BFS: breadth first search
107. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II
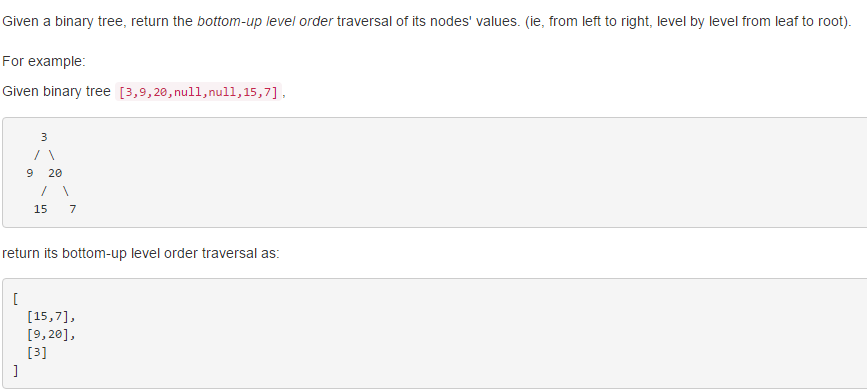
解题思路:
本来我是用map<int,int>存所有节点的值和深度(root是0),然后遍历map,result[depth].push_back(val)。但是因为map是无序的,所以
插入的时候,result[i]里元素的顺序会有问题,比如

后面改用下面的方法。先计算树的最大深度,然后遍历树的时候直接插入。后面自己写了个测试,有点丑(微笑脸)。
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <ctime>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
// if leaf node, depth=1
int Depth(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root)
return 0;
return max(Depth(root->left), Depth(root->right)) + 1;
}
void make(TreeNode* root, int depth, vector<vector<int> >& result) {
if (!root)
return;
// insert
result[depth].push_back(root->val);
make(root->left, depth-1, result);
make(root->right, depth-1, result);
}
vector<vector<int> > levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) {
int depth = Depth(root);
// result needs initialization
vector<vector<int> > result(depth, vector<int> {});
make(root, depth-1, result);
return result;
}
};
int main() {
Solution s;
TreeNode temp(3);
TreeNode* root = &temp;
TreeNode a(9);
root->left = &a;
TreeNode b(20);
root->right = &b;
TreeNode c(15);
root->right->left = &c;
TreeNode d(7);
root->right->right = &d;
vector<vector<int> > re = s.levelOrderBottom(root);
// cout << re.empty();
vector<vector<int> >::iterator it1;
vector<int>::iterator it2;
for (it1 = re.begin(); it1 != re.end(); it1++) {
cout << "*" << " ";
for (it2 = it1->begin(); it2 != it1->end(); it2++)
cout << *it2 << " ";
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
类似的题目有:
102. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
Given a binary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes' values. (ie, from left to right, level by level).
解题思路:
这个是要正序输出,那么只要改动make中
make(root->left, depth+1, result); make(root->right, depth+1, result);
改动levelOrder中
make(root, 0, result);
即可。
类似的还有:
515. Find Largest Value in Each Tree Row
解题思路:可以用上面的方法找每行的元素,然后取最大值就可以了。不过比较慢。
改进了一下,只存最大值就好了。需要注意的是,测试用例中有负数。。不只是int型,所以用一个超小值做初始值。
vector<int> largestValues(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result2;
if (!root)
return result2;
int depth = Depth(root);
int size = depth;
// result needs initialization
vector<int> result(depth, -2147483648);
make(root, 0, result);
return result;
}
// if leaf node, depth=1
int Depth(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root)
return 0;
return max(Depth(root->left), Depth(root->right)) + 1;
}
void make(TreeNode* root, int depth, vector<int>& result) {
if (!root)
return;
if (root->val > result[depth])
result[depth] = root->val;
make(root->left, depth+1, result);
make(root->right, depth+1, result);
}
好吧,类似的还有这道:
513. Find Bottom Left Tree Value

解题思路:
仍然是复用上面的代码,改
return result[result.size()-1][0];
不过显然这样效率很低。我想的改进是,增加一个记录树深度的变量d,在make函数中,push_back后增加一个判断,
如果已经到了最后一层,就终止,不再压后面的栈。这样的话,时间从22s->12s。
if (depth == d-1)
return;