js 手撕代码高频面试题
1、debounce(防抖)
触发高频时间后n秒内函数只会执行一次,如果n秒内高频时间再次触发,则重新计算时间。
const debounce = (fn, time) => { let timeout = null; console.log('我来了') // 我来了 return function() { // console.log('--aa--', timeout) clearTimeout(timeout) // timeout是定时器一个数字标识 // console.log(timeout,'--bb--', clearTimeout(timeout)) timeout = setTimeout(() => { // console.log('过了3秒我才执行哦,中间有操作会被清0,重新被计时') fn.apply(this, arguments); }, time); // console.log('--cc--', timeout) } };
防抖常应用于用户进行搜索输入节约请求资源,window触发resize事件时进行防抖只触发一次。
使用
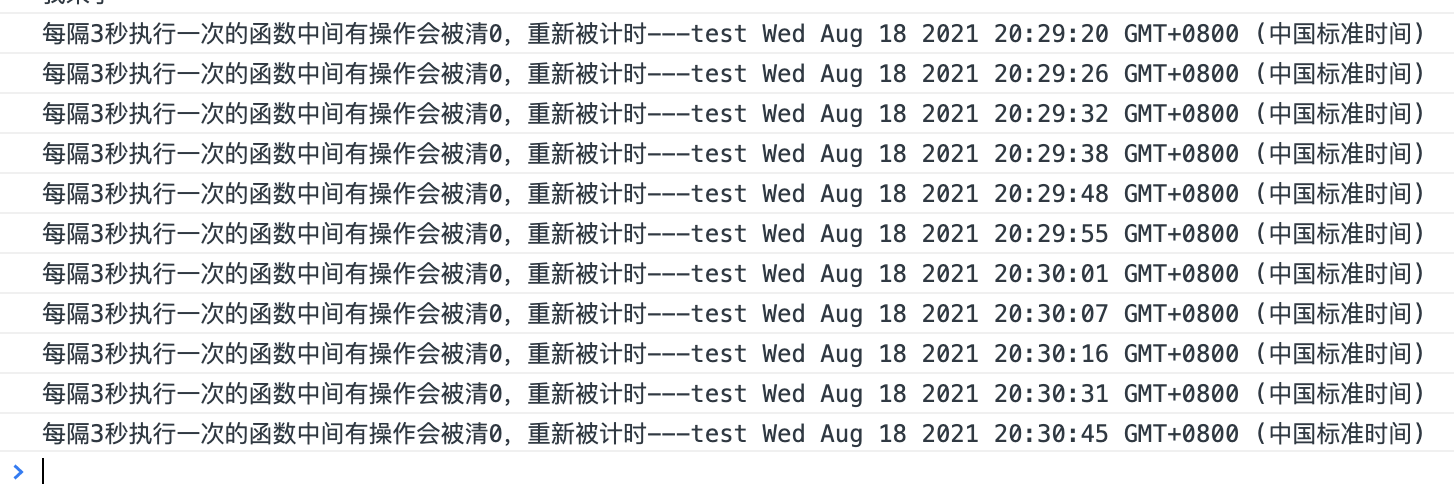
function A(){ console.log('每隔3秒执行一次的函数中间有操作会被清0,重新被计时---test', new Date()) // console.log('test') } var testDebounce = debounce(A, 3000) // window.onresize = function(){ // testDebounce() // } window.onresize = testDebounce
timeout是定时器一个数字标识

每隔三秒执行一次,中间有操作会请0重新计时,也就是设定的时间就是执行最短时间
2、throttle(节流)
高频时间触发,但n秒内只会执行一次,所以节流会稀释函数的执行频率。
节流常应用于鼠标不断点击触发、监听滚动事件。
const throttle = (fn, time) => { let flag = true; return function() { if (!flag) return; flag = false; setTimeout(() => { fn.apply(this, arguments); flag = true; }, time); } }
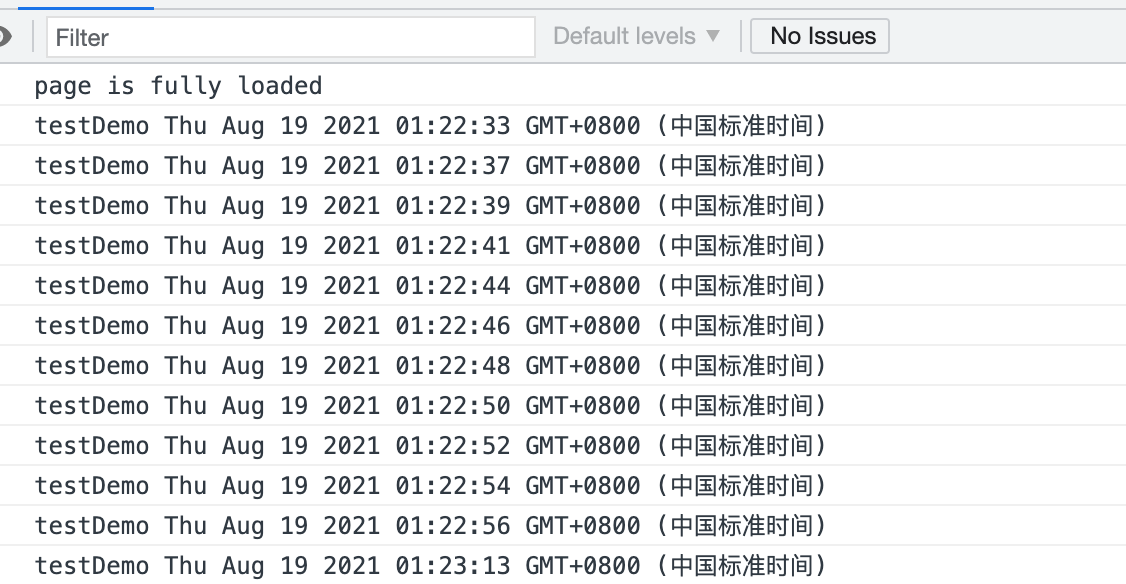
window.onload = (event) => { console.log('page is fully loaded'); let btn2 = document.getElementById("myBtn2") const throFn = throttle(testFn, 2000) btn2.addEventListener('click', throFn, false) }; <button id="myBtn2">节流点击</button>
3、 模拟一个new 运算符
3.1 第一种实现方式
new 运算符创建一个用户定义的对象类型的实例或具有构造函数的内置对象的实例。
function Car(make, model, year) { this.make = make; this.model = model; this.year = year; } const car1 = new Car('Eagle', 'Talon TSi', 1993); console.log(car1.make); // expected output: "Eagle"
语法
new constructor[([arguments])]
参数
constructor一个指定对象实例的类型的类或函数。
arguments
一个用于被 constructor 调用的参数列表。
描述
new 关键字会进行如下的操作:
创建一个空的简单JavaScript对象(即{});
为步骤1新创建的对象添加属性__proto__,将该属性链接至构造函数的原型对象 ;
将步骤1新创建的对象作为this的上下文 ;
如果该函数没有返回对象,则返回this。
模拟一个
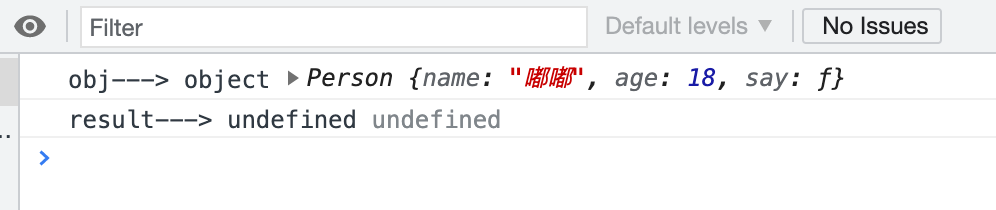
