neo4j实现疾病知识图谱实战
1. neo4j安装
linux下安装,直接创建脚本Neo4j_setup.sh安装脚本,执行安装即可,安装完成后,打开浏览器http:// localhost:7474,默认用户名/密码为neo4j/neo4j,首次登录需要修改密码
#!/bin/bash #neo4j 安装 #1)设置hosts绑定 IP=`ifconfig|sed -n 2p|awk '{print $2}'|cut -d ":" -f2` echo "$IP neo4j" >>/etc/hosts #2)下载安装neo4j cd /home/tools wget -c https://neo4j.com/artifact.php?name=neo4j-community-3.4.14-unix.tar.gz tar zxvf artifact.php?name=neo4j-community-3.4.14-unix.tar.gz -C /usr/local/ ln -s /usr/local/neo4j-community-3.4.14 /usr/local/neo4j-community #3)配置环境变量 cat >/etc/profile.d/neo4j <<EOF export NEO4J_HOME=/usr/local/neo4j export PATH=$PATH:$NEO4J_HOME/bin EOF source /etc/profile.d/neo4j #4) 配置资源 sed -i 's/#dbms.memory.heap.initial_size=512m/dbms.memory.heap.initial_size=2048m/g' /usr/local/neo4j-community/conf/neo4j.conf sed -i 's/#dbms.memory.heap.max_size=512m/dbms.memory.heap.max_size=2048m/g' /usr/local/neo4j-community/conf/neo4j.conf sed -i 's/#dbms.connectors.default_listen_address=0.0.0.0/dbms.connectors.default_listen_address=neo4j/g' /usr/local/neo4j-community/conf/neo4j.conf #5) 配置neo4j启动脚本 cat >/etc/init.d/neo4j <<EOF #!/bin/bash ### BEGIN REDHAT INFO # chkconfig: 2345 99 20 # description: Neo4j Graph Database server SCRIPTNAME=$0 NEO4J_CONF=/usr/local/neo4j-community/conf NEO4J_HOME=/usr/local/neo4j-community NEO_USER=root NEO4J_ULIMIT_NOFILE=60000 PATH=/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin NAME=neo4j DAEMON=${NEO4J_HOME}/bin/${NAME} PIDDIR=${NEO4J_HOME}/run PIDFILE=${PIDDIR}/neo4j.pid SCRIPTNAME=/etc/init.d/${NAME} SYSTEMCTL_SKIP_REDIRECT=1 [ -x "$DAEMON" ] || exit 0 #[ -r ${NEO4J_CONF}/${NAME}.conf ] && . ${NEO4J_CONF}/${NAME}.conf [ -n "${NEO_USER}" ] || NEO_USER=${NAME} # Debian distros and SUSE has_lsb_init() { test -f "/lib/lsb/init-functions" } # RedHat/Centos distros has_init() { test -f "/etc/init.d/functions" } if has_lsb_init ; then . /lib/lsb/init-functions elif has_init ; then . /etc/init.d/functions else echo "Error: your platform is not supported by ${NAME}" >&2 exit 1 fi do_start() { do_ulimit [ -d "${PIDDIR}" ] || mkdir -p "${PIDDIR}" chown "${NEO_USER}:" "${PIDDIR}" if has_lsb_init ; then start-stop-daemon --chuid ${NEO_USER} --start --quiet --oknodo --pidfile ${PIDFILE} --exec ${DAEMON} -- start else daemon --user="${NEO_USER}" --pidfile="${PIDFILE}" "${DAEMON} start > /dev/null 2>&1 &" fi } do_stop() { ${DAEMON} stop } do_status() { if has_lsb_init ; then status_of_proc -p "${PIDFILE}" "${DAEMON}" "${NAME}" else status -p "${PIDFILE}" "${NAME}" fi } do_ulimit() { if [ -n "${NEO4J_ULIMIT_NOFILE}" ]; then ulimit -n "${NEO4J_ULIMIT_NOFILE}" fi } case "$1" in start) do_start ;; stop) do_stop ;; status) do_status ;; restart|force-reload) do_stop && do_start ;; *) echo "Usage: $SCRIPTNAME {start|stop|status|restart|force-reload}" >&2 exit 3 ;; esac EOF #6) 设置权限 chmod +x /etc/init.d/neo4j #7) 启动neo4j service neo4j start #8) 配置开机自启动 chkconfig neo4j on echo 'Neo4j install done'
2. neo4j图数据库简介
Neo4j是一款是由java语言实现的图数据库,图形数据库将数据以图的数据结构进行存储和管理,并且能够以高度可问的方式优雅地表示任何种类的数据,而Neo4j是基于属性图模型(Property Graph Model)的数据库
在属性图中存在如下元素:
1、 实体(Entity)
a) 节点(Node)
b) 关系(Relationship)
2、 边/路径(Path)
3、 记号(Token)
a) 标签(Label)
b) 关系类型(Relationship Type)
c) 属性key(Property Key)
4、 属性(Property)
参考https://www.cnblogs.com/jpfss/p/11268835.html
3. neo4j基本语法
3.1 Cypher
neo4j的查询语言为Cypher,是一个描述性的图形查询语言
