题目链接
(A. Park Lighting)
(Description:)
给出 (n imes m) 的矩阵,你需要用灯照亮矩阵的每个单元格,灯只能摆放在单元格的边框上(具体参考原题里的图),如果某个单元格的边框上有一盏灯,那么该单元格将被照亮,问最少需要多少个单元格?
(Solution:)
贪心即可。
(Code:)
/*
@Author: nonameless
@Date: 2020-05-27 15:54:25
@Email: 2835391726@qq.com
@Blog: https://www.cnblogs.com/nonameless/
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define x first
#define y second
#define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
#define sz(x) (int)x.size()
#define pb push_back
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PLL;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
const double eps = 1e-8;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll LNF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f;
inline int gcd(int a, int b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; }
inline ll gcd(ll a, ll b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; }
inline int lcm(int a, int b) { return a * b / gcd(a, b); }
int main(){
int t; cin >> t;
while(t --){
int n, m; cin >> n >> m;
int ans = 0;
ans = n / 2 * m;
if(n & 1){
ans += m / 2 + (m % 2);
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}
(B. Maria Breaks the Self-isolation)
(Description:)
给定长度为 (n) 的数组 (a),现有一个院子,院子里最初有一个人,那么他要叫其他 (n) 个人来,每个人来的条件是 (a_i leq) 院子里的人 (+) 和他一起来的人的个数(可以一次叫多个人来),问最后院子里最多有几个人?
(Solution:)
给 (a) 排序,从小到大遍历一边,如果对于 (i) 来说,他不满足条件,那么我们就让他等待(即等后面的人一起去),直到遇到 (j) 满足 (a_j leq cnt + ans),(cnt) 是当前等待的人,(ans) 是当前院子里的人数。此时 (j) 是满足条件的,那么由于 (a_i leq a_j),那么 (i) 显然也是符合条件的。
(Code:)
/*
@Author: nonameless
@Date: 2020-05-27 16:00:38
@Email: 2835391726@qq.com
@Blog: https://www.cnblogs.com/nonameless/
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define x first
#define y second
#define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
#define sz(x) (int)x.size()
#define pb push_back
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PLL;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
const double eps = 1e-8;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll LNF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f;
inline int gcd(int a, int b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; }
inline ll gcd(ll a, ll b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; }
inline int lcm(int a, int b) { return a * b / gcd(a, b); }
int main(){
int t; cin>> t;
while(t --){
vector<int> vec;
int n; cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
int x; scanf("%d", &x);
vec.pb(x);
}
sort(all(vec));
int ans = 1, cnt = 0; // cnt 是未进去的
for(int i = 0; i < sz(vec); i ++){
if(vec[i] <= ans + cnt){
ans += cnt + 1;
cnt = 0; // 全部进去
} else cnt ++; // 等待的人的个数 ++
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}
(C. Celex Update)
(Description:)
给定如下矩阵:
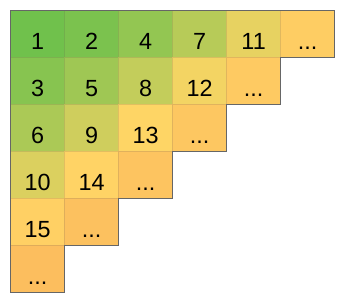
给定 ((x_1,y_1),(x_2,y_2)),从 ((x_1,y_1)) 走到 ((x_2,y_2)),可以向右和向下走,显然有多条路径,对于一条路径上的各个数字,我们可以求出他的和,问有几个不同的和?
(Solution:)
最开始光凭脑袋想一点思路没有,然后动手模拟了几遍,就发现了规律:
- 先一直向右走,再一直向下走,就得到了最小值
- 先一直向下走,再一直向右走,就得到了最大值
那么我们用最大值 (-) 最小值 (+1) 就是答案了。那么我们要如何求到了,通过观察可以发现对于上面两种方式走的每一步,都会产生差值:(0,1,2,3,...,x,x,x,x...,x-1,x-2,...,0)。该数列的和 (=) 最大值减去最小值,设 (t) 是我们一共走的步数,那么 (t = x_2-x_1+y_2-y_1),那么由 (0) 到 (x-1) 和 (x-1) 到 (0) 一共有 (2x) 个数,即还剩下 (t - 2x) 个 (x),通过观察可以发现 (x = min(x_2-x_1,y_2-y_1)),那么设 (a = min(x_2-x_1,y_2-y_1); b = max(x_2-x_1,y_2-y_1)),即 (x = a),且 (t = a + b),那么总和就为:
最后别忘了 (+1)。
(Code:)
/*
@Author: nonameless
@Date: 2020-05-27 20:14:51
@Email: 2835391726@qq.com
@Blog: https://www.cnblogs.com/nonameless/
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define x first
#define y second
#define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
#define sz(x) (int)x.size()
#define pb push_back
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PLL;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
const double eps = 1e-8;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll LNF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f;
inline int gcd(int a, int b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; }
inline ll gcd(ll a, ll b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; }
inline int lcm(int a, int b) { return a * b / gcd(a, b); }
