1 目录
* MATLAB随机数的产生
- Uniform,Normal & Custom distributions
* 蒙特卡洛仿真
* 产生股票价格路径
* 期权定价
- 经典公式
- 和蒙特卡洛方法比较
- 方差减小技巧
- Exotic Options
* 多变量仿真
- Basket Option
- Portfolio Value at Risk
2 重点内容讲解
2.1 蒙特卡洛仿真
- 依赖随机数生成
- rand,randn,randi
注:rand:产生平均分布随机数
randn:产生正太分布随机数
randi:产生随机整数随机数
-支持的随机分布
- 随机分布拟合
2.2 在统计工具箱里面有更多的随机数生成函数
2.3 基于MATLAB常用随机数的举例
举例:生成随机数
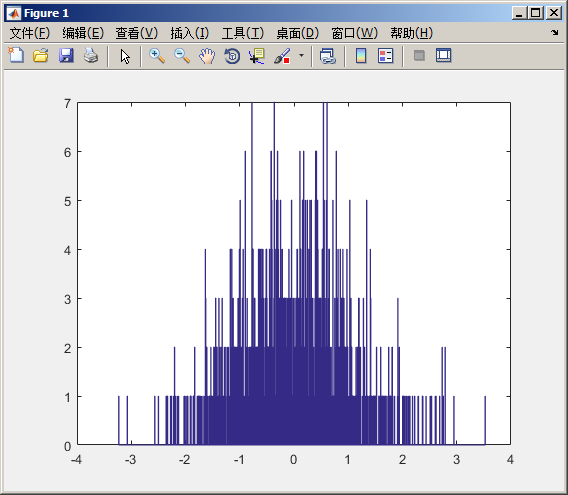
%% Uniform distribution % % Numbers uniformly distributed along [0 1] % 产生100个随机分布的随机数在[0 1]这个闭区间内 % rand的参数为n*n的矩阵 rU = rand(1,10); hist(rU,10);
图示:

举例:生成正太分布随机数
%% Normal distribution % % Numbers normally distribution with mean0,std1 % 基于均值为0,标准差为1的正态分布随机数。 % randn的参数为n*n的矩阵 rN = randn(1,1000); hist(rN,1000);
图示:
举例:设计随机种子的方式生成随机数
%% Setting the behaviour of the random numbers % % There are many implementations of pseudo-random number generator in % MATLAB,we will be working with % % mt19937ar - Mersenne Twister,which has an approximate period of % 2^19937-1 % We can set the behaviour in a number of ways % Seed the generator % 以设定种子的方式设置随机数 rng(0) [randn(1),randn(1),randn(1),randn(1)] rng(0); [randn(1),randn(1),randn(1),randn(1)] % 由于设定的种子都是一样的,因此生成的两组随机数也是一样的 % ans = % 0.5377 1.8339 -2.2588 0.8622 % ans = % 0.5377 1.8339 -2.2588 0.8622
举例:其他产生随机数的方法
%% Generating random numbers from different distributions
%
% Lets see a list of the supported distributions
