1 Intent概念
1.1 Intent的作用
- 指明Intent所要启动的对象
- 提供将要启动对象组件运行需要的数据
| 组件类型 | 启动方法 |
| Activity |
startActivity(Intent intent) startActivityForResult(Intent intent, int requestCode) |
| Service |
ComponentName startService(Intent service) boolean bindService(Intent intent, ServiceConnection conn, int flags) |
| BroadcastReceiver |
sendBroadcast(Intent intent) sendBroadcast(Intent intent,String receivePermission) sendOrderedBroadcast(Intent intent, String receiverPermission, ...) sendStick |
1.2 Intent的工作原理
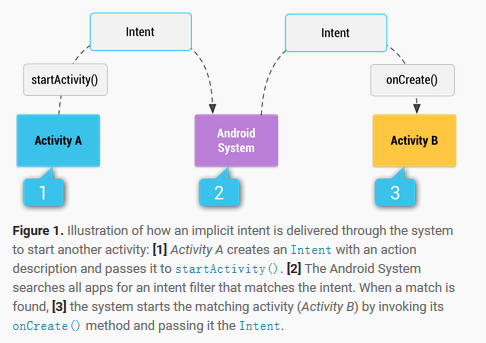
2 Intent的类型
2.1 显式Intent(explicit)
- 通过一个完全限定的字符串明确只能Intent所要启动的组件。
- 在App内部启动都用explicit方式,如果要启动另外一个App则需要使用隐式Intent
- Service启动必须采用显式Intent,且API 21对于隐式启动Service抛出异常。
- 不要求<activity>中有<intent-fliters>元素
2.2 隐式Intent
- 是为Intent的指定一个抽象的动作,允许该组件调用另外一个APP完成该Action
- <Activity>中必须定义<intent-filters>元素
- Intent根据自身内容去寻找特性匹配的Activity
- Intent-fliter是向系统注册该Activity的特性
3 创建Intent
3.1 Intent的属性
- Component属性:是可选的,指定将要启动组件的包名与类名;显式Intent必须指定该属性
- Action属性:代表Intent索要完成的一个抽象动作,该属性只指定一个抽象动作,并不具体指定哪个组件;一个Intent只能包含一个Action
- Category属性:用于为Action增加额外的类别信息,与Action结合使用,决定调用那个组件;一个Intent可以包含多个category。category默认为CATEGORY_DEFAULT=android.intent.category.DEFAULT
- Data属性:通常向Action属性提供操作的数据,Data属性接受一个Uri对象,一个Uri对象通常形式为:schema://host:port/path
- Type属性:用于指定该Data所指定Uri对应的MIME类型,需要为符合adc/xyz格式的字符串
3.2 <intent-fliter>
<intent-fliter>是androidmaifest.xml文件<activity>元素的子元素,用于配置该Activity所能响应的Intent。该元素包含3个子元素:
- 0-N个<Action>
- 0-N个<category>
- 0-1个<data>
3.3 Data属性与Type属性的关系
- 如果为Intent先设置Data属性,后设置Type属性,那么Type属性将会覆盖Data属性
- 如果为Intent先设置Type属性,后设置Data属性,那么Data将会覆盖Type
- 如果希望Intent既有Data属性,也有Type属性,应该调用Intent的setDataAndType()
3.4 在Androidmainfest.xml中Data与Type是通过<data>元素的属性来设置
- mimeType:用于表明该组件所能匹配的Intent的Type属性
- schema:用于声明该组件所能匹配的Intent的Data属性的schema部分
- host:用于声明该组件所能匹配的Intent的Data的host部分
- port:用于声明该组件所能匹配的Intent的Data的port部分
- path:用于声明该组件所能匹配的Intent的Data的path部分
- pathPrefix:用于声明该组件所能匹配的Intent的Data的path前缀
- pathPattern:用于声明该组件所能匹配的Intent的Data的path部分
4 PendingIntent的用法
简单说,PendingIntent是一个延迟执行的Intent。PendingIntent打包当前的Content与intent,保留Intent执行的现场环境,再后期需要执行的时候进行执行。主要使用场景有如下三种:
- 当执行通知用户的操作时,用户可能不会立即执行该Intent,故使用PendingIntent
- 用户将要对于桌面小部件执行Intent时,用pendingIntent
- 指定一个Intent将要在某个特定的时间执行
5 Intent与componet匹配规则
5.1 Action test
- 若Intent有1个action(其只能有1个),filter有Action,则必须有1个以上匹配可通过。
- 若Intent有1个Action,filter有0个Action,则不能pass
- 若Intent有0个action,则必通过
5.2 category test
- 非必需检查,intent没有category将通过,
- 否则filter必须大于等于intent的category的集合(都允许多余1个)
5.3 data属性的依赖性
- 若不指定scheme,则host可以忽略
- 若不指定host,则port可以忽略
- 若scheme与host都不指定,则path可以忽略
5.4 URI的匹配
- 若filter只指明scheme,则所有与scheme匹配的Intent URI通过
- 若filter指明scheme、host、port,则URI有同样的scheme、host、port通过
- 若filter指明scheme、host、port、path;则URI所有都需匹配
5.5 URI MEME type的匹配
- Intent的URI和MIME都未指明,只有当filter也不包含URI和MIME Type
- intent中有URI无MIME type(neither explicit nor inferable from the URI),则仅当filter的URI匹配,但没有MiME type 通过
- intent中无URI有MIME type,则仅当filter中有同样的MiME type, 没有URI通过
- Intent中有URI和MIME type,只要filter的MIME type匹配即可通过,URI免检(该规则意味着app可以从a file or content provider得到数据)