1.准备环境
drop tablespace jch8 including contents and datafiles;
--jch801代表第8课
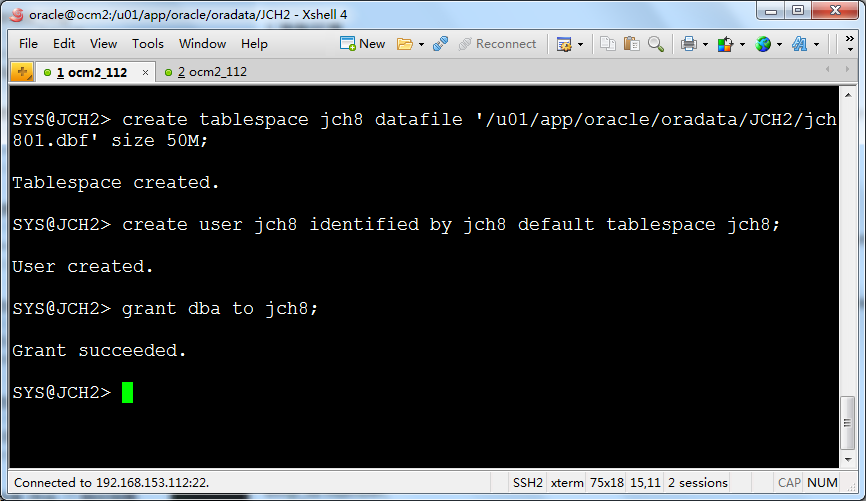
create tablespace jch8 datafile '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/JCH2/jch801.dbf' size 50M;
drop user jch8 cascade;
create user jch8 identified by jch8 default tablespace jch8;
grant dba to jch8;
conn jch8/jch8
drop table employee purge;
create table employee (emp_id number constraint pk_employee primary key,emp_name varchar2(20));
drop table work purge;
create table work (work_id number constraint pk_work primary key,work_name varchar2(20));
2.创建IOT表
drop table jch_iot purge;
create table jch_iot
(
work_id number,
emp_id number,
constraint pk_jch_iot primary key(work_id,emp_id))
organization index tablespace jch8
pctthreshold 20
including emp_id
overflow tablespace users;
注:如果主键包含2列,2列组合值必须唯一且非空
pctthreshold 20 一条记录如果超出索引块的20%就放入溢出段中
including emp_id 在emp_id段之后都放入溢出段
overflow tablespace user 溢出段放入users表空间
select segment_name,segment_type,tablespace_name from user_segments;
select table_name,tablespace_name from user_tables;
select object_id,object_name from user_objects where object_id=18215;
3.插入测试数据
insert into employee values(1,'JCH');
insert into employee values(2,'ALAN');
insert into work values(1,'DBA');
insert into work values(2,'DBA MANAGER');
commit;
select * from employee;
select * from work;
insert into jch_iot values(1,1);
insert into jch_iot values(1,2);
insert into jch_iot values(2,1);
insert into jch_iot values(2,2);
commit;
select * from jch_iot;
二 索引使用场景
1.B tree 索引
场景:重复度较低列上可使用Btree索引
create index 索引名 on 表名(列名);
conn jch8/jch8
drop table t purge;
create table t(id number);
create index idx_btree on t(id);
2.bitmap 索引
场景:列的基数很少重复值很多,数据不会经常更新可使用bitmap索引
create bitmap index 索引名 on 表名(列名);
conn jch8/jch8
drop table t1 purge;
create table t1(sex number);
create bitmap index idx_bitmap on t1(sex);
3.reverse 索引
场景:列值持续增1,不是随机数,导致索引二叉树倾斜,使用反向索引来平衡二叉树。
create index 索引名 on 表名(列名)reverse;
conn jch8/jch8
drop table t2 purge;
create table t2(a number);
create index idx_reverse on t2(a) reverse;
4.函数索引
场景:当where子句中使用函数的列上可使用function索引
create index 索引名 on 表名(函数(列名));
conn jch8/jch8
drop table t3 purge;
create table t3(b varchar2(20));
create index idx_function on t3(upper(b));
5.复合压缩索引
场景:同时查询多列时要建复合压缩索引,把重复值较多的列放在最前面进行压缩,重复值越高压缩效果越好
例如:where x and y
conn jch8/jch8
drop table t4 purge;
create table t4(a int,b int,c int);
create index idx_compress on t4(a,b,c) compress 1;
三 缓解SQL硬解析
目标:提高执行效率,减小系统开销
SQL硬解析:当一条SQL语句第一次执行,在library_cache中生成执行计划并保存,这一过程叫SQL硬解析,硬解析对CPU开销较大。
SQL软解析:直接从library_cache中读取已经解析的SQL语句执行计划并重用,这一过程叫软解析。
要求对SQL语句执行计划调优,解决硬解析严重的问题
官方文档:Reference->CURSOR_SHARING
1.查看cursor_sharing参数默认值
show parameter cursor_sharing
alter system set cursor_sharing=exact;
cursor_sharing参数默认值是EXACT,将其调整为SIMILAR或FORCE。
EXACT:只允许完全相同的sql语句共享一个游标(sql语句)
SIMILAR:允许相似的sql语句可共享一个游标(sql语句)
FORCE:强制全部sql语句共享游标(sql语句)
2.调整cursor_sharing参数为SIMILAR
alter system set cursor_sharing=similar;
3.调整cursor_sharing参数为FORCE
alter system set cursor_sharing=force;
4.检查cursor_sharing参数值
show parameter cursor_sharing
四 移动表
官方文档:SQL Reference -> 搜索“alter table”和“alter index”关键字
要求将一张表及其索引移动到另一个表空间
特点:
(1)不支持在线读/写
(2)表在移动的过程中是锁定状态不能操作,块内记录顺序不变,只移动块区,所有行的rowid都会变化
(3)表在移动后表上的索引会失效,必须rebuild重建
(4)可以整合碎片
1.创建表空间
drop tablespace move_tbs including contents and datafiles;
create tablespace move_tbs datafile '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/JCH2/move_tbs.dbf' size 20M;
2.创建表和索引
conn jch8/jch8
drop table t purge;
create table t (a int,b int);
create index idx_t on t(a);
insert into t values(1,2);
insert into t values(3,4);
insert into t values(5,6);
commit;
select * from t;
select segment_name,segment_type,tablespace_name from user_segments where segment_name='T';
3.移动表t
alter table t move tablespace move_tbs;
4.需要重建索引
select index_name,table_name,tablespace_name,status from user_indexes where index_name='IDX_T';
alter index idx_t rebuild tablespace move_tbs; 索引在重建过程中锁定表 ,rebuild之后,status变为了VALID
alter index idx_t rebuild tablespace move_tbs online;
online作用:加online可以在重建索引的过程中对表进行DML操作,不加online必须等待索引重建完成后才能对表进行DML操作(因为在重建过程中锁定表)
select index_name,table_name,tablespace_name,status from user_indexes where index_name='IDX_T';
