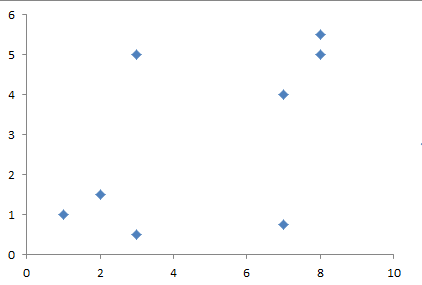
数据集如下所示:
1,1,1 2,1.5,1 3,0.5,1 3,5,-1 7,0.75,-1 7,4,2 8,5,2 8,5.5,2
数据集有三个属性,分别是二维坐标中的x和y,第三个属性是所属的类,-1代表为孤立点,坐标系如下图所示:
源代码如下:
package neugle.dbscan; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileReader; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Random; public class DBScan { private List<Point> pointList = new ArrayList<DBScan.Point>();// 读入的样本数据 private List<List<Point>> clusterList = new ArrayList<List<Point>>();// 最终分类结果 private List<Point> noiseList = new ArrayList<DBScan.Point>();// 噪声数据集合 private List<Point> npointList = new ArrayList<DBScan.Point>();// 候选数据集合 private List<Integer> unvisitedList = new ArrayList<Integer>();// unvisited集合 private double eps;// 邻域半径 private int minPts;// 密度 class Point { public double x; public double y; public String point_type; public boolean isVisited = false; } public DBScan(double eps, int minPts) { this.eps = eps; this.minPts = minPts; } // 读取数据 public List<Point> ReadFile(String filePath) { FileReader fr = null; BufferedReader br = null; try { fr = new FileReader(filePath); br = new BufferedReader(fr); String line = null; while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { Point point = new Point(); String[] agrs = line.split(","); point.x = Double.parseDouble(agrs[0]); point.y = Double.parseDouble(agrs[1]); point.point_type = agrs[2]; this.pointList.add(point); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { br.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return pointList; } // DBScan主方法 public void DBScanFun(String filePath) { this.ReadFile(filePath); // this.Norm(); while (this.IsOver()) { Point p = this.pointList.get(this.RandomNum());// 随机找到unvisited节点 p.isVisited = true;// 标记p为visited List<Point> neighborList = this.GetNeighbors(p);// 找到满足最小密度的邻居节点 if (neighborList.size() < this.minPts) {// 添加噪声数据 this.noiseList.add(p);// 将p放入噪声集合 } else { List<Point> clist = new ArrayList<DBScan.Point>();// 新建一个簇C clist.add(p);// 将p放到簇C中 this.npointList = neighborList;// 令N为p的邻域对象的集合 for (int i = 0; i < this.npointList.size(); i++) { if (this.npointList.get(i).isVisited == false) {// 查找p'中unvisited的节点 this.npointList.get(i).isVisited = true;// 标记p'为visited List<Point> neighborLists = this .GetNeighbors(this.npointList.get(i));// 计算p'满足邻域的节点集合 if (neighborLists.size() >= this.minPts) { for (int j = 0; j < neighborLists.size(); j++) { this.npointList.add(neighborLists.get(j));// 将p'的邻域节点加入到N } } clist.add(this.npointList.get(i));// 将p'添加到簇C } } this.clusterList.add(clist); } } } // 在未访问的集合中随机选取 private int RandomNum() { int num = this.unvisitedList.size(); Random rand = new Random(); int randNum = rand.nextInt(num); return this.unvisitedList.get(randNum); } // 获得邻域集合 private List<Point> GetNeighbors(Point p) { List<Point> list = new ArrayList<DBScan.Point>(); for (int i = 0; i < this.pointList.size(); i++) { double value = this.DistanceCalculate(this.pointList.get(i), p); if (value != 0 && value <= this.eps) { list.add(this.pointList.get(i)); } } return list; } // 欧几里得距离公式 private double DistanceCalculate(Point iris1, Point iris2) { double sum = Math.sqrt(Math.pow((iris1.x - iris2.x), 2) + Math.pow((iris1.y - iris2.y), 2)); return sum; } // 判断数据是否都被访问完 private boolean IsOver() { this.unvisitedList = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for (int i = 0; i < this.pointList.size(); i++) { if (this.pointList.get(i).isVisited == false) { unvisitedList.add(i); } } if (this.unvisitedList.size() > 0) { return true; } return false; } public void Print() { System.out.println("聚为" + this.clusterList.size() + "类"); for (int i = 0; i < this.clusterList.size(); i++) { List<Point> c = this.clusterList.get(i); System.out.println("------------"); for (int j = 0; j < c.size(); j++) { System.out.println(c.get(j).x + " " + c.get(j).y + " " + c.get(j).point_type); } System.out.println(c.size()); System.out.println("------------"); } System.out.println("噪声点有" + this.noiseList.size() + "个"); System.out.println("------------"); for (int i = 0; i < this.noiseList.size(); i++) { System.out.println(this.noiseList.get(i).x + " " + this.noiseList.get(i).y + " " + this.noiseList.get(i).point_type); } System.out.println("------------"); } public static void main(String[] args) { DBScan c = new DBScan(2.5, 2); c.DBScanFun("D:\data\DBScan\test.data"); c.Print(); } }
实验结果如下所示:
聚为2类 ------------ 8.0 5.5 2 7.0 4.0 2 8.0 5.0 2 3 ------------ ------------ 3.0 0.5 1 1.0 1.0 1 2.0 1.5 1 3 ------------ 噪声点有2个 ------------ 3.0 5.0 -1 7.0 0.75 -1 ------------