一、字节缓冲输入流
1、BufferedInputStream 概述
BufferedInputStream 是一个套接在字节输入流上面的处理流,能够提高写入速度。
2、BufferedInputStream 类结构
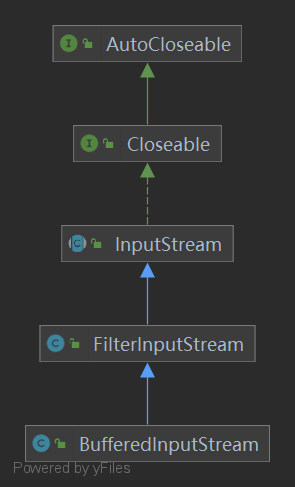
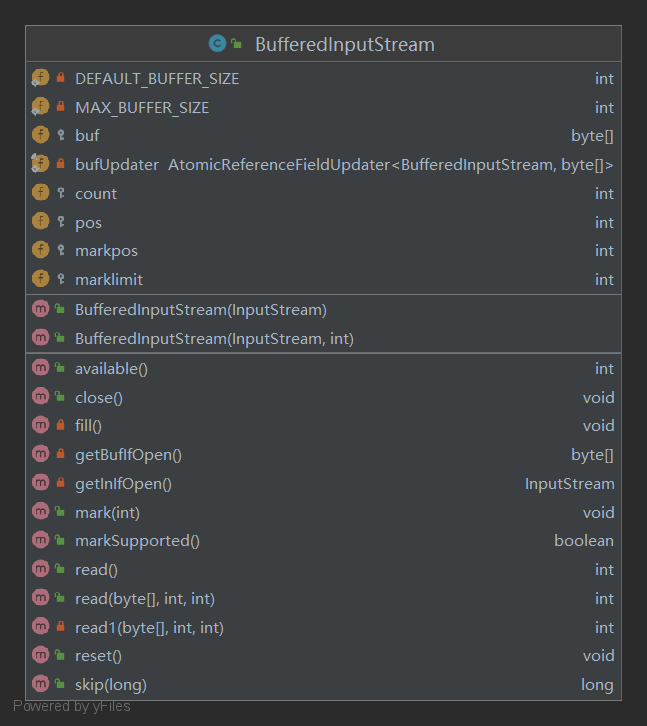
3、构造方法
BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) 创建一个 BufferedInputStream 并保存其参数,即输入流 in,以便将来使用。
BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size) 创建具有指定缓冲区大小的 BufferedInputStream 并保存其参数,即输入流 in,以便将来使用。
参数:
InputStream in:字节输入流,可以传递FileInputStream,缓冲流会给FileInputStream增加一个缓冲区,提高FileInputStream的读取效率
int size:指定缓冲流内部缓冲区的大小,不指定默认。
4、常用方法
int read()从输入流中读取数据的下一个字节。
int read(byte[] b) 从输入流中读取一定数量的字节,并将其存储在缓冲区数组 b 中。
void close() 关闭此输入流并释放与该流关联的所有系统资源。
5、使用步骤
① 创建FileInputStream对象,构造方法中绑定要读取的数据源;
② 创建BufferedInputStream对象,构造方法中传递FileInputStream对象,提高FileInputStream对象的读取效率;
③ 使用BufferedInputStream对象中的方法read,读取文件;
④ 释放资源;
6、案例
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
2 //1.创建FileInputStream对象,构造方法中绑定要读取的数据源
3 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("10_IO\a.txt");
4 //2.创建BufferedInputStream对象,构造方法中传递FileInputStream对象,提高FileInputStream对象的读取效率
5 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
6 //3.使用BufferedInputStream对象中的方法read,读取文件
7 //int read()从输入流中读取数据的下一个字节。
8 /*int len = 0;//记录每次读取到的字节
9 while((len = bis.read())!=-1){
10 System.out.println(len);
11 }*/
12
13 //int read(byte[] b) 从输入流中读取一定数量的字节,并将其存储在缓冲区数组 b 中。
14 byte[] bytes =new byte[1024];//存储每次读取的数据
15 int len = 0; //记录每次读取的有效字节个数
16 while((len = bis.read(bytes))!=-1){
17 System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,len));
18 }
19
20 //4.释放资源
21 bis.close();
22 }
二、字节缓冲输出流
1、BufferedOutputStream 概述
BufferedOutputStream 是一个套接在字节输出流上面的处理流,能够提高输出速度。
2、BufferedOutputStream 类结构
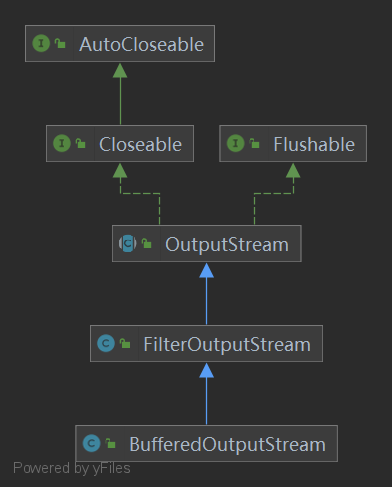
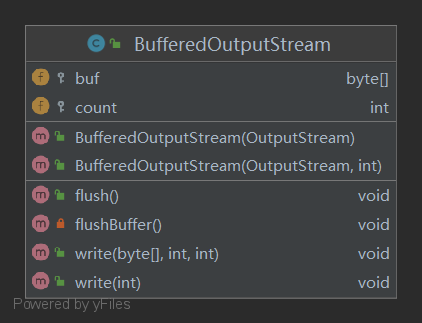
3、构造方法
BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out) 创建一个新的缓冲输出流,以将数据写入指定的底层输出流。
BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out, int size) 创建一个新的缓冲输出流,以将具有指定缓冲区大小的数据写入指定的底层输出流。
参数:
OutputStream out:字节输出流,可以传递 FileOutputStream,缓冲流会给FileOutputStream增加一个缓冲区,提高FileOutputStream的写入效率
int size:指定缓冲流内部缓冲区的大小,不指定默认。
4、常用方法
public void close() :关闭此输出流并释放与此流相关联的任何系统资源。
