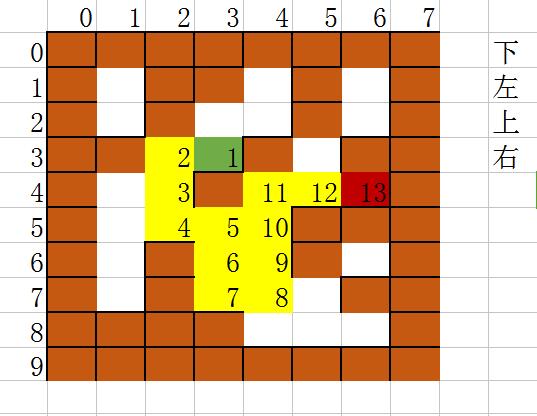
题目描述
迷宫是一个二维矩阵,其中1为墙,0为路,3为入口,4为出口.要求从入口开始,从出口结束,按照 下,左,上,右 的顺序来搜索路径.
输入
迷宫宽度w 迷宫高度h
迷宫第一行
迷宫第二行
...
迷宫第h 行
输出
入口横坐标1 入口纵坐标1
横坐标2 纵坐标2
横坐标3 纵坐标3
横坐标4 纵坐标4
...
横坐标n-1 纵坐标n-1
出口横坐标n 出口纵坐标n
样例输入
8 10
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1
1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1
1 1 0 3 1 0 1 1
1 0 0 1 0 0 4 1
1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1
1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1
1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1
1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
样例输出
3 3
2 3
2 4
2 5
3 5
3 6
3 7
4 7
4 6
4 5
4 4
5 4
6 4
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <stack>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int w, h;
const int maxn = 1000;
int maze[maxn][maxn];
struct node
{
int x,y;//1,2,3,4 下 左 上 右
};
node op, ed;
stack <node> sk;
stack <node> tmp;
bool check(const node& next)
{
if(next.x < w && next.x >= 0 &&
next.y < h && next.y >= 0 &&
maze[next.y][next.x] == 0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool path()
{
node cur; cur.x = op.x; cur.y = op.y;
node next;
//将起点入栈
sk.push(cur);
while(!sk.empty())
{
cur = sk.top();
//判断是否到了终点
if(cur.x == ed.x && cur.y == ed.y)return true;
//将该点标记为已经访问
maze[cur.y][cur.x] = -1;
//向下运动
next = cur;
next.y++;
if(check(next))
{
cur = next;
sk.push(cur);
continue;
}
//向左运动
next = cur;
next.x--;
if(check(next))
{
cur = next;
sk.push(cur);
continue;
}
//向上运动
next = cur;
next.y--;
if(check(next))
{
cur = next;
sk.push(cur);
continue;
}
//向右运动
next = cur;
next.x++;
if(check(next))
{
cur = next;
sk.push(cur);
continue;
}
// cur = sk.top();
sk.pop();
// maze[cur.x][cur.y] = 0;
}
return false;
}
void print()
{
for(int i = 0; i < h ; i++)
{
for(int j = 0 ; j < w ; j++)
{
cout << maze[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
// freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
//这个地图比较奇怪,横纵正好反过来了
cin >> w >> h;
memset(maze,0,sizeof(maze));
for(int i = 0 ; i < h ; i++)
{
for(int j = 0 ; j < w ; j++)
{
int tt;
cin >> tt;
if(tt == 3)
{
op.y = i;
op.x = j;
maze[i][j] = 0;
// cout << op.x << " " << op.y << endl;
continue;
}
if(tt == 4)
{
ed.y = i;
ed.x = j;
maze[i][j] = 0;
// cout << ed.x << " " << ed.y << endl;
continue;
}
maze[i][j] = tt;
}
}
if(path())
{
while(!sk.empty())
{
node t = sk.top();
tmp.push(t);
sk.pop();
// cout << t.x << " " << t.y << endl;
}
while(!tmp.empty())
{
node t = tmp.top();
tmp.pop();
cout << t.x << " " << t.y << endl;
}
}
else
{
cout << "++_++" << endl;
}
return 0;
}