一、第一句Python代码
在 /home/dev/ 目录下创建 hello.py 文件,内容如下:
1 [root@python-3 scripts]# cat hello.py 2 #!/usr/bin/env python 3 4 print("Hello World!")
输出结果:
1 [root@python-3 scripts]# python hello.py 2 Hello World!
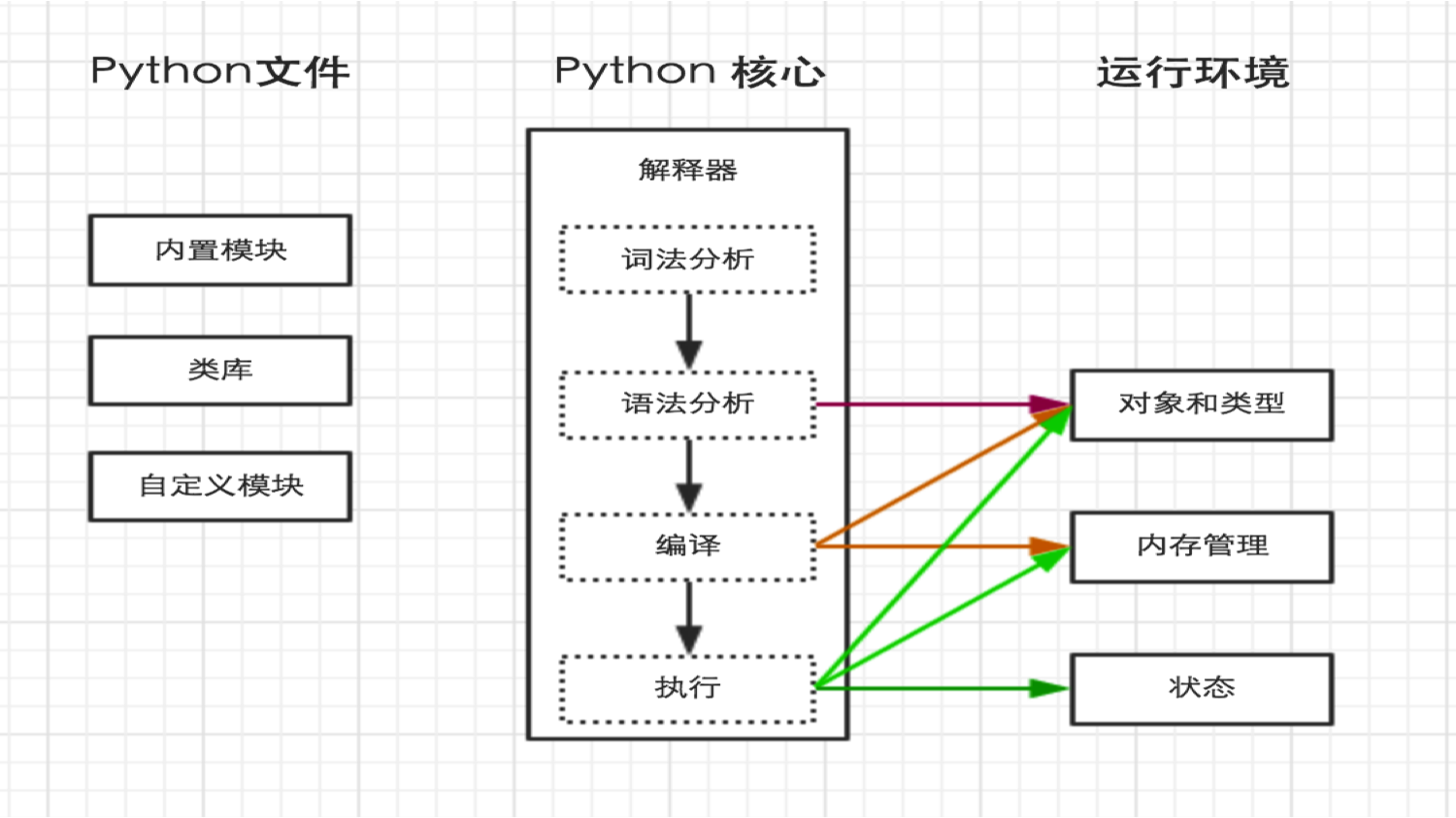
二、解释器
上一步中执行 python /home/dev/hello.py 时,明确的指出 hello.py 脚本由 python 解释器来执行。
如果想要类似于执行shell脚本一样执行python脚本,例: ./hello.py ,那么就需要在 hello.py 文件的头部指定解释器,如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python print "hello,world"
如此一来,执行: ./hello.py 即可。
ps:执行前需给予 hello.py 执行权限,chmod 755 hello.py 否则会报错!