五 缓存大对象
大对象:只要代码容量超过50K就算大对象(包、存储过程、函数、触发器)
目的:把大对象加载到library_cache中,反复使用,加快执行效率,减少系统逻辑I/O和物理I/O开销
要求使用DBMS_SHARED_POOL包将STANDARD包加载到Shared Pool(library_cache)中
官方文档:PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference ->97 DBMS_SHARED_POOL
1.创建DBMS_SHARED_POOL包,默认这个包是没有的
@?/rdbms/admin/dbmspool.sql
2.使用DBMS_SHARED_POOL把standard包加载到shared pool缓冲池中
检查一下standard包是否被保存到shared pool中
col owner for a10;
col name for a30;
col kept for a4;
select owner,name,type,kept from v$db_object_cache where name='STANDARD';
最后一列KEPT值为“NO”表明STANDARD包此时没有被保存到Shared Pool
为“YES”表明STANDARD包此时已经被保存到Shared Pool,还代表不能被踢出缓冲区
加载standard包到shared pool
exec dbms_shared_pool.keep('standard','p');
再次确认standard包是否被保存到shared pool中
select owner,name,type,kept from v$db_object_cache where name='STANDARD';
把standard包从shared pool卸载出
exec dbms_shared_pool.unkeep('standard','p');
Kept=NO 代表大对象现在可以踢出缓冲区,但不代表已经踢出缓冲区
创建一个视图获得所有shared pool中大小超过50K的包、存储过程、触发器、函数对象
drop view jch8_view;
create view jch8_view
as
select name,type,sharable_mem
from v$db_object_cache
where sharable_mem>51200
and type in ('PACKAGE',
'PACKAGE BODY',
'PROCEDURE',
'TRIGGER',
'FUNCTION');
注:sharable_mem :对象在共享池中的大小(单位字节),把大于50k对象抽取出来
type:对象类型包括 包头 包体 存储过程 触发器 函数
select * from jch8_view;
![clipboard[1] clipboard[1]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151324516643355.png)
![clipboard[2] clipboard[2]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151324574133845.png)
![clipboard[3] clipboard[3]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151325036708191.png)
![clipboard[4] clipboard[4]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151325060046336.png)
![clipboard[5] clipboard[5]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151325098844226.png)
![clipboard[6] clipboard[6]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151325124009427.png)
![clipboard[7] clipboard[7]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151325292976853.png)
![clipboard[8] clipboard[8]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151325335444085.png)
![clipboard[9] clipboard[9]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151325453493623.png)
![clipboard[10] clipboard[10]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151325583559333.png)
![clipboard[11] clipboard[11]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151326031795436.png)
![clipboard[12] clipboard[12]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151326089862413.png)
![clipboard[13] clipboard[13]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151326115139086.png)
![clipboard[14] clipboard[14]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151326138922246.png)
![clipboard[15] clipboard[15]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151326256643539.png)
![clipboard[16] clipboard[16]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151326289796856.png)
![clipboard[17] clipboard[17]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151326328265030.png)
![clipboard[18] clipboard[18]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151326388925549.png)
![clipboard[19] clipboard[19]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151326429271780.png)
![clipboard[20] clipboard[20]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151326454241211.png)
![clipboard[21] clipboard[21]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151326473837540.png)
![clipboard[22] clipboard[22]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151326512387187.png)
![clipboard[23] clipboard[23]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151326532813545.png)
![clipboard[24] clipboard[24]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151326577167833.png)
![clipboard[25] clipboard[25]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151327006614565.png)
![clipboard[26] clipboard[26]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151327038096596.png)
![clipboard[27] clipboard[27]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151327067609098.png)
![clipboard[28] clipboard[28]](https://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/520504/201402/151327122059559.png)