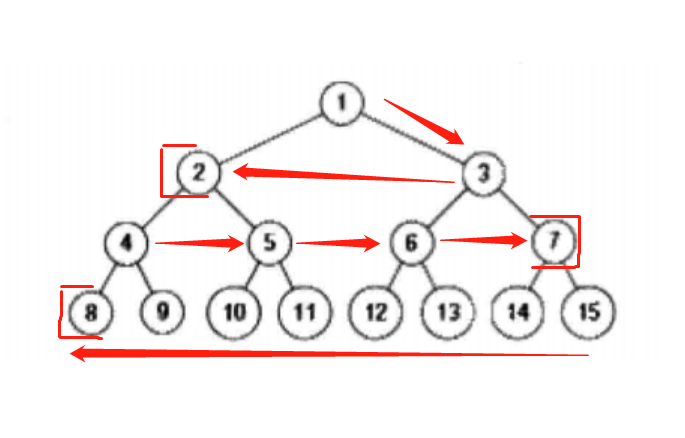
输出顺序:
1
3 2
4 5 6 7
15 14 13 12 12 10 9 8
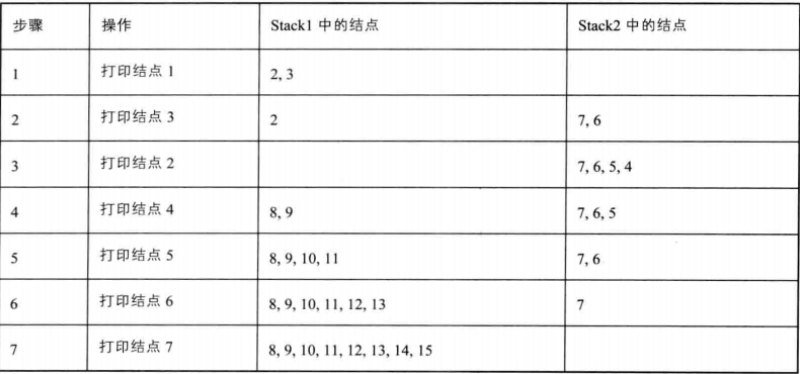
使用两个栈作为辅助容器。打印某一层节点时,把下一层的子节点保存到栈内。如果当前打印的是奇数层,则先保存左子树节点再保存右子树节点到第一个栈内;如果当前打印的是偶数层,则先保存右子树在保存左子树节点到第二个栈内。
1 /* 2 struct TreeNode { 3 int val; 4 struct TreeNode *left; 5 struct TreeNode *right; 6 TreeNode(int x) : 7 val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) { 8 } 9 }; 10 */ 11 class Solution { 12 public: 13 vector<vector<int> > Print(TreeNode* pRoot) { 14 vector<vector<int> > result; 15 vector<int> vec_tmp; 16 //边界 17 if(pRoot==nullptr) return result; 18 //辅助容器:两个栈 19 //声明变量时后面加个[]表示是数组 20 stack<TreeNode*> s[2];//s[0]是奇数层,s[1]是偶数层;栈数组 21 int now=0; 22 int next=1; 23 TreeNode* temp=pRoot; 24 //根节点入栈 25 s[now].push(temp); 26 //遍历两个栈,当两个栈都为空时,跳出循环 27 while(!s[now].empty() || !s[next].empty()){ 28 //存储遍历结果 29 temp = s[now].top(); 30 vec_tmp.push_back(temp->val); 31 s[now].pop(); 32 //当前层是奇数层还是偶数层 33 if(now==0){ 34 if(temp->left) s[next].push(temp->left); 35 if(temp->right) s[next].push(temp->right); 36 } 37 else{ 38 if(temp->right) s[next].push(temp->right); 39 if(temp->left) s[next].push(temp->left); 40 } 41 //当前层为空时,打印下一层 42 if(s[now].empty()){ 43 result.push_back(vec_tmp); 44 vec_tmp.clear(); 45 now = 1-now; 46 next=1-next; 47 } 48 } 49 return result; 50 } 51 };