三、内容编码
python解释器在加载 .py 文件中的代码时,会对内容进行编码(默认ascill)
ASCII(American Standard Code for Information Interchange,美国标准信息交换代码)是基于拉丁字母的一套电脑编码系统,主要用于显示现代英语和其他西欧语言,其最多只能用 8 位来表示(一个字节),即:2**8 = 256,所以,ASCII码最多只能表示 256 个符号。

显然ASCII码无法将世界上的各种文字和符号全部表示,所以,就需要新出一种可以代表所有字符和符号的编码,即:Unicode
Unicode(统一码、万国码、单一码)是一种在计算机上使用的字符编码。Unicode 是为了解决传统的字符编码方案的局限而产生的,它为每种语言中的每个字符设定了统一并且唯一的二进制编码,规定虽有的字符和符号最少由 16 位来表示(2个字节),即:2 **16 = 65536,
注:此处说的的是最少2个字节,可能更多
UTF-8,是对Unicode编码的压缩和优化,他不再使用最少使用2个字节,而是将所有的字符和符号进行分类:ascii码中的内容用1个字节保存、欧洲的字符用2个字节保存,东亚的字符用3个字节保存...
所以,python解释器在加载 .py 文件中的代码时,会对内容进行编码(默认ascill),如果是如下代码的话:
报错:ascii码无法表示中文
1 #!/usr/bin/env python #python3.0的格式 2 3 print "你好,世界"
改正:应该显示的告诉python解释器,用什么编码来执行源代码,即
1 #!/usr/bin/env python #python2.7的格式 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- #Python2.7 每个文件中只要出现中文,头部必须加 3 4 print "你好,世界"
编码解释如下:
1 8位:所有英文,字符,数字,ASCII 2 3 01001010 - 2**8 =256 4 A 65 '0b1000001' 5 6 7 万国码 unicode 8 A 65 '000000000b1000001' 9 最少用2个字节(16): 10 1byte = 8bit =01010101 11 2 16 0101010101010101 =2**16 12 13 汉字占3个字节: 14 刘小明 15 三个汉字=9字节 16 010101010101010101010100 17 18 UTF-8 19 unicode加工 20 英文:8位 21 欧洲:16位 22 中文:24位
四、注释
当行注视:# 被注释内容
多行注释:""" 被注释内容 """
ps:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: huzhihua 4 5 ''' #这就是注释 6 7 a = "alex" 8 b = a.capitalize() 9 print(a) 10 print(b) 11 12 ''' #这就是注释
五、执行脚本传入参数
Python有大量的模块,从而使得开发Python程序非常简洁。类库有包括三中:
- Python内部提供的模块
- 业内开源的模块
- 程序员自己开发的模块
Python内部提供一个 sys 的模块,其中的 sys.argv 用来捕获执行执行python脚本时传入的参数.
