MongoDB Transaction
init replset mongodb env
$mkdir db1 && mkdir db2 && mkdir db3
$mongod --port 27017 --dbpath ./db --replSet rstest1
$mongod --port 37017 --dbpath ./db2 --replSet rstest1
$mongod --port 47017 --dbpath ./db3 --replSet rstest1
$mongo --port 27017
rs.initiate( { _id : "rstest1", members: [ { _id: 0, host: "127.0.0.1:27017" }, { _id: 1, host: "127.0.0.1:37017" }, { _id: 1, host: "127.0.0.1:47017" }, ] })
const mongoose = require('mongoose')
const mongoUri = 'mongodb://localhost:27017,localhost:37017,localhost:47017/test'
const client = mongoose.createConnection(mongoUri, { replicaSet: 'rstest' })
let Acc = client.model('Account', new mongoose.Schema({
name: String,
balance: Number
}))
async function initTest() {
await Acc.create({ 'name': 'James', 'balance': 3000 })
await Acc.create({ 'name': 'Wade', 'balance': 0 })
}
async function afterWork() {
await Acc.remove({ 'name': 'James' })
await Acc.remove({ 'name': 'Wade' })
}
async function transferTest(transfer) {
let session = await Acc.startSession()
session.startTransaction()
try {
const opts = { session, new: true }
let a = await Acc.findOneAndUpdate({
'name': 'James'
}, {
$inc: { 'balance': -transfer }
}, opts)
console.log(a.toObject());
let b = await Acc.findOneAndUpdate({
'name': 'Wade',
}, {
$inc: { 'balance': transfer }
}, opts)
console.log(b.toObject());
await session.commitTransaction()
} catch (err) {
session.abortTransaction()
console.error(err)
} finally {
session.endSession()
}
}
async function test() {
await afterWork()
await initTest()
await transferTest(100)
// await afterWork()
}
test()
set a debug point or sleep point at
console.log(a.toObject());
to stop the process
then run code to read them
`
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5cb752de57e8791edf030e9d"), "name" : "James", "balance" : 3000, "__v" : 0 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5cb752de57e8791edf030e9e"), "name" : "Wade", "balance" : 0, "__v" : 0 }
`
it works fine
then run :
`
rstest:PRIMARY> db.accounts.update({"name":"Wade"}, { $inc:{'balance':10}})
WriteResult({ "nMatched" : 1, "nUpserted" : 0, "nModified" : 1 })
`
this will return immediately, when the debug point continue, it ran into exception
null: MongoError: WriteConflict MongoError: Attempted illegal state transition from [TRANSACTION_ABORTED] to [TRANSACTION_ABORTED] ....
PAY attention
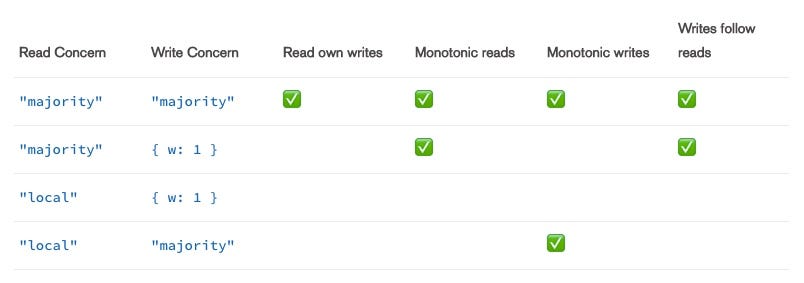
In MongoDB, clients can see the results of writes before the writes are durable:
clients using "local" by default can see the result of a write operation before the write operation is acknowledged to the issuing client.
read isolation
Thus , in the case of we need to read own writes we need to read concern set "majority", wirte concern "majority"
how to config this
read concern : you can disable read concern by setting either:
- -- enableMajorityReadConcern command line option to false.
- replication.enableMajorityReadConcern configuration file setting to false
write concern : your code write-concern option, example :
const schema = new Schema({ name: String }, {
writeConcern: {
w: 'majority',
j: true
}
});