一开始没看明白,直接把句子缩短了,输出结果看字典的用法
1 stuff = {'name': 'Zed', 'age': 39, 'height': 6 * 12 + 2} 2 stuff['city'] = "San Francisco" 3 stuff[1] = "Wow" 4 stuff[2] = "Neato" 5 print(stuff)
运行了3次,输出不同结果,就贴两个吧。。

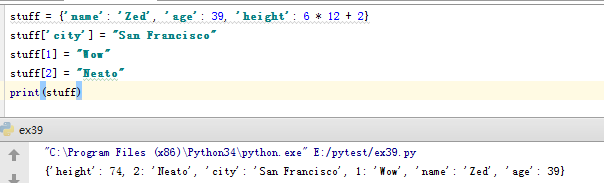
运行结果,键及对应值的顺序都不同。
字典中的值并没有特殊的顺序,但都存储在一个特定的键(Key)里。键可以是数字、字符串甚至是元组。(python基础教程p55)
以下原文代码:
1 # create a mapping of state to abbreviation 2 states = { 3 'Oregon': 'OR', 4 'Florida': 'FL', 5 'California': 'CA', 6 'New York': 'NY', 7 'Michigan': 'MI' 8 } 9 10 # create a basic set of states and some cities in them 11 cities = { 12 'CA': 'San Francisco', 13 'MI': 'Detroit', 14 'FL': 'Jacksonville' 15 } 16 17 # add some more cities 18 cities['NY'] = 'New York' 19 cities['OR'] = 'Portland' 20 21 # print out some cities 22 print('-' * 10) 23 print("NY State has: ", cities['NY']) 24 print("OR State has: ", cities['OR']) 25 26 # print some states 27 print('-' * 10) 28 print("Michigan's abbreviation is: ", states['Michigan']) 29 print("Florida's abbreviation is: ", states['Florida']) 30 31 # do it by using the state then cities dict 32 print('-' * 10) 33 print("Michigan has: ", cities[states['Michigan']]) 34 print("Florida has: ", cities[states['Florida']]) 35 36 # print every state abbreviation 37 print('-' * 10) 38 for state, abbrev in states.items(): 39 print("%s is abbreviated %s" % (state, abbrev)) 40 41 # print every city in state 42 print('-' * 10) 43 for abbrev, city in cities.items(): 44 print("%s has the city %s" % (abbrev, city)) 45 46 # now do both at the same time 47 print('-' * 10) 48 for state, abbrev in states.items(): 49 print("%s state is abbreviated %s and has city %s" % ( 50 state, abbrev, cities[abbrev])) 51 52 print('-' * 10) 53 # safely get a abbreviation by state that might not be there 54 state = states.get('Texas') 55 56 if not state: 57 print("Sorry, no Texas.") 58 59 # get a city with a default value 60 city = cities.get('TX', 'Does Not Exist') 61 print("The city for the state 'TX' is: %s" % city)
基本字典操作:
k in d(d为字典)检查d中是否有含有键为k的项,查找的是键,而不是值(判断是否存在)
a.items:将字典项以列表方式返回,返回时没有特殊顺序(键+值)
a.get(key,default):访问字典中不存在的项时,输出default,存在时,输出对应值