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 4 import sys 5 6 print sys.argv
六、 pyc 文件
执行Python代码时,如果导入了其他的 .py 文件,那么,执行过程中会自动生成一个与其同名的 .pyc 文件,该文件就是Python解释器编译之后产生的字节码。
ps:代码经过编译可以产生字节码;字节码通过反编译也可以得到代码。
七、变量
1、声明变量
1 #!/usr/bin/env python #解释器 2 3 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- #写python2.7必须把这段代码加上,因为2.7默认用的是ASCII码。如果是python3.0就不需要这段代码,因为他默认就是utf-8,utf-8默认就支持中文。 4 5 name = "nulige"
上述代码声明了一个变量,变量名为: name,变量name的值为:"nulige"
变量的作用:昵称,其代指内存里某个地址中保存的内容

变量定义的规则:
- 变量名只能是 字母、数字或下划线的任意组合
- 变量名的第一个字符不能是数字
- 以下关键字不能声明为变量名
['and', 'as', 'assert', 'break', 'class', 'continue', 'def', 'del', 'elif', 'else', 'except', 'exec', 'finally', 'for', 'from', 'global', 'if', 'import', 'in', 'is', 'lambda', 'not', 'or', 'pass', 'print', 'raise', 'return', 'try', 'while', 'with', 'yield'] - 最好不好和python内置的东西重复
2、变量的赋值
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 4 name1 = "nulige" 5 name2 = "alex"

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 4 name1 = "nulige" 5 name2 = name1

3、变量的赋值示例
1 #Author: huzhihua 2 name = "Alex li" 3 name2 = name 4 print("My name is " ,name,name2) 5 6 name = "PaoChe Ge" 7 print(name,name2)
执行结果:
1 My name is Alex li Alex li 2 PaoChe Ge Alex li
4、变量的几种常用用法
1 1) 2 _name = "Alex li" 3 4 2) 5 name = "Alex li" 6 7 3) 8 gf_gf_oldboy ="Chen rong hua" 9 10 4) 11 GFOfOldboy = "Chen rong hua"
八、输入
执行一个操作
提醒用户输入:用户和密码
获取用户名和密码,检测:用户名=root 密码=root
正确:登录成功
错误:登陆失败
input的用法,永远等待,直到用户输入了值,就会将输入的值赋值给一个东西
1 n1 = input('请输入用户名:') 2 n1 = input('请输入密码:') 3 4 print(n1) 5 print(n2)
判断用户输入用户名和密码
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: nulige 4 5 n1 = input("请输入用户名:") 6 n2 = input("请输入密码:") 7 if n1 == "root" and n2 == "root!23": 8 print("登录成功") 9 else: 10 print("登录失败")
执行结果:
1 请输入用户名:root 2 请输入密码:root!23 3 登录成功
python2.7 和3.0 inpu用法的区别
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 4 # 将用户输入的内容赋值给 name 变量 5 name = raw_input("请输入用户名:") #python2.7的用法 6 #name = input("请输入用户名:") #python3.0的用法
7 # 打印输入的内容 8 print name
输入密码时,如果想要不可见,需要利用getpass 模块中的 getpass方法,即:
ps1:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 4 import getpass 5 6 # 将用户输入的内容赋值给 name 变量 7 pwd = getpass.getpass("请输入密码:") 8 9 # 打印输入的内容 10 print pwd
ps2:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: nulige 4 5 #写各种各样的功能 6 #找到lib.py,将文件内容替换 import lib 7 #import lib 8 9 #print('index') 10 import getpass 11 12 #等待用户输入用户名,用户输入之后 13 #将输入的用户名 赋值给i1,即:i1代指用户名 14 15 i1 = raw_input("UserName:") #python2.7 16 17 #i2 =raw_input("请输入密码:") 18 #等待用户输入密码,用户输入之后 19 #将输入的密码,赋值给i2,即:i2代指密码, 20 i2 = getpass.getpass("PassWord:") 21 print(i1) 22 print(i2)
创建一个基本的py文件的流程如下:
1、创建xxx.py 文件
ps:不要有中文路径
2、写代码
a、头部两行
b、写功能代码
3、执行代码
a、打开终端
功能键+R
b、python 代码文件的路径
九、流程控制和缩进
1 条件语句 2 缩进用4个空格 3 a. 4 n1 = input('>>>') 5 6 if "alex" == "alex": 7 n2 = input('>>>') 8 if n2 == "确认": 9 print('alex SB') 10 else: 11 print('alex DB') 12 else: 13 print('error') 14 15 注意: 16 n1 = "alex" 赋值 17 n1 == 'alex' 比较, 18 19 b. 20 if 条件1: 21 pass 22 elif 条件2: 23 pass 24 elif 条件3: 25 pass 26 else: 27 pass 28 29 print('end') 30 31 c.条件1 32 and or 33 34 if n1 == "alex" or n2 == "alex!23": 35 print('OK') 36 else: 37 print('OK') 38 39 PS: 40 pass 代指空代码,无意义,仅仅用于表示代码块
需求一、用户登陆验证
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: encoding -*- 3 4 # 提示输入用户名和密码 5 6 # 验证用户名和密码 7 # 如果错误,则输出用户名或密码错误 8 # 如果成功,则输出 欢迎,XXX! 9 10 11 import getpass 12 13 14 name = raw_input('请输入用户名:') 15 pwd = getpass.getpass('请输入密码:') 16 17 if name == "alex" and pwd == "cmd": 18 print "欢迎,alex!" 19 else: 20 print "用户名和密码错误"
需求二、根据用户输入内容输出其权限
1 # 根据用户输入内容打印其权限 2 3 # alex --> 超级管理员 4 # eric --> 普通管理员 5 # tony,rain --> 业务主管 6 # 其他 --> 普通用户 7 8 name = raw_input('请输入用户名:') 9 10 if name == "alex": 11 print "超级管理员" 12 elif name == "eric": 13 print "普通管理员" 14 elif name == "tony" or name == "rain": 15 print "业务主管" 16 else: 17 print "普通用户"
需求三: 判断输入用户和密码是否正确
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: huzhihua 4 #import getpass 5 6 _username = 'nulige' 7 _password = '123456' 8 username = input("username:") 9 #password = getpass.getpass("password:") 10 password = input("password:") 11 if _username == username and _password == password: 12 print("Welcome user {name} login...".format(name=username)) 13 else: 14 print("Invalid username or password!")
