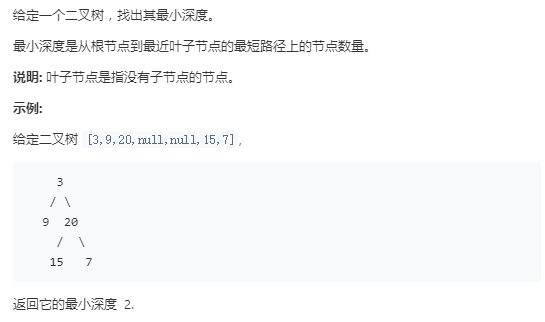
解法一:递归 遇到叶子节点不递归,否则接着往子树递归,每次递归层数加1
要确定的是,一定要保证初始输入的节点是有子节点的。因为可能出现只有单子树的情况,所以要先确认这种情况。
具体过程:
1、分析初始条件
空指针:深度为0
单节点:深度为1
1、先确定递归基本条件:
节点指针为空,说明深度为0,返回深度0;
如果到了叶节点,说明其左右两节点指针就是空,也就是在深度为0的基础上加上该节点所在的一层,即1+调用空指针的递归函数
2、找最近的叶节点,也就是左右指针都是空的叶节点的时候。
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 8 * }; 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public: 12 int minDepth(TreeNode* root) { 13 if(root==NULL) return 0;//root节点是空节点,深度为0 14 15 if(!root->right && !root->left) return 1;//只有一个节点,深度就是1 16 if(!root->left){//左节点空,右节点非空,在右子树里面找最近的叶子节点 17 return 1+minDepth(root->right); 18 } 19 if(!root->right){//右节点空,左节点非空,在左子树里面找最近的叶子节点 20 return 1+minDepth(root->left); 21 } 22 //两个节点都非空,那就继续迭代下一层 23 return 1+min(minDepth(root->left),minDepth(root->right)); 24 } 25 };
方法二:
BFS,广度优先搜索 每次把一层节点压入队列,同时判断这些节点中是否含有叶子节点(即左右指针都为空),若有,说明找到了最近的那个叶子节点,返回层数。
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int minDepth(TreeNode* root) { 4 if(root==NULL) return 0; //判空 5 queue<pair<TreeNode*,int>> que; //把节点和所在的层数绑定 6 que.push(make_pair(root,1)); //压入根节点,层数为1 7 while(1) 8 { 9 TreeNode* node=que.front().first; //当前节点 10 int level=que.front().second; //层数 11 que.pop(); 12 if (!node->left && !node->right) return level;//遇到叶子节点 13 if(node->left) //压入左节点 14 que.push(make_pair(node->left,level+1)); 15 if(node->right)//压入右节点 16 que.push(make_pair(node->right,level+1)); 17 } 18 } 19 };