public void flush() :刷新此输出流并强制任何缓冲的输出字节被写出。
public void write(byte[] b):将 b.length字节从指定的字节数组写入此输出流。
public void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) :从指定的字节数组写入 len字节,从偏移量 off开始输出到此输出流。
public abstract void write(int b) :将指定的字节输出流。
5、使用步骤
① 创建FileOutputStream对象,构造方法中绑定要输出的目的地;
② 创建BufferedOutputStream对象,构造方法中传递FileOutputStream对象对象,提高FileOutputStream对象效率;
③ 使用BufferedOutputStream对象中的方法write,把数据写入到内部缓冲区中;
④ 使用BufferedOutputStream对象中的方法flush,把内部缓冲区中的数据,刷新到文件中;
⑤ 释放资源(会先调用flush方法刷新数据);
6、案例
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
2 //1.创建FileOutputStream对象,构造方法中绑定要输出的目的地
3 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("E:\a.txt");
4 //2.创建BufferedOutputStream对象,构造方法中传递FileOutputStream对象对象,提高FileOutputStream对象效率
5 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
6 //3.使用BufferedOutputStream对象中的方法write,把数据写入到内部缓冲区中
7 bos.write("我把数据写入到内部缓冲区中".getBytes());
8 //4.使用BufferedOutputStream对象中的方法flush,把内部缓冲区中的数据,刷新到文件中
9 bos.flush();
10 //5.释放资源(会先调用flush方法刷新数据,第4部可以省略)
11 bos.close();
12 }
三、案例
1、实现非文本文件的复制
1 @Test
2 public void BufferedStreamTest() throws FileNotFoundException {
3 BufferedInputStream bis = null;
4 BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
5
6 try {
7 //1.造文件
8 File srcFile = new File("a.jpg");
9 File destFile = new File("b.jpg");
10 //2.造流
11 //2.1 造节点流
12 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream((srcFile));
13 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
14 //2.2 造缓冲流
15 bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
16 bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
17
18 //3.复制的细节:读取、写入
19 byte[] buffer = new byte[10];
20 int len;
21 while((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1){
22 bos.write(buffer,0,len);
23
24 // bos.flush();//刷新缓冲区
25
26 }
27 } catch (IOException e) {
28 e.printStackTrace();
29 } finally {
30 //4.资源关闭
31 //要求:先关闭外层的流,再关闭内层的流
32 if(bos != null){
33 try {
34 bos.close();
35 } catch (IOException e) {
36 e.printStackTrace();
37 }
38
39 }
40 if(bis != null){
41 try {
42 bis.close();
43 } catch (IOException e) {
44 e.printStackTrace();
45 }
46
47 }
48 //说明:关闭外层流的同时,内层流也会自动的进行关闭。关于内层流的关闭,我们可以省略.
49 // fos.close();
50 // fis.close();
51 }
52
53 }
2、复制文件的方法
1 public void copyFileWithBuffered(String srcPath,String destPath){
2 BufferedInputStream bis = null;
3 BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
4
5 try {
6 //1.造文件
7 File srcFile = new File(srcPath);
8 File destFile = new File(destPath);
9 //2.造流
10 //2.1 造节点流
11 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream((srcFile));
12 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
13 //2.2 造缓冲流
14 bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
15 bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
16
17 //3.复制的细节:读取、写入
18 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
19 int len;
20 while((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1){
21 bos.write(buffer,0,len);
22 }
23 } catch (IOException e) {
24 e.printStackTrace();
25 } finally {
26 //4.资源关闭
27 //要求:先关闭外层的流,再关闭内层的流
28 if(bos != null){
29 try {
30 bos.close();
31 } catch (IOException e) {
32 e.printStackTrace();
33 }
34
35 }
36 if(bis != null){
37 try {
38 bis.close();
39 } catch (IOException e) {
40 e.printStackTrace();
41 }
42
43 }
44 //说明:关闭外层流的同时,内层流也会自动的进行关闭。关于内层流的关闭,我们可以省略.
45 // fos.close();
46 // fis.close();
47 }
48 }
3、使用字节流实现图片加密操作
(1)加密
1 @Test
2 public void test1() {
3
4 FileInputStream fis = null;
5 FileOutputStream fos = null;
6 try {
7 fis = new FileInputStream("爱情与友情.jpg");
8 fos = new FileOutputStream("爱情与友情secret.jpg");
9
10 byte[] buffer = new byte[20];
11 int len;
12 while ((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
13 //字节数组进行修改
14 //错误的
15 // for(byte b : buffer){
16 // b = (byte) (b ^ 5);
17 // }
18 //正确的
19 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
20 buffer[i] = (byte) (buffer[i] ^ 5);
21 }
22
23
24 fos.write(buffer, 0, len);
25 }
26 } catch (IOException e) {
27 e.printStackTrace();
28 } finally {
29 if (fos != null) {
30 try {
31 fos.close();
32 } catch (IOException e) {
33 e.printStackTrace();
34 }
35
36 }
37 if (fis != null) {
38 try {
39 fis.close();
40 } catch (IOException e) {
41 e.printStackTrace();
42 }
43
44 }
45 }
46 }
(2)解密
1 @Test
2 public void test() {
3
4 FileInputStream fis = null;
5 FileOutputStream fos = null;
6 try {
7 fis = new FileInputStream("爱情与友情secret.jpg");
8 fos = new FileOutputStream("爱情与友情2.jpg");
9
10 byte[] buffer = new byte[20];
11 int len;
12 while ((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
13 //字节数组进行修改
14 //错误的
15 // for(byte b : buffer){
16 // b = (byte) (b ^ 5);
17 // }
18 //正确的
19 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
20 buffer[i] = (byte) (buffer[i] ^ 5);
21 }
22
23 fos.write(buffer, 0, len);
24 }
25 } catch (IOException e) {
26 e.printStackTrace();
27 } finally {
28 if (fos != null) {
29 try {
30 fos.close();
31 } catch (IOException e) {
32 e.printStackTrace();
33 }
34
35 }
36 if (fis != null) {
37 try {
38 fis.close();
39 } catch (IOException e) {
40 e.printStackTrace();
41 }
42
43 }
44 }
45 }