(color{#0066ff}{题目描述})

对于给定的开区间集合 I 和正整数 k,计算开区间集合 I 的最长 k可重区间集的长度。
(color{#0066ff}{输入格式})
第 1 行有 2 个正整数 n和 k,分别表示开区间的个数和开区间的可重迭数。接下来的 n行,每行有 2 个整数,表示开区间的左右端点坐标。
(color{#0066ff}{输出格式})
将计算出的最长 k可重区间集的长度输出
(color{#0066ff}{输入样例})
4 2
1 7
6 8
7 10
9 13
(color{#0066ff}{输出样例})
15
(color{#0066ff}{数据范围与提示})
对于100%的数据,(1le nle 500,1le kle 3)
(color{#0066ff}{题解})
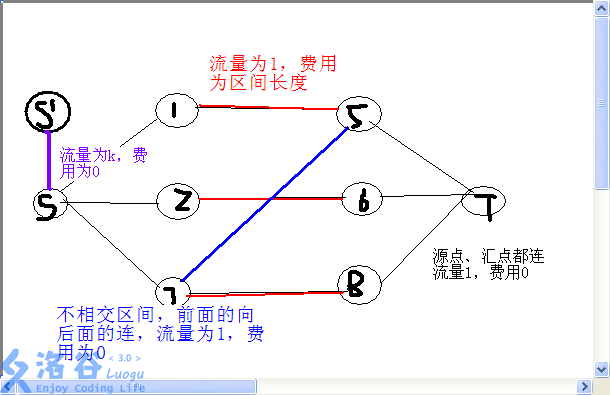
区间端点离散化
起点根1连,权为k(保证不超过k),终点根末端连
每个点直接连容量inf
区间左右端点连容量为1(只用一次) ,权为len的边
引用xuxinyu的blog的图
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _ 0
#define LL long long
inline LL in() {
LL x = 0, f = 1; char ch;
while(!isdigit(ch = getchar()))(ch == '-') && (f = -f);
while(isdigit(ch)) x = x * 10 + (ch ^ 48), ch = getchar();
return x * f;
}
struct node {
int to, dis, can;
node *nxt, *pre;
node(int to = 0, int dis = 0, int can = 0, node *nxt = NULL)
:to(to), dis(dis), can(can), nxt(nxt) {}
void *operator new (size_t) {
static node *S = NULL, *T = NULL;
return (S == T) && (T = (S = new node[1024]) + 1024), S++;
}
};
std::queue<int> q;
typedef node* nod;
int n, k, s, t, cnt;
const int maxn = 5050;
const int inf = 0x7fffffff;
int dis[maxn], change[maxn], l[maxn], r[maxn], B[maxn];
nod head[maxn], road[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
void add(int from, int to, int can, int dis) {
nod o = new node(to, dis, can, head[from]);
head[from] = o;
}
void link(int from, int to, int can, int dis) {
add(from, to, can, dis);
add(to, from, 0, -dis);
head[from]->pre = head[to];
head[to]->pre = head[from];
}
bool spfa() {
for(int i = s; i <= t; i++) dis[i] = -inf, change[i] = inf;
dis[s] = 0;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty()) {
int tp = q.front(); q.pop();
vis[tp] = false;
for(nod i = head[tp]; i; i = i->nxt)
if(dis[i->to] < dis[tp] + i->dis && i->can) {
dis[i->to] = dis[tp] + i->dis;
road[i->to] = i;
change[i->to] = std::min(change[tp], i->can);
if(!vis[i->to]) vis[i->to] = true, q.push(i->to);
}
}
return change[t] != inf;
}
void mcmf() {
int cost = 0;
while(spfa()) {
cost += dis[t] * change[t];
for(int i = t; i != s; i = road[i]->pre->to) {
road[i]->can -= change[t];
road[i]->pre->can += change[t];
}
}
printf("%d", cost);
}
int main() {
n = in(), k = in();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
l[i] = in(), r[i] = in();
B[++cnt] = l[i], B[++cnt] = r[i];
}
std::sort(B + 1, B + cnt + 1);
int len = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= cnt; i++)
if(B[i] != B[i - 1])
B[++len] = B[i];
cnt = len;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
l[i] = std::lower_bound(B + 1, B + cnt + 1, l[i]) - B;
r[i] = std::lower_bound(B + 1, B + cnt + 1, r[i]) - B;
}
s = 0, t = cnt + 1;
link(s, 1, k, 0);
link(cnt, t, inf, 0);
for(int i = 1; i < cnt; i++) link(i, i + 1, inf, 0);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) link(l[i], r[i], 1, B[r[i]] - B[l[i]]);
mcmf();
return 0;
}