function create() { // 创建一个空的对象 let obj = new Object() // 将arguments转换成数组,再调用shift方法返回第一个参数,也就是构造函数 let Con = [].shift.call(arguments) // 链接到原型 obj.__proto__ = Con.prototype // 绑定this,执行构造函数(因为apply会自动执行函数,注意现在的argument里面只有传递进来的属性值) let result = Con.apply(obj, arguments) console.log('obj--->', typeof obj, obj) console.log('result--->', typeof result, result) // 这里进行判断,如果构造函数最后有return操作,那就返回构造函数里面那个对象,没有则返回obj // 其实就是对应我们上面所说的那个隐形返回 return typeof result === 'object' ? result : obj }
关于最后return模拟返回值, 来举例子打印一下一下明白了
function Person (name, age) { this.name = name this.age = age this.say=function(){ console.log('hello') } return this } let a = create(Person, '嘟嘟', 18) // {name = '嘟嘟', age = 18}
返回this

不返回this
function Person (name, age) { this.name = name this.age = age this.say=function(){ console.log('hello') } // return this } let a = create(Person, '嘟嘟', 18) // {name = '嘟嘟', age = 18}
3.2 、第二种实现方式
function newOperator(ctor, ...args) { if (typeof ctor !== 'function') { throw new TypeError('Type Error'); } const obj = Object.create(ctor.prototype); const res = ctor.apply(obj, args); const isObject = typeof res === 'object' && res !== null; const isFunction = typeof res === 'function'; return isObject || isFunction ? res : obj; }
4、模拟一个instanceof
instanceof 运算符用于检测构造函数的 prototype 属性是否出现在某个实例对象的原型链上
使用场景:
function Car(make, model, year) { this.make = make; this.model = model; this.year = year; } const auto = new Car('Honda', 'Accord', 1998); console.log(auto instanceof Car); // expected output: true console.log(auto instanceof Object); // expected output: true
模拟一个
const myInstanceof = (left, right) => { // 基本数据类型都返回false if (typeof left !== 'object' || left === null) return false; let proto = Object.getPrototypeOf(left); while (true) { if (proto === null) return false; if (proto === right.prototype) return true; proto = Object.getPrototypeOf(proto); } }
5、如何实现Promise.allSettled()方法
const promise1 = Promise.resolve(3); const promise2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => setTimeout(reject, 100, 'foo')); const promises = [ promise1, promise2];
