DataAnnotations - Key Attribute:
Key attribute can be applied to properties of a class. Default Code-First convention creates a primary key column for a property whose name is "Id" or {Class Name} + "Id". Key attribute overrides this default convention. You can apply Key attribute to a property with any name, which you want to create a primary key for.
Consider the following example.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations; public class Student { public Student() { } [Key] public int StudentKey { get; set; } public string StudentName { get; set; } }
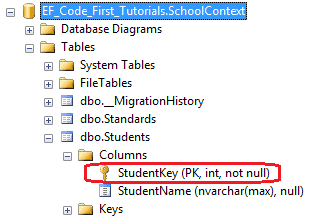
As you can see in the above example, Key attribute is applied to StudentKey property of the Student class. So, Code First will override default conventions and create a primary key column StudentKey in the Student table as shown below.
You can also create a composite primary key and make two columns as PK using Key attribute and Column attribute as shown below.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations; public class Student { public Student() { } [Key] [Column(Order=1)] public int StudentKey1 { get; set; } [Key] [Column(Order=2)] public int StudentKey2 { get; set; } public string StudentName { get; set; } }
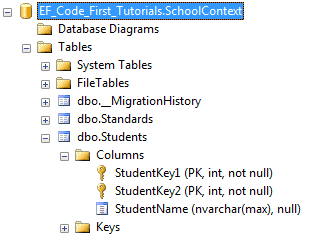
The above code creates composite primary key columns StudentKey1 and StudentKey2 in Student table as shown below.
Note: Key attribute creates a PK with identity column when applied to a single integer type property. Composite key does not create an identity column for integer property. Also, Key attribute can be applied to a property of any data type except unsinged integers, e.g. string, datetime, decimal etc.