题意:
有n条直线,问他们两两在横坐标开区间(L,R)之间相交的个数
n=50000,暴力肯定就不用想了,如果在纸上画一画可以发现如果两条直线在(L,R)内相交,那么他们与x= L和x=R的交点序数是相反的
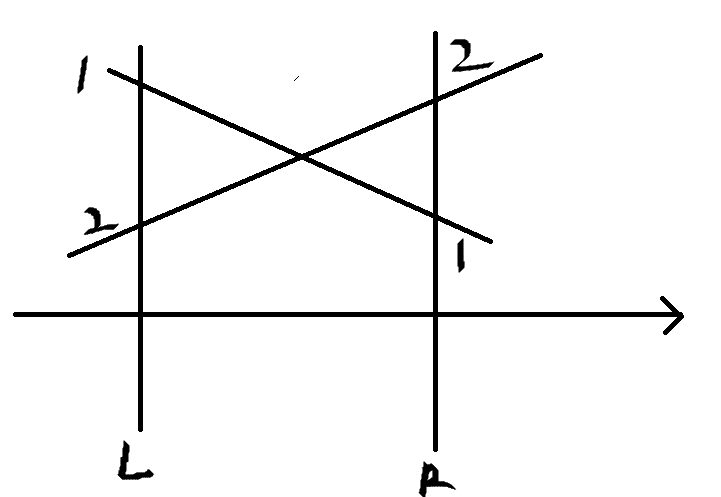
所以我们只需要算与x=L的交点,然后根据这些点排序编个号,在与R相交,根据新的交点排个逆序,根据编号求逆序数即可。
需要注意的一点:两种特殊情况如果不与L,R相交,那么如果再这个区间内,必定所有直线都会与之相交,记录下数量。
另一种情况就是,如果两个直线的交点正巧在x=L和x=R时, 这种情况是不能记录在内的,那么在之前排序的时候与L相交的交点按升序排列
如果交点坐标相同按R交点坐标升序,再根据R的坐标排降序的时候,如果R坐标相同,根据L的坐标排降序,就可以避免这种情况计算在内了。
求逆序数的时候是不会计算在里面的。
求逆序数树状数组即可。
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <queue> 5 #include <vector> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 #include <stack> 8 #include <set> 9 #include <map> 10 #include <cmath> 11 #define pb push_back 12 #define CLR(a) memset(a, 0, sizeof(a)); 13 #define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a)); 14 #define fi first 15 #define se second 16 17 using namespace std; 18 19 typedef long long ll; 20 21 const int MAXN = 50007; 22 const int MAXV = 207; 23 const int MAXE = 207; 24 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 25 26 int n; 27 28 struct Node 29 { 30 double a, b; 31 int nu; 32 Node () {} 33 Node (double a, double b) : a(a), b(b) {} 34 }node[MAXN]; 35 double L, R; 36 37 bool cmpl(Node n1, Node n2) 38 { 39 if (n1.a == n2.a) 40 return n1.b < n2.b; 41 else return n1.a < n2.a; 42 } 43 bool cmpr(Node n1, Node n2) 44 { 45 if (n1.b == n2.b) 46 return n1.a > n2.a; 47 else return n1.b > n2.b; 48 } 49 int cnt = 0; 50 int c[MAXN << 1]; 51 int lowbit(int x) 52 { 53 return x&(-x); 54 } 55 void modify(int x, int data) 56 { 57 for (int i = x; i < MAXN; i+= lowbit(i)) 58 c[i] += data; 59 } 60 int getsum(int x) 61 { 62 int res = 0; 63 for (int i = x; i > 0; i -= lowbit(i)) 64 res += c[i]; 65 return res; 66 } 67 68 int main() 69 { 70 while (~scanf("%d", &n)) 71 { 72 CLR(node); 73 CLR(c); 74 scanf("%lf%lf", &L, &R); 75 cnt = 0; 76 int vrtcl = 0; 77 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 78 { 79 double x1, y1, x2, y2; 80 scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf", &x1, &y1, &x2, &y2); 81 if (x1 == x2) 82 { 83 if (x1 > L && x1 < R) vrtcl++; 84 continue; 85 } 86 double k = (y2-y1)/(x2-x1); 87 double b = y2 - k*x2; 88 double l = k*L+b, r = k*R+b; 89 node[cnt++] = Node(l, r); 90 } 91 sort(node, node+cnt, cmpl); 92 for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) node[i].nu = i+1; 93 sort(node, node+cnt, cmpr); 94 //for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) cout << node[i].nu << endl; 95 int ans = 0; 96 for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) 97 { 98 ans += getsum(node[i].nu); 99 modify(node[i].nu, 1); 100 } 101 ans += cnt*vrtcl; 102 cout << ans << endl; 103 } 104 return 0; 105 }