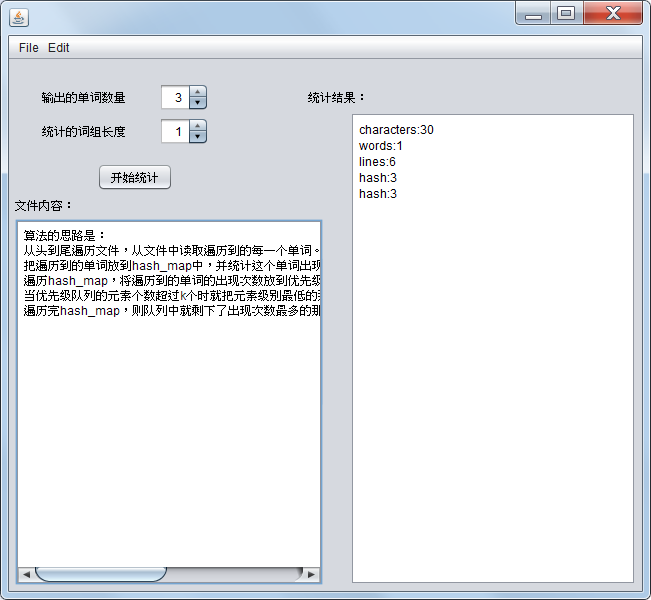

test3.txt
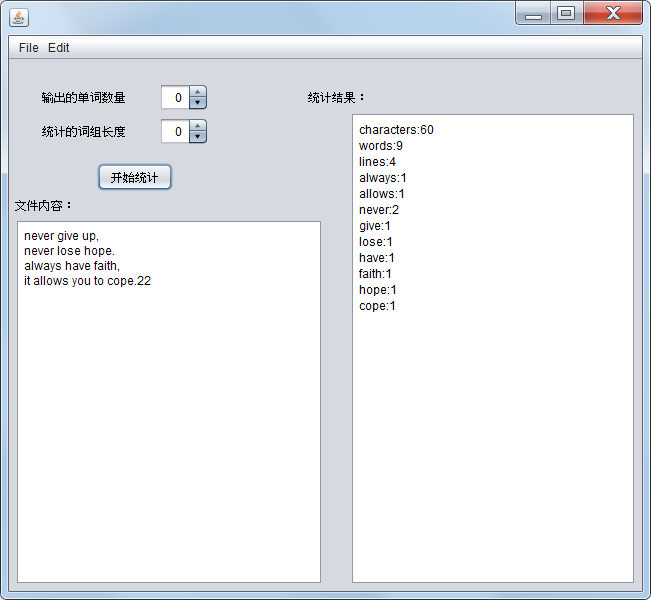

test4.txt

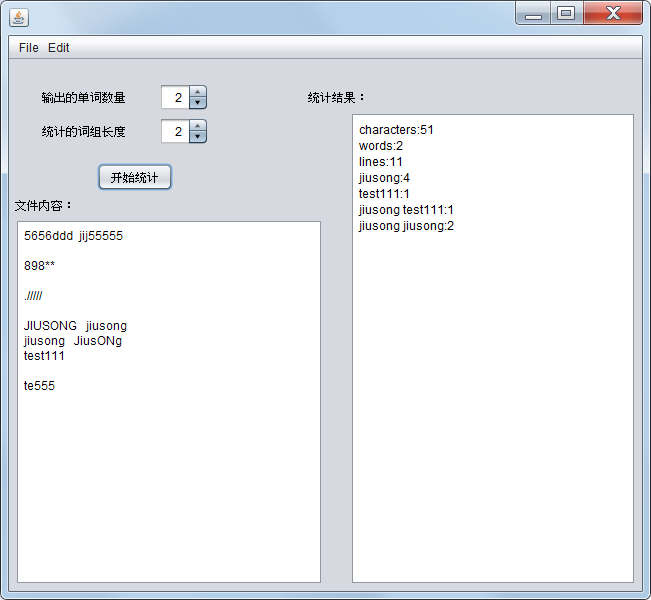
test5.txt


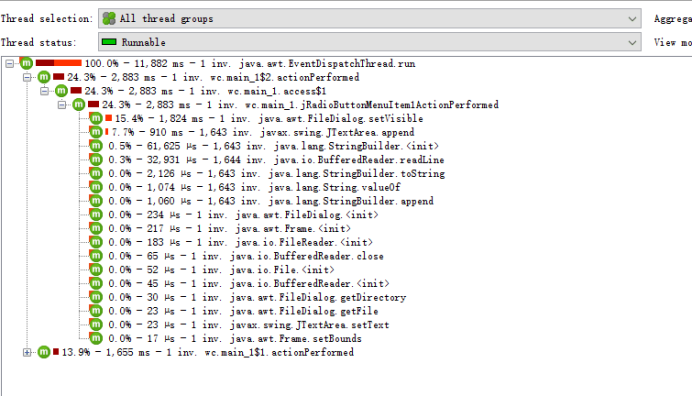
Task8:效能分析



Task9:心得体会



在这次实验中,双人结对编程将编写代码从单人奋斗变成了一起奋斗,这中间我们有很多次沟通交流,很多次选择实现方法,还有任务的分配。通过这次实验我理解了书上写的编写代码的规范,如果编写代码规范上不够严格处理,那么对于结队的队友是一个极大的考验。。。花费在理解代码上的时间会更多。不过总的来说还是完成了任务,虽然因为假期我们回家导致两个人分割异地,但是我们还是坚持在QQ上聊天以及通视频,完成两个程序员之间的亲密交流。总的来说,两人合作的话缺点在于如果不能及时沟通,可能会导致浪费时间的不必要做功,但是可以制定更加完备的方案,考虑问题更加全面,如果再来一次还是结队能学到对方的一些小诀窍,做事上的思维宽度可以拓宽。