int main(){
int t; cin >> t;
while(t --){
ll x1, x2, y1, y2;
cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2;
cout << (x2 - x1) * (y2 - y1) + 1 << endl;
}
return 0;
}
(D. The Best Vacation)
(Description:)
一年有 (n) 个月,每个月有 (d[i]) 天,其中,第 (j) 的价值为 (j),问连续 (x) 天的价值最大可以是多少?(可以跨年)
(Solution:)
要想价值最大,那我们显然是要选择到 (d[i]) 这一天的,即月尾,那么月尾是放在中间还是最后一天呢?对于放在中间,后续还有一系列的数,但显然价值都是很小的,因为又是从 (1) 开始的了,所以我们考虑把月尾放在最后一天,然后我们遍历每个月即可。
(Code:)
/*
@Author: nonameless
@Date: 2020-05-28 14:27:16
@Email: 2835391726@qq.com
@Blog: https://www.cnblogs.com/nonameless/
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define x first
#define y second
#define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
#define sz(x) (int)x.size()
#define pb push_back
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PLL;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
const double eps = 1e-8;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll LNF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f;
inline int gcd(int a, int b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; }
inline ll gcd(ll a, ll b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; }
inline int lcm(int a, int b) { return a * b / gcd(a, b); }
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n;
ll x, sd[N * 2], v[N * 2], sv[N * 2];
int d[N * 2];
int main(){
cin >> n >> x;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
scanf("%d", &d[i]);
d[i + n] = d[i]; // 由于是循环的,但 x < d1 + d2 + .. + dn 的,所以我们存两遍即可
}
sd[0] = 0; // 前缀和数组
for(int i = 1; i <= n + n; i ++) {
sd[i] = sd[i - 1] + d[i];
v[i] = 1ll * d[i] * (d[i] + 1) / 2; // v[i] 是对于 i 这个月的总价值
sv[i] = sv[i - 1] + v[i]; // 前缀和
}
ll ans = 0;
for(int i = n + 1; i <= n + n; i ++){
ll t = sd[i] - x; // 从第 i 个月最后一天往前走 x 天
// 最后停止第 j 个月,也就是说从第 j 个月的某一天开始到 第 i 月的最后一天
int j = lower_bound(sd + 1, sd + 2 * n + 1, t) - sd;
ll s = sd[i] - sd[j]; // 算出 [j + 1, i] 共多少天
t = x - s; // 在第 j 个月还有 t 天
ll tmp = sv[i] - sv[j]; // 这里是 [j + 1, i] 的总价值
tmp += 1ll * (d[j] + d[j] - t + 1) * t / 2; // 加上第 j 个月的 t 天
ans = max(ans, tmp);
// printf("i = %d j = %d t = %lld
", i, j, t);
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
(E. Are You Fired?)
(Description:)
给定长度为 (n) 的数组 (a),问是否存在一个 (k) 使得数组任意一个长度为 (k) 的子序列的和 (>0),特别的是:数组中区间为 ([frac{n+1}{2}+1, n]) 的数都为 (x)。
(Solution:)
由于后面的数都是一样的,比较特殊,所以我们可以从这里突破。设 (sum[i]) 代表 ([1,i]) 的和
- (x > 0)
- (sum[n] leq 0)
显然是无解的 - (sum[n] > 0)
(k = n)
- (sum[n] leq 0)
- (x leq 0)
设 (m = n - frac{n+1}{2}),那么 (k > m),否则在 ([m+1,n]) 就存在一个长度为 (k) 的子序列的和 (leq 0)。那么我们遍历一遍,算出 (k) 的一个可行范围即可。首先假设 (k = n),对于 (i = 1) 来说,和就是 (sum[k]),大于 (0) 就不要管,如果 (leq 0),那么我们就需要 (-x),来使和变大,随之 (k --),直到 (sum[k] > 0),接下来一次类推。
(Code:)
/*
@Author: nonameless
@Date: 2020-05-28 15:50:31
@Email: 2835391726@qq.com
@Blog: https://www.cnblogs.com/nonameless/
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define x first
#define y second
#define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
#define sz(x) (int)x.size()
#define pb push_back
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PLL;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
const double eps = 1e-8;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll LNF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f;
inline int gcd(int a, int b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; }
inline ll gcd(ll a, ll b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; }
inline int lcm(int a, int b) { return a * b / gcd(a, b); }
const int N = 5e5 + 10;
int n, x;
int a[N];
ll sum[N];
int main(){
cin >> n;
int m = n + 1 >> 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++){
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + a[i];
}
scanf("%d", &x);
for(int i = m + 1; i <= n; i ++){
a[i] = x;
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + x;
}
if(x > 0){
if(sum[n] > 0) cout << n << endl;
else puts("-1");
} else{
int k = n;
m = n - m;
for(int l = 1; l <= n; l ++){
int r = l + k - 1; // 区间的右端点
if(r > n) break;
ll tmp = sum[r] - sum[l - 1]; // [l, r] 的和
while(tmp <= 0 && k > m) tmp -= x, k --;
if(k <= m) break;
}
if(k <= m) puts("-1");
else cout << k << endl;
}
return 0;
}