还是直接上代码
package com.sbtufss.test; import java.util.Arrays; /** * 所谓的顺序存储结构,实际上就是用数组来存储队列的元素 * @author sbtufss * */ public class ArrayQueue<T> { private int tLenght=3;//数组的大小,或者每次增加的大小 //初始化能存放tLenght个元素的数组 private Object[] t=new Object[tLenght]; private int front;//对头 private int rear;//队尾 private int size;//队列的大小,非常重要,一方面是为了防止指针溢出,另一方面,实际上是记录队列的大小,数组的大小不是队列的大小 public ArrayQueue(){ super(); front=0; rear=0; size=0; } /** * 数据插入从队尾插入 * @param data */ public void add(T data){ t[rear++]=data; size++; if(size==t.length){//如果队列的大小等于数组的大小,我们要对数组进行扩容之后,再玩里面插入数据 expansLength(); } if(rear==t.length){ rear=0;//如果此时的队尾处于数组的最后一位,那么就要将队尾移到第一位 } } /** * 从队头弹出数据,并且返回该数据,在这里我没有将t[front]赋值为null,是参考了win的删除文件一样,只是把指针移到别的位置,并没有真正的清空 */ public T poll(){ Object o=null; if(size>0){ o=t[front]; //然后我们就来处理front的数值 if(front==(t.length-1)){//如果我们读取是是数组的最后一位,那么就队头就移到数组的第一位 front=0; }else{ front++; } size--;//返回数值之前要把队列的大小-1 return (T)o; } return null; } public int getSize(){ return size; } /** * 对数组进行扩容 */ private void expansLength(){ //对数组扩容,我们要在队头和队尾中间插入一定长度的数组 Object[] copy=new Object[t.length+tLenght];//扩容tLenght个元素 if(front==0){ System.arraycopy(t, 0, copy, 0, t.length); }else{ System.arraycopy(t, front, copy, copy.length-size+rear,size-front); System.arraycopy(t, 0, copy, 0, rear); //重新给front赋值 front=copy.length-size+rear; } t=copy; } @Override public String toString() { int temp=size; int index=front; StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder(); sb.append("["); while(temp>0){ sb.append(t[index]).append(","); if(index==(t.length-1)){ index=0; }else{ index++; } temp--; } if(sb.length()!=1){ sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length()-1); } sb.append("]"); return sb.toString(); } public String toTString(){ return Arrays.toString(t); } }
我们简单的测试一下
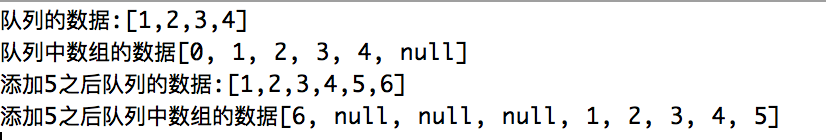
package com.sbtufss.test; public class Test { private static ArrayQueue<Integer> queue=new ArrayQueue<>(); public static void main(String[] args) { queue.add(0);//目前队列中的数据为[0] 数组为[0,null,null] queue.add(1);//目前队列中的数据为[0,1] 数组为[0,1,null] queue.add(2);//目前队列中的数据为[0,1,2] 数组为[0,1,2,null,null,null] //取出先进队列的数,并且删除他(假的删除) queue.poll();//目前队列中的数据为[1,2] 数组为[0,1,2,null,null,null] queue.add(3);//目前队列中的数据为[1,2,3] 数组为[0,1,2,3,null,null] //然后我们在添加两个数,让他们数组自增长 queue.add(4);//目前队列中的数据为[1,2,3,4] 数组为[0,1,2,3,4,null] System.out.println("队列的数据:"+queue); System.out.println("队列中数组的数据"+queue.toTString()); queue.add(5);//目前队列中的数据为[1,2,3,4,5] 数组为[0,1,2,3,4,5] queue.add(6);//目前队列中的数据为[1,2,3,4,5,6] 数组为[6,null,null,null,1,2,3,4,5] System.out.println("添加5之后队列的数据:"+queue); System.out.println("添加5之后队列中数组的数据"+queue.toTString()); } }
测试结果