docsearch Continuous Distributions
% 用random产生随机数,按照随机规则产生,具体规则在doc,查看flag内容
%% Now,lets choose a number of draws from one of these,say the exponential
% 产生指数的随机数,[]为矩阵形状,3为参数,exp为flag
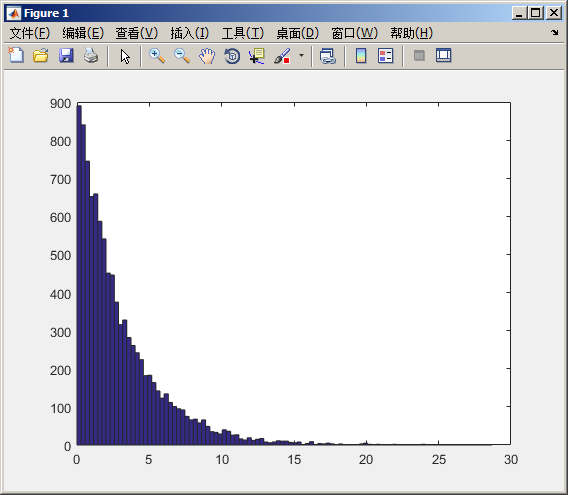
rB = random('exp',3,[1 10000]);
hist(rB,100);
图示:
2.3 对数据进行拟合fitdist
2.4 产生股票价格路径

2.5 公开函数:随机蒙特卡洛价格路径:
function mat = pricePaths(S,r,T,sigma,nSims,nSteps) % S ==>> 起始价格 % r ==>> 无风险回报率 % T ==>> 时间宽度 % sigma ==>> 波动率 % nSims ==>> 做多少次蒙特卡洛放在 % nSteps ==>> 在T时间内取多大的步长 % Generate asset price paths using geometric brownian motion % Determine the timestep % 根据时间长度和步长,求出每个均匀分布点是多少长 Dt = T/(nSteps); % Generate the random numbers % 初步随机数,多少蒙特卡罗仿真*多少步长的矩阵 mat = randn(nSteps,nSims); % Generate the returns scaled using the relevant equation % 布朗运动公式 mat = exp((r-sigma^2/2)*Dt + sigma*sqrt(Dt).*mat); % Generate price paths mat = cumprod(mat,1); % 按照列的方向累乘,从某一天累计的回报率 % Scale with the initial asset price % 初始价格*实际价格=实际价格回报率后的价格 mat = [repmat(S,1,nSims); mat.*S]; end
应用实例:
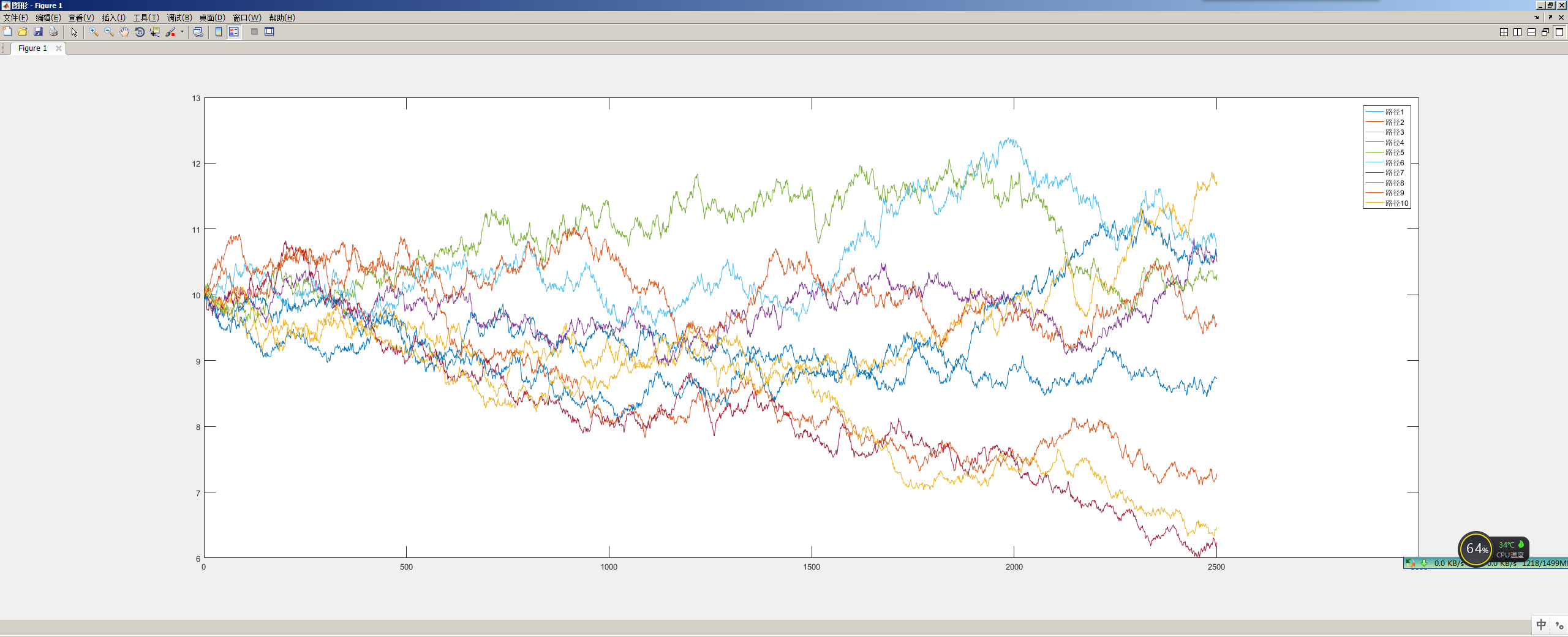
%% S = 10; % 股票起始价格 r = 0.03; % 无风险收益率 T = 1; % 时间跨度 sigma = 0.2; % 波动率 nSims = 10; % 多少条路径(多少次蒙特卡洛实验) nSteps = 250*10; % 步长是多少 这里是2500个步长 paths = pricePaths(S,r,T,sigma,nSims,nSteps); %% Plotting figure; plot(paths);
图示:我们可以看到以10为起始价格,生成10条蒙特卡洛的随机股票价格路径。生成这些随机的股票价格可以进行一些模型的压力检测。不仅在样本内可以进行检测,而且在可能会产生的不可知价格路径下,模型的鲁棒性效果如何(Robust)。
再比如我们可以把初始价格设置为3000个点也会生成如下路径: