1、property属性
一种用起来像是使用的实例属性一样的特殊属性,可以对应于某个方法
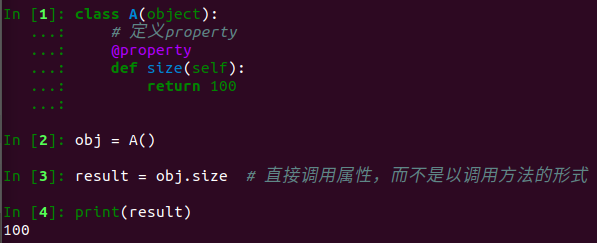
property属性的定义和调用要注意:
(1)定义时,在实例方法的基础上添加@property装饰器,并且仅有一个self参数
(2)调用时,无需括号
property属性的功能是:property属性内部进行一系列的逻辑计算,最终将计算结果返回。
2、property的属性有两种定义方式
(1)装饰器 即:在方法上应用装饰器
(2)类属性 即:在类中定义值为property对象的类属性
2.1 装饰器方式
在类的实例方法上应用@property装饰器
python中的类有经典类和新式类,新式类的属性比经典类的属性丰富。(如果类继承object,那么该类是新式类)
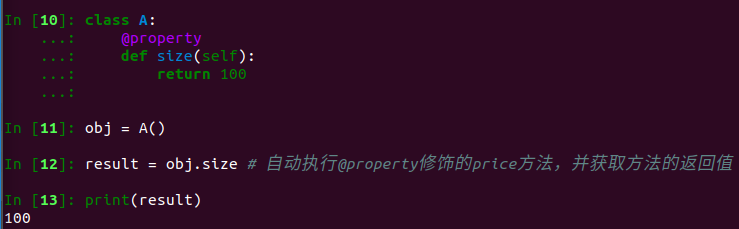
2.1.1 经典类,具有一种@property装饰器
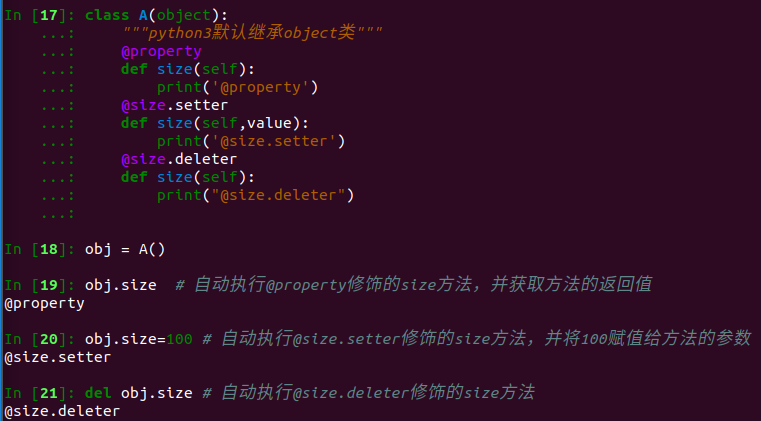
2.1.2 新式类,具有三种@property装饰器
说明:(1)经典类中的属性只有一种访问方式,其对应被 @property 修饰的方法
(2)新式类中的属性有三种访问方式,并分别对应了三个被@property、@方法名.setter、@方法名.deleter修饰的方法
由于新式类中具有三种访问方式,我们可以根据它们几个属性的访问特点,分别将三个方法定义为对同一个属性:获取、修改、删除
2.2 类属性方式,创建值为property对象的类属性
当使用类属性的方式创建property属性时,经典类和新式类无区别
class Foo: def get_bar(self): return 'laowang' BAR = property(get_bar) obj = Foo() reuslt = obj.BAR # 自动调用get_bar方法,并获取方法的返回值 print(reuslt)
property方法中有四个参数
(1)第一个参数是方法名,调用 对象.属性 时自动触发执行方法
(2)第二个参数是方法名,调用 对象.属性 = XXX 时自动触发执行方法
(3)第三个参数是方法名,调用 del 对象.属性 时自动触发执行方法
(4)第四个参数是字符串,调用 对象.属性.__doc__ ,此参数是该属性的描述信息
class Foo(object): def get_bar(self): print("getter...") return 'laowang' def set_bar(self, value): """必须两个参数""" print("setter...") return 'set value' + value def del_bar(self): print("deleter...") return 'laowang' BAR = property(get_bar, set_bar, del_bar, "description...") obj = Foo() obj.BAR # 自动调用第一个参数中定义的方法:get_bar obj.BAR = "alex" # 自动调用第二个参数中定义的方法:set_bar方法,并将“alex”当作参数传入 desc = Foo.BAR.__doc__ # 自动获取第四个参数中设置的值:description... print(desc) del obj.BAR # 自动调用第三个参数中定义的方法:del_bar方法
由于类属性方式创建property属性具有3种访问方式,我们可以根据它们几个属性的访问特点,分别将三个方法定义为对同一个属性:获取、修改、删除
class Goods(object): def __init__(self): # 原价 self.original_price = 100 # 折扣 self.discount = 0.8 def get_price(self): # 实际价格 = 原价 * 折扣 new_price = self.original_price * self.discount return new_price def set_price(self, value): self.original_price = value def del_price(self): del self.original_price PRICE = property(get_price, set_price, del_price, '价格属性描述...') obj = Goods() obj.PRICE # 获取商品价格 obj.PRICE = 200 # 修改商品原价 del obj.PRICE # 删除商品原价
3、property属性的应用
3.1 私有属性添加getter和setter方法
class Money(object): def __init__(self): self.__money = 0 def getMoney(self): return self.__money def setMoney(self, value): if isinstance(value, int): self.__money = value else: print("error:不是整型数字") # 定义一个属性,当对这个money设置值时调用setMoney,当获取值时调用getMoney money = property(getMoney, setMoney) a = Money() a.money = 100 # 调用setMoney方法 print(a.money) # 调用getMoney方法 #100
3.2 使用property取代getter和setter方法
重新实现一个属性的设置和读取方法,可做边界判定
class Money(object): def __init__(self): self.__money = 0 # 使用装饰器对money进行装饰,那么会自动添加一个叫money的属性,当调用获取money的值时,调用装饰的方法 @property def money(self): return self.__money # 使用装饰器对money进行装饰,当对money设置值时,调用装饰的方法 @money.setter def money(self, value): if isinstance(value, int): self.__money = value else: print("error:不是整型数字") a = Money() a.money = 100 print(a.money)