执行结果:
输入正确的用户名和密码,提示:Welcome user nulige login...
1 username:nulige 2 password:123456 3 Welcome user nulige login...
输入错误的用户名和密码,提示:Invalid username or password!
1 username:nulige 2 password:321211 3 Invalid username or password!
需求四:判断年龄
示例1
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: huzhihua 4 5 age_of_oldboy = 56 6 guess_age = int(input("guess age:")) 7 if guess_age == age_of_oldboy: 8 print("yes, you got it. ") 9 elif guess_age > age_of_oldboy: 10 print("think smaller... ") 11 else: 12 print("think bigger!")
执行结果:
1 guess age:23 2 think bigger!
1 guess age:58 2 think smaller...
1 guess age:56 2 yes, you got it.
示例2
输入三次,就会打印出 you have tried too many times..fuck off 这段话
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: nulige 4 5 age_of_oldboy = 56 6 count = 0 7 8 while count <3: 9 guess_age = int(input("guess age:")) 10 if guess_age == age_of_oldboy : 11 print("yes, you got it. ") 12 break 13 elif guess_age > age_of_oldboy: 14 print("think smaller... ") 15 else: 16 print("think bigger!") 17 count +=1 18 if count == 3: 19 print("you have tried too many times..fuck off")
执行结果:
1 guess age:1 2 think bigger! 3 guess age:2 4 think bigger! 5 guess age:3 6 think bigger! 7 you have tried too many times..fuck off
示例3
输入三次进行条件判断
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: nulige 4 5 age_of_oldboy = 56 6 count = 0 7 8 while count <3: 9 guess_age = int(input("guess age:")) 10 if guess_age == age_of_oldboy : 11 print("yes, you got it. ") 12 break 13 elif guess_age > age_of_oldboy: 14 print("think smaller... ") 15 else: 16 print("think bigger!") 17 count +=1 18 else: 19 print("you have tried too many times..fuck off")
执行结果:
1 guess age:23 2 think bigger! 3 guess age:45 4 think bigger! 5 guess age:67 6 think smaller... 7 you have tried too many times..fuck off
原理图:

十、while循环
1、基本循环
1 while 条件: 2 3 # 循环体 4 5 # 如果条件为真,那么循环体则执行 6 # 如果条件为假,那么循环体不执行
示例
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: huzhihua 4 5 count = 0 6 while True: 7 print("count:",count) 8 count = count +1 #count +=1 9
2、break
break用于退出所有循环
示例1:
1 while True: 2 print ("123") 3 break 4 print ("456")
执行结果:
1 123
示例2:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: nulige 4 5 count = 0 6 while True: 7 print("count:",count) 8 count = count +1 #count +=1
执行结果:
1 count: 605452 2 count: 605453 3 count: 605454 4 count: 605455 5 count: 605456 6 count: 605457 7 count: 605458 8 count: 605459 9 count: 605460 10 count: 605461 后面省略.....
