参考学习:https://www.cnblogs.com/gongyanc/p/6703532.html
https://www.wandouip.com/t5i89622/
https://blog.csdn.net/asialee_bird/article/details/80491256
https://blog.csdn.net/jsh306/article/details/86536707
https://blog.csdn.net/macalzheng/article/details/46580859
https://blog.csdn.net/isinstance/article/details/51328794
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_14998713/article/details/79912892
1.文件的相关用法:open //打开文件格式可以是csv也可以是xlsx或。。。
csv.reader csv.writer
xlsx格式可以转换为csv格式,从而对excel格式读取
kddcup99自己添加的代码使程序正常运行:
2. row=row[0].split(’,’); //使单个字符串数组转换为多个字符串数组
3. [i for i in range(0,5) if i>2] - Python的for循环的另一种方式
a = [i for i in range(0,5) if i>2]
b = []
for i in range(0,5):
if i>2:
b.append(i)
print(‘大佬循环’,a)
print(‘普通for循环’,b)
结果截图:
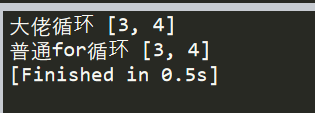
大家可以看到运用这两种for循环其实是一种效果,前者减少了很多代码量,而且在数据量打的时候速度也会非常快,接下来我会利用jupter notebook 进行运行时间精确到ms的一个对比

4.range(len(y)) //从0到len(y)
len(y) //y对象的长度
#kdd99数据集预处理
#将kdd99符号型数据转化为数值型数据
#coding:utf-8
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import csv
import time
global label_list #label_list为全局变量
#定义kdd99数据预处理函数
def preHandel_data():
source_file='11.csv'
handled_file='corrected5.csv'
data_file=open(handled_file,'w',newline='') #python3.x中添加newline=''这一参数使写入的文件没有多余的空行
with open(source_file,'r') as data_source:
csv_reader=csv.reader(data_source)
csv_writer=csv.writer(data_file)
count=0 #记录数据的行数,初始化为0
for row in csv_reader:
row=row[0].split(',');
temp_line=np.array(row) #将每行数据存入temp_line数组里
temp_line[1]=handleProtocol(row) #将源文件行中3种协议类型转换成数字标识
temp_line[2]=handleService(row) #将源文件行中70种网络服务类型转换成数字标识
temp_line[3]=handleFlag(row) #将源文件行中11种网络连接状态转换成数字标识
temp_line[41]=handleLabel(row) #将源文件行中23种攻击类型转换成数字标识
csv_writer.writerow(temp_line)
count+=1
#输出每行数据中所修改后的状态
print(count,'status:',temp_line[1],temp_line[2],temp_line[3],temp_line[41])
data_file.close()
#将相应的非数字类型转换为数字标识即符号型数据转化为数值型数据
def find_index(x,y):
return [i for i in range(len(y)) if y[i]==x]
#定义将源文件行中3种协议类型转换成数字标识的函数
def handleProtocol(input):
protocol_list=['tcp','udp','icmp']
if input[1] in protocol_list:
return find_index(input[1],protocol_list)[0]
#定义将源文件行中70种网络服务类型转换成数字标识的函数
def handleService(input):
service_list=['aol','auth','bgp','courier','csnet_ns','ctf','daytime','discard','domain','domain_u',
'echo','eco_i','ecr_i','efs','exec','finger','ftp','ftp_data','gopher','harvest','hostnames',
'http','http_2784','http_443','http_8001','imap4','IRC','iso_tsap','klogin','kshell','ldap',
'link','login','mtp','name','netbios_dgm','netbios_ns','netbios_ssn','netstat','nnsp','nntp',
'ntp_u','other','pm_dump','pop_2','pop_3','printer','private','red_i','remote_job','rje','shell',
'smtp','sql_net','ssh','sunrpc','supdup','systat','telnet','tftp_u','tim_i','time','urh_i','urp_i',
'uucp','uucp_path','vmnet','whois','X11','Z39_50']
if input[2] in service_list:
return find_index(input[2],service_list)[0]
#定义将源文件行中11种网络连接状态转换成数字标识的函数
def handleFlag(input):
flag_list=['OTH','REJ','RSTO','RSTOS0','RSTR','S0','S1','S2','S3','SF','SH']
if input[3] in flag_list:
return find_index(input[3],flag_list)[0]
#定义将源文件行中攻击类型转换成数字标识的函数(训练集中共出现了22个攻击类型,而剩下的17种只在测试集中出现)
def handleLabel(input):
#label_list=['normal.', 'buffer_overflow.', 'loadmodule.', 'perl.', 'neptune.', 'smurf.',
# 'guess_passwd.', 'pod.', 'teardrop.', 'portsweep.', 'ipsweep.', 'land.', 'ftp_write.',
# 'back.', 'imap.', 'satan.', 'phf.', 'nmap.', 'multihop.', 'warezmaster.', 'warezclient.',
# 'spy.', 'rootkit.']
global label_list #在函数内部使用全局变量并修改它
if input[41] in label_list:
return find_index(input[41],label_list)[0]
else:
label_list.append(input[41])
return find_index(input[41],label_list)[0]
if __name__=='__main__':
start_time=time.time();
global label_list #声明一个全局变量的列表并初始化为空
label_list=[]
preHandel_data()
end_time=time.time();
print("Running time:",(end_time-start_time)) #输出程序运行时间