说明:()内代表节点,[]代表关系,->关系方向,{}代表属性,:后面跟记号如节点的标签、关系的类型
节点:(Variable:Lable{Key1:Value1,Key2,Value2,...})
关系:[Variable:RelationshipType{Key1:Value1,Key2:Value2,...}]
3.2 语法
l 新节点、新关系、无属性
create ()-[]->()
l 新节点、新关系、有属性
create (:{})-[:{}]->(:{})
l 已有节点、新关系、无属性
MATCH (:),(:) create ()-[:]->()
先用match找到两个节点,再给节点添加关系(如果不用match,则会新建节点)
另外,同时执行时(一个分号内),前面节点会在新建关系时被识别(不用match),否则,会认为是新的节点
新节点可以与已有节点名称、标签、属性都相同(如同年同月同日生同名同性别的人),但是会自动生成唯一标识id以区分
l merge
merge(:{})
可以看成是match和create的合体,找不到则创建节点,找到则更新节点
l 同时匹配两标签
match (n) where any(label in labels(n) WHERE label in ['label1', 'label2']) return n
4. 实战应用
4.1 诊断归一知识图谱
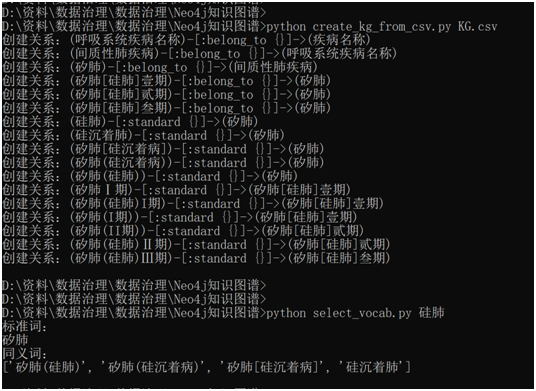
create (disease1:顶级节点:diagnosis{name:'疾病名称'}) create (disease2:顶级节点:diagnosis{name:'呼吸系统疾病名称'}) create (disease2)-[:belong_to]->(disease1) create (standard01:标准词:diagnosis{name:'间质性肺疾病'}) create (standard02:标准词:diagnosis{name:'矽肺'}) create (standard1:标准词:diagnosis{name:'矽肺[硅肺]壹期'}) create (standard2:标准词:diagnosis{name:'矽肺[硅肺]贰期'}) create (standard3:标准词:diagnosis{name:'矽肺[硅肺]叁期'}) create (standard01)-[:belong_to]->(disease2) create (standard02)-[:belong_to]->(standard01) create (standard1)-[:belong_to]->(standard02) create (standard2)-[:belong_to]->(standard02) create (standard3)-[:belong_to]->(standard02) create (origin1:原始词:diagnosis{name:'硅肺'}) create (origin2:原始词:diagnosis{name:'硅沉着肺'}) create (origin3:原始词:diagnosis{name:'矽肺[硅沉着病]'}) create (origin4:原始词:diagnosis{name:'矽肺(硅沉着病)'}) create (origin5:原始词:diagnosis{name:'矽肺(硅肺)'}) create (origin6:原始词:diagnosis{name:'矽肺Ⅰ期'}) create (origin7:原始词:diagnosis{name:'矽肺(硅肺)I期'}) create (origin8:原始词:diagnosis{name:'矽肺(I期)'}) create (origin9:原始词:diagnosis{name:'矽肺(II期)'}) create (origin10:原始词:diagnosis{name:'矽肺(硅肺)Ⅱ期'}) create (origin11:原始词:diagnosis{name:'矽肺(硅肺)Ⅲ期'}) create (origin1)-[:standardized]->(standard02) create (origin2)-[:standardized]->(standard02) create (origin3)-[:standardized]->(standard02) create (origin4)-[:standardized]->(standard02) create (origin5)-[:standardized]->(standard02) create (origin6)-[:standardized]->(standard1) create (origin7)-[:standardized]->(standard1) create (origin8)-[:standardized]->(standard1) create (origin9)-[:standardized]->(standard2) create (origin10)-[:standardized]->(standard2) create (origin11)-[:standardized]->(standard3)
4.2 图形效果

5. Python实现输入与查询
5.1 Python环境
Anaconda官网下载安装即可,Anaconda包含了conda、Python在内的超过180个科学包及其依赖项,内置spyder、jupyter调试工具
5.2 读取csv/excel
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Created on Wed Sep 30 10:29:49 2020 @author:Quentin """ from py2neo import Graph, Node, Relationship,NodeMatcher import pandas as pd import re import os import sys class CreateGraph: def __init__(self,csv_name): #当前目录 cur_dir = '/'.join(os.path.abspath('__file__').split('/')[:-1]) self.data_path = os.path.join(cur_dir, csv_name) self.graph = Graph("http://192.168.31.240:7474", username="neo4j", password="123456") def read_file(self): all_data = pd.read_csv(self.data_path, encoding='utf-8').loc[:, :].values return all_data def create_graph(self): all_data = self.read_file() top_node = 'undefined' matcher = NodeMatcher(self.graph) if (all_data[0][1] == '顶级节点'): top_node = all_data[0][0] #创建节点 for row_data in all_data: #判断node是否存在 node_match = matcher.match(row_data[1],name = row_data[0],topNode = top_node).first() if