一、 FI/SD 自动记账
FI/SD通过tcode VKOA(path:IMG-->sales and distribution-->basic function-->account assignment/costing-->revenue account determination-->assign G/L account)为billing设置过帐科目,用户可以创建自己的科目定义数据表。 科目是做到COA级的,通过KOFI/KOFK(KOFI=account determination;KOFK=account Determin. with CO)这两个condition type确定分别过帐到FI和CO凭证中。 由于PricingProc.是同SalesOrg.相关联的,所以科目在Organization上首先要做到SalesOrg. 级,其后的AccountKey是在PricingProc.中和不同的PriceConditionType相关联的,决定着最终销售收入、折扣、附加费用、预提等过到不同科目上。
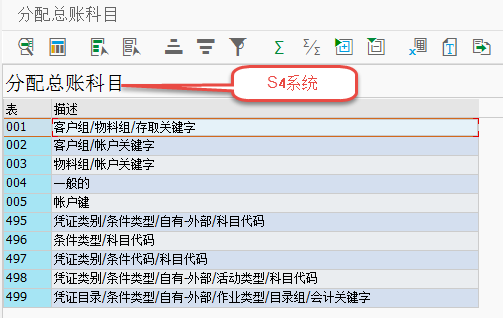
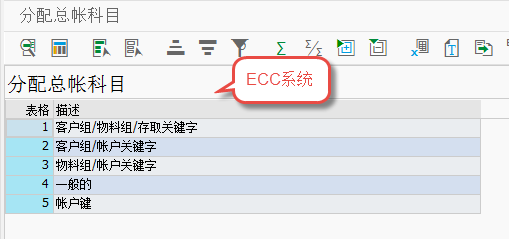
double click the first one,then display as below:
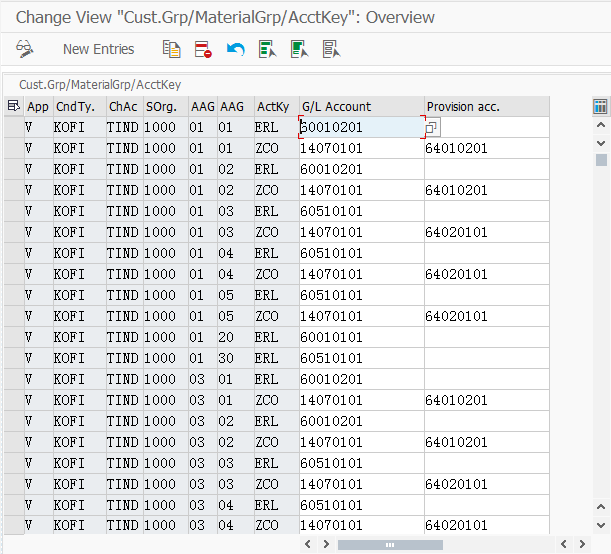
here:
1)APP:v= sales and distribution ;
2)CndTy:condtion type KOFI/KOFK,usually KOFI;
3)ChAc: Chart of account;
4)SOrg.: sales organization;
5)AAG 1: custome group(grouping customes from the revenue perspective);
6)AAG 2: material group(grouping materials from the revenue perspective;this is in the material master data sales views);
7)ActKy: ERL/ERS and so on,stands for the incoming discount and so on;incoming
二、Stander Costing Condition Type and Paraprase
VRPS:
n In the standard version, condition type VPRS is used to retrieve the standard cost of the material.
n It is used as a statistical value by the pricing procedure.
n Using condition category G, VPRS accesses the valuation segment of the material master locating either the standard cost or the moving average cost, as specified in the material master.
n Condition category S will always access the standard cost, while condition category T will always access the moving average cost.
n The profit margin is calculated using formula 11 in the pricing procedure. This formula subtracts the cost from the net value 2 subtotal.
SKTO:
n In the standard system, condition type SKTO is used to retrieve the cash discount rate.
n It is used as a statistical value by the pricing procedure.
n Table T052 is accessed using condition category E and an amount is calculated from the first percentage rate of the item payment terms.
EDI1 & EDI2:
n The customer expected price can either be entered manually in the order, or retrieved from the incoming IDoc in an EDI environment.
n Condition type EDI1 is used to compare the net price for each item. Condition type EDI2 is used to compare the overall item value (net price * quantity).
n Calculation formula 9 is assigned to condition type EDI1 in the pricing procedure. This formula tests for a maximum deviation of 0,05 currency units.
n Calculation formula 8 is assigned to condition type EDI2 in the pricing procedure. This formula tests for a maximum deviation of 1.0 currency units.
n If the customer expected price differs from the automatically determined price or value by more that the maximum difference allowed, the system will regard this order as incomplete when it is saved.
n You may process lists of orders having differences in prices, allowing the system to use or correct the price it determined.
What is the difference between VPRS (cost) and EK01 ( actual cost) and where these are used?
VPRS
VPRS cost is mainly used to determine weather the material is having the standard price or moving average price
The condition type VPRS is labeled as a statistical condition in the pricing procedure.
in this ,Using the condition category G, the condition type VPRS goes into the valuation segment of the material master and determines from here the standard or average price.
The condition category S always accesses the standard price whereas condition category T always accesses the average price.
EK01
1)EK01 can be used as a basis for determining a price for the make-to-order item.
2) EK02 is a statistical condition which can used instead of VPRS to calculate the profit margin for the assembly item.
3)Condition type EK01 is mainly used for cost-plus contracts in which the sales price depends on the expected costs.
4)Condition type EK01 is selected for sales document type TA (standard order). This means that the value from the cost estimate goes directly into pricing. A surcharge is calculated from this value and the net value for the sales order item is calculated.
三、Trasaction accounting
Delivery
Debit: cost of goods sales
Credit: Inventory
Billing
Debit:customer receivable
Credit:Main business revenue+Output tax