示例3:
意思是:执行到10就中间(从0-9)
1 count = 0 2 while True: 3 print("count:",count) 4 count = count +1 #count +=1 5 if count == 10: 6 break
执行结果:
1 count: 0 2 count: 1 3 count: 2 4 count: 3 5 count: 4 6 count: 5 7 count: 6 8 count: 7 9 count: 8 10 count: 9
练习题
1、使用while循环输入 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 10
法一:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: nulige 4 5 n = 1 6 while n < 11: 7 if n == 7: 8 pass 9 else: 10 print(n) 11 n = n + 1
法二:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: nulige 4 5 i = 1 6 while i<=10: 7 if i==7: 8 i += 1 9 else: 10 print(i) 11 i+=1
执行结果:
1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 8 8 9 9 10
2、求1-100的所有数的和
法一:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: nulige 4 5 n = 1 6 s = 0 7 while n < 101: 8 s = s + n 9 n = n + 1 10 11 print(s)
法二:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: nulige 4 5 i = 1 6 sum = 0 7 while i<=100: 8 sum += i 9 i += 1 10 print(sum)
执行结果:
1 5050
法三:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: nulige 4 5 n = 0 6 for x in range(101): 7 n = n + x 8 print(n)
执行结果:
1 5050
法四:
用求和函数方法实现
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: nulige 4 5 print (sum(range(1, 101)))
执行结果:
1 5050
Linux的实现方法:
1 [root@python-3 scripts]# awk 'BEGIN{i=1;do{sum+=i;i++}while (i<=100);print sum}' 2 5050 3 [root@python-3 scripts]# awk 'BEGIN{i=1;while (i<=100){sum+=i;i++};print sum}' 4 5050 5 [root@python-3 scripts]# awk 'BEGIN{sum=0;for (i=1;i<=100;i++)sum+=i;print sum}' 6 5050 7 [root@python-3 scripts]# declare sum=0;for i in `seq 1 100`;do let sum+=$i;done;echo $sum 8 5050
3、输出 1-100 内的所有奇数
知识点:整数中,能被2整除的数是偶数,不能被2整除的数是奇数
ps:
奇数就是单数、如:1,3,5,7,9,11等。
法一:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: nulige 4 5 n = 1 6 while n < 101: 7 temp = n % 2 8 if temp == 0: 9 pass 10 else: 11 print(n) 12 n = n + 1
法二:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: nulige 4 5 count = 1 6 while count < 101: 7 num=count%2 8 if num == 1: 9 print(count) 10 count += 1
执行结果:
1 1 2 3 3 5 4 7 5 9 6 11 7 13 8 15 9 17 10 19 11 21 12 23 13 25 14 27 15 29 16 31 17 33 18 35 19 37 20 39 21 41 22 43 23 45 24 47 25 49 26 51 27 53 28 55 29 57 30 59 31 61 32 63 33 65 34 67 35 69 36 71 37 73 38 75 39 77 40 79 41 81 42 83 43 85 44 87 45 89 46 91 47 93 48 95 49 97 50 99
法三:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: nulige 4 5 inte = 1 6 #输出1到100间的奇数 7 while inte <= 100: 8 if inte % 2 == 1: 9 print (inte) 10 inte = inte + 1
执行结果:
1 1 2 3 3 5 4 7 5 9 6 11 7 13 8 15 9 17 10 19 11 21 12 23 13 25 14 27 15 29 16 31 17 33 18 35 19 37 20 39 21 41 22 43 23 45 24 47 25 49 26 51 27 53 28 55 29 57 30 59 31 61 32 63 33 65 34 67 35 69 36 71 37 73 38 75 39 77 40 79 41 81 42 83 43 85 44 87 45 89 46 91 47 93 48 95 49 97 50 99
4、输出 1-100 内的所有偶数
知识点:整数中,能被2整除的数是偶数,不能被2整除的数是奇数
ps:
双数就是偶数、如:0,2,4,6,8,10等。
法一:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: nulige 4 5 n = 1 6 while n < 101: 7 temp = n % 2 8 if temp == 0: 9 print(n) 10 else: 11 pass 12 n = n + 1
