代理模式:为一个对象提供一个替身,以控制对这个对象的访问
被代理的对象可以是远程对象、创建开销大的对象或需要安全控制的对象
代理模式有很多变体,都是为了控制与管理对象访问
①远程代理:远程对象的本地代表,通过它可以让远程对象当本地对象来调用。远程代理是通过网络和真正的远程对象沟通信息。
实例代码:
定义一个接口继承自Remote
import java.rmi.Remote; import java.rmi.RemoteException; public interface MyRemote extends Remote{ public State getState() throws RemoteException; }
定义一个继承该接口的类
import java.net.MalformedURLException; import java.rmi.Naming; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject; public class MyRemoteImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements MyRemote { private Light light; protected MyRemoteImpl(Light light) throws RemoteException { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } @Override public State getState() throws RemoteException { return light.getState(); } public static void main(String[] args) throws RemoteException, MalformedURLException { Light light=new Light(); light.setState(State.On); MyRemoteImpl impl = new MyRemoteImpl(light); Naming.rebind("rmi:127.0.0.1:10023/RemoteGetState", impl); } }
其中的Light.java
public class Light { private State state; public State getState() { return state; } public void setState(State state) { this.state = state; } }
State.java
public enum State { On,Off; }
并且在main方法里面绑定了该远程服务
剩下的只需要在网络找寻找该远程服务就可以了
代码如下
public class MyRemoteClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws MalformedURLException, RemoteException, NotBoundException { MyRemote remote = (MyRemote) Naming.lookup("rmi:127.0.0.1:10023/RemoteGetState"); System.out.println(remote.getState()); } }
②动态代理:运行时动态地创建代理类,并将方法调用转发到指定类
先定义一个接口IPerson.java
public interface IPerson { public int getAge(); public void setAge(int age); public String getName(); public void setName(String name); }
再定义一个实现IPerson.java的类Person.java
public class Person implements IPerson{ private int age; private String name; public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
下面是动态代理的核心代码
public static void main(String[] args) { Person p = new Person(); System.out.println(p); System.out.println("-------------------------------------"); IPerson iPerson = (IPerson) Proxy.newProxyInstance( Person.class.getClassLoader(), Person.class.getInterfaces(), new PersonInvocationHandler(p)); iPerson.setAge(12); System.out.println(iPerson); System.out.println(iPerson.getAge()); }
其中的PersonInvocationHandler.java代码如下
public class PersonInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler{ private Person p; public PersonInvocationHandler(Person p){ this.p=p; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { return method.invoke(p, args); } }
运行结果如下;
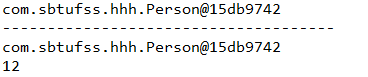
可以看出,代理对象和被代理对象是同一片内存区域,也就是同一个对象。
③保护代理:对目标对象访问的控制和管理
保护代理实际上是动态代理,动态代理的代码不动,只动PersonInvocationHandler.java
代码如下
public class PersonInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler{ private Person p; public PersonInvocationHandler(Person p){ this.p=p; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { if(method.getName().startsWith("set")){ return new IllegalAccessException(); } return method.invoke(p, args);
} }
运行结果:

在方法里面我屏蔽了有关于set的方法,所以无论你set什么东西进去都不能成功的,但是get方法就可以