文件操作流程
1.打开文件,得到文件句柄并赋值给一个变量
2.通过句柄对文件进行操作
3.关闭文件
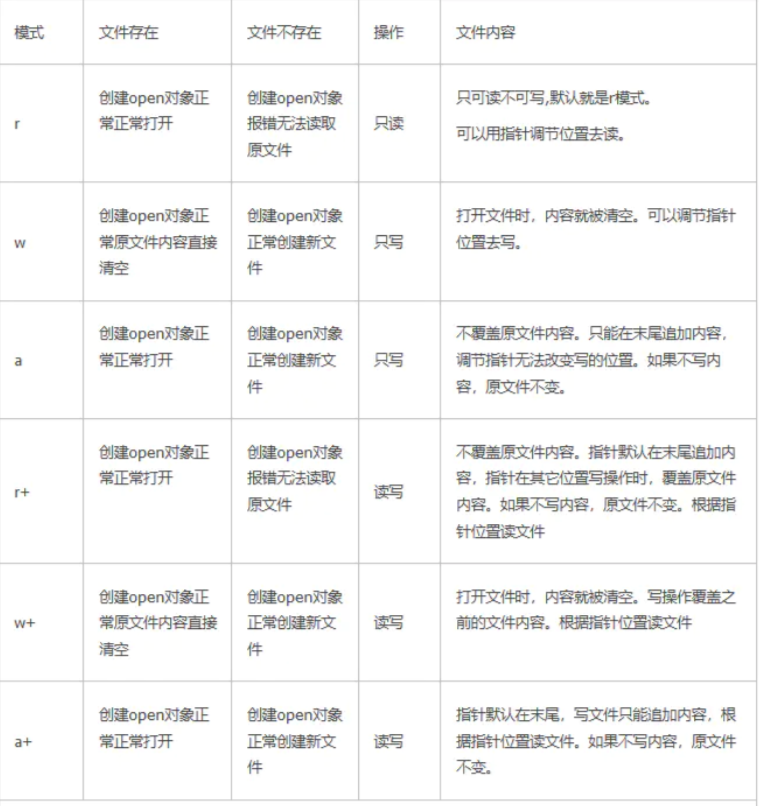
打开模式
python中有神奇的三种读操作:read、readline和readlines
read() : 一次性读取整个文件内容。推荐使用read(size)方法,size越大运行时间越长
readline() :每次读取一行内容。内存不够时使用,一般不太用
readlines() :一次性读取整个文件内容,并按行返回到list,方便我们遍历
读取文件及光标控制:
"""
读取文件示例
只有读取时候才受光标的影响
"""
###全部读取
f=open("yesterday",mode="r",encoding="utf-8")
print(f.tell()) #告诉当前光标位置
#>>>0
print(f.readlines()) ##读取文件全部内容,返回list
#>>>[all file content]
print(f.tell()) #告诉当前光标,
#>>> 235
print("round 2:",f.read())
#>>>round 2: ##因为光标位置在尾部,所以读取不到任何信息
f.seek(0) #把光标移动到开始位置
print("round 3 : ",f.read())
#>>>all file content
同时读写文件:
f=open("yesterday",mode="r+",encoding="utf-8")
w=open("new_yesterday",mode="w",encoding="utf-8")
for line in f: ##遍历文件内容最常用方法,适用于大文件
if "test3" in line:
line=line.replace("test3","TEST3")
w.write(line)
f.close() ###文件打开后必须关闭,否则浪费内存
flush()方法:
将缓冲区中的数据立刻写入文件,同时清空缓冲区,不需要是被动的等待输出缓冲区写入。
w=open("flush_demo",mode="r+",encoding="utf-8")
for i in range(10):
w.write(str(i))
w.flush() ##把缓冲区的内容刷到文件里
print(w.name) ###打印文件名
w.close()
with语句
为了避免打开文件后忘记关闭,可以通过管理上下文,即:
with open("yesterday",mode="r+",encoding="utf-8") as f:
for line in f:
print(line)
####支持同时打开多个文件
with open("yesterday",mode="r+",encoding="utf-8") as f1, open("new_yesterday",mode="r+",encoding="utf-8") as f2:
for line1 in f1:
print(line1)
示例:
读取文件示例:
import os
Filename=raw_input("please input filename that you will open: ")
if os.path.exists(Filename):##检查文件是否存在
try:
Filehandle=open(Filename,"r")
except Exception,e: ##捕获Exception的错误 存储到e里面。其中Exception是异常的基类
print e
else:
for words in Filehandle:
print words
Filehandle.close()
else:
print "%s not exits"%Filename
写入文件示例:
import os
lnend=os.linesep ##windows行结束符号是“
”
FileName=raw_input("please input filename:")
while True:##检查该文件是否存在,当执行到break时跳出while循环
if os.path.exists(FileName):##检索脚本所在目录的位置
print "%s already exits" %FileName
FileName=raw_input("please input filename:")
else:
break
ALL=[]##创建空的列表用于存储输入内容
print "please input words (ok to stop inputing)
"
while True:##当执行到break时跳出while循环
words=raw_input(">>")
if words=="ok":
break
else:
ALL.append(words)##循环的往列表添加内容
FileHandle=open(FileName,"w")
FileHandle.writelines(["%s%s" %(x,lnend) for x in ALL] )##函数writelines(list)可以将list写入到文件中,但是不会在list每个元素后加换行符,因此需要lnend换行符。同样write(str)把str写到文件中,write()也不会在str后加上一个换行符
FileHandle.close()
print "DONE"