法二:
1 count = 1 2 while count < 101: 3 num=count%2 4 if num == 0: 5 print(count) 6 count += 1
执行结果:
1 2 2 4 3 6 4 8 5 10 6 12 7 14 8 16 9 18 10 20 11 22 12 24 13 26 14 28 15 30 16 32 17 34 18 36 19 38 20 40 21 42 22 44 23 46 24 48 25 50 26 52 27 54 28 56 29 58 30 60 31 62 32 64 33 66 34 68 35 70 36 72 37 74 38 76 39 78 40 80 41 82 42 84 43 86 44 88 45 90 46 92 47 94 48 96 49 98 50 100
5、求1-2+3-4+5 ... 99的所有数的和
法一:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: nulige 4 5 n = 1 6 s = 0 # s是之前所有数的总和 7 while n < 100: 8 temp = n % 2 9 if temp == 0: 10 s = s - n 11 else: 12 s = s + n 13 n = n + 1 14 15 print(s)
法二:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: nulige 4 5 count = 1 6 while count < 100: 7 if count == 1: 8 num = count 9 elif count%2 == 1: 10 num = num + count 11 elif count%2 == 0: 12 num = num - count 13 count += 1 14 print(num)
执行结果:
1 50
6、用户登陆(三次机会重试)
流程图
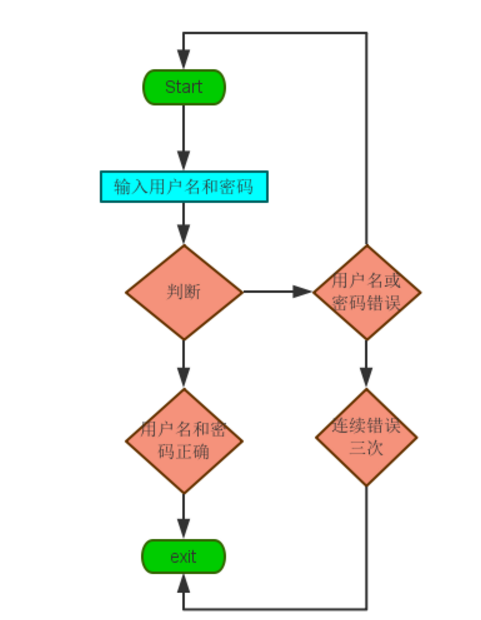
法一:
1 count = 0 2 while count < 3: 3 user = input('>>>') 4 pwd = input('>>>') 5 if user == 'alex' and pwd == '123': 6 print('欢迎登陆') 7 print('..........') 8 break 9 else: 10 print('用户名或者密码错误') 11 count = count + 1
法二:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 #Author: nulige 4 5 _username,_password,i = "nulige","123456",1 6 while i < 4: 7 input_name = input("Username:") 8 input_passwd = input("Password:") 9 if input_name == _username and input_passwd == _password: 10 print("login is successful!") 11 break 12 else: 13 print("The user name or password you entered is incorrect. Please enter again.") 14 i += 1 15 continue 16 print("Enter more than 3 times, This program will exit")
执行结果:
输入错误的用户名和密码
1 Username:111 2 Password:2222 3 The user name or password you entered is incorrect. Please enter again. 4 Username:2222 5 Password:2222 6 The user name or password you entered is incorrect. Please enter again. 7 Username:2222 8 Password:222 9 The user name or password you entered is incorrect. Please enter again. 10 Enter more than 3 times, This program will exit
输入正确的用户名和密码
1 Username:nulige 2 Password:123456 3 login is successful! 4 Enter more than 3 times, This program will exit
法三:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 # Author: nulige 4 5 count = 3 6 while count > 0: 7 username = input("Please enter your username:") 8 pwd = input("Please enter your password:") 9 if username == "nulige" and pwd == "123456": 10 print("User:",username,",Login successful ! ") 11 break 12 else: 13 count -= 1 14 if count != 0: 15 print("Login failed",count) 16 else: 17 print("Enter more than 3 times, This program will exit")
执行结果:
输入错误的用户名和密码
1 Please enter your username:111 2 Please enter your password:222 3 Login failed 2 4 Please enter your username:111 5 Please enter your password:222 6 Login failed 1 7 Please enter your username:111 8 Please enter your password:222 9 Enter more than 3 times, This program will exit
输入正确的用户名和密码
1 Please enter your username:nulige 2 Please enter your password:123456 3 User: nulige ,Login successful !