node_match is None: node = Node(row_data[1],name = row_data[0],topNode = top_node) self.graph.create(node) print('创建新节点:' + str(node).encode('utf-8').decode('unicode_escape')) #创建关系 for row_data in all_data: if len(str(row_data[2])) > 0 and str(row_data[2]) != 'nan': node1 = matcher.match(row_data[1],name = row_data[0],topNode = top_node).first() node2 = self.node_std_or_top(matcher,row_data[2],top_node) if node1 is not None and node2 is not None: if str(row_data[1]) == '原始词': relation = Relationship(node1,'standard',node2) else: relation = Relationship(node1,'belong_to',node2) self.graph.create(relation) print('创建关系:' + str(relation)) def node_std_or_top(self,matcher,name,topNode): node = matcher.match('标准词',name = name,topNode = topNode).first() if node is None : node = matcher.match('顶级节点',name = name,topNode = topNode).first() return node if __name__ == "__main__": str_csv = sys.argv[1] handler = CreateGraph(str_csv) handler.create_graph()
5.3 词表查找
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Created on Wed Sep 30 10:29:49 2020 @author: Quentin """ from py2neo import Graph, Node, Relationship,NodeMatcher import pandas as pd import re import os import sys class SelectStandard: def __init__(self): self.graph = Graph("http://192.168.31.240:7474", username="neo4j", password="123456") #查询上级词(标准词) def select_upper_vocab(self,orig,top_node='',label='原始词'): """ 查找输入词的上级节点 Parameters ---------- orig : 输入词 原始词、标准词都可 top_node : 顶级节点, optional The default is ''. label : label类型,原始词、标准词, optional The default is '原始词'. Returns ------- 返回上级节点,字符型 """ if top_node == '': query = "match(n:%s)-[r]->(m) where n.name = '%s' return m.name" %(label,orig) result = self.graph.run(query).to_ndarray() else: query = "match(n:%s)-[r]->(m) where n.name = '%s' and n.topNode = '%s' return m.name" %(label,orig,top_node) result = self.graph.run(query).to_ndarray() if len(result) > 0: return result[0][0] else: return '无' #查询同级词(原始词) def select_equal_vocab(self,orig,top_node='',label='原始词'): """ 查找输入词的同级节点 Parameters ---------- orig : 输入词 原始词、标准词都可 top_node : 顶级节点, optional The default is ''. label : label类型,原始词、标准词, optional The default is '原始词'. Returns ------- 返回同级节点,数组 """ if top_node == '': query = "match(n1:%s)-[r1]->(m1) where n1.name ='%s' match(n2:%s)-[r2]->(m1) where n2.name <> '%s' return n2.name" %(label,orig,label,orig) result = self.graph.run(query).to_ndarray() else: query = "match(n1:%s)-[r1]->(m1) where n1.name ='%s' and n1.topNode = '%s' match(n2:%s)-[r2]->(m1) where n2.name <> '%s' and n2.topNode = '%s' return n2.name" %(label,orig,top_node,label,orig,top_node) result = self.graph.run(query).to_ndarray() if len(result) > 0: rs_arr = [] for rs in result: rs_arr.append(rs[0]) return rs_arr else: return '无' if __name__ == "__main__": #输入参数 str_vocab = sys.argv upper_vocab_param = ['','','原始词'] equal_vocab_param = ['','','原始词'] for i in range(0,min(3,len(str_vocab)-1)): upper_vocab_param[i] = str_vocab[i+1] equal_vocab_param[i] = str_vocab[i+1] #输出结果 handler = SelectStandard() upper_vocab = handler.select_upper_vocab(upper_vocab_param[0],upper_vocab_param[1],upper_vocab_param[2]) print("标准词:") print(upper_vocab) equal_vocab = handler.select_equal_vocab(equal_vocab_param[0],equal_vocab_param[1],equal_vocab_param[2]) print("同义词:") print(equal_vocab)
5.4 输出结果