如何实现Promise.allSettled()方法
输入:
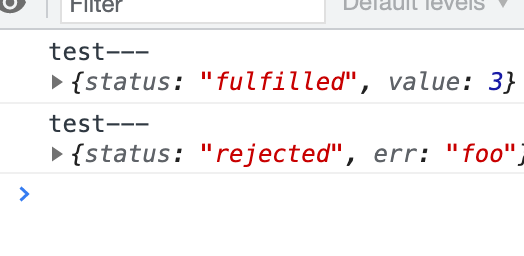
Promise.allSettledDemo(promises).then((results) => results.forEach((result) => console.log(result)));输出结果: {status:"fulfilled",value:3} {status:"rejected",err: "foo"}
打印window看下


注意点 1、Promise.allSettled()本来就有,一开始我方法写错了,运行结果是对的,其实调用的并不是我的方法为了区别名字,改个区别一下 2、Promise本来就是一个构造函数,如果需要用到里面的方法 需要new 一个也就是实例化一个对象。 3、也不要挂载prototype上否则会报错not function
模拟代码
Promise.allSettledDemo= function(promises){ return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{ let arr=[] let fulfilledCount = 0 const itemNum = promises.length for(let i=0; i< promises.length; i++){ promises[i].then((res)=>{ fulfilledCount++; arr.push({status: "fulfilled", value: res}) if (fulfilledCount === itemNum) { resolve(arr); } }).catch((error)=>{ fulfilledCount++; arr.push({status: "rejected", err: error}) if (fulfilledCount === itemNum) { resolve(arr); } }) } }) }
输入:
Promise.allSettledDemo(promises).
then((results) => results.forEach((result) => console.log('test---', result)));
6、如何实现Promise.all() 方法
Promise.all()方法用于将多个 Promise 实例,包装成一个新的 Promise 实例。
Promise.myAll = function (promiseArr) { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { const ans = []; let index = 0; for (let i = 0; i < promiseArr.length; i++) { promiseArr[i].then(res => { ans[i] = res; index++; if (index === promiseArr.length) { resolve(ans); } }) .catch(err => reject(err)); } }) }
打印结果:
const p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(() => resolve('p1'), 1000) }) const p2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(() => resolve('p2'), 5000) }) Promise.myAll([p1, p2]).then(rets => { console.log('myAll---->', rets) // ['p1','p2'] })
7、如何实现Promise.race() 方法
Promise.race = function(promiseArr) { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { promiseArr.forEach(p => { // 如果不是Promise实例需要转化为Promise实例 Promise.resolve(p).then( val => resolve(val), err => reject(err), ) }) }) }
-------陆续更新中-------