


正态分布

import numpy as np #数学计算的框架 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #绘图的框架 #这里相当于是随即X维度X1,rand是随机均匀分布 X=2*np.random.rand(100,1)#rand返回100行1列[0,1) 均匀分布 #人为的设置真是的Y一列,randn是设置error,ranndn是标准正态分布 Y=4+3*X+np.random.randn(100,1) #randn 标准正态分布 #4*X0(X0为1嘛)+3*X 看成预测值 np.random.randn(100,1)看成随机误差【独立服从正态分布,这里用标准正态分布模拟】 #整合X0与X1 #numpy.c_(就是英文单词conbine的意思) X_b=np.c_[np.ones((100,1)),X] # print(X_b) #linalg线性代数 inv(inverse)求逆 .T就是转置 .dot(点乘 进行矩阵运算) theta_best=np.linalg.inv(X_b.T.dot(X_b)).dot(X_b.T).dot(Y) print(theta_best) #theta_best 2行1列 #可以知道包括X0在内有几组X的值,W0~~Wn即theta_best就有几行1列的值 #创建测试机里面的X1 X_new=np.array([[0],[2]]) X_new_b=np.c_[(np.ones((2,1))),X_new] #n行2列 # print(X_new_b) y_predict=X_new_b.dot(theta_best) print(y_predict) plt.plot(X_new,y_predict,'r-')#红色用-绘图 预测值 plt.plot(X,Y,'b.')#蓝色用.绘制 实际值 plt.axis([0,2,0,15])#X轴范围0-2 Y轴范围0-15 plt.show()
使用sklearn
import numpy as np from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression #线性回归 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt X=2*np.random.rand(100,1)#rand返回100行1列[0,1) 均匀分布 Y=4+3*X+np.random.randn(100,1) lin_reg=LinearRegression() #fit 训练 这个方法指的研究 lin_reg.fit(X,Y) #intercept_截距W0 coef_其他的参数W1~Wn print(lin_reg.intercept_,lin_reg.coef_) #使用predict去预测 X_new=np.array([[0],[2]]) print(lin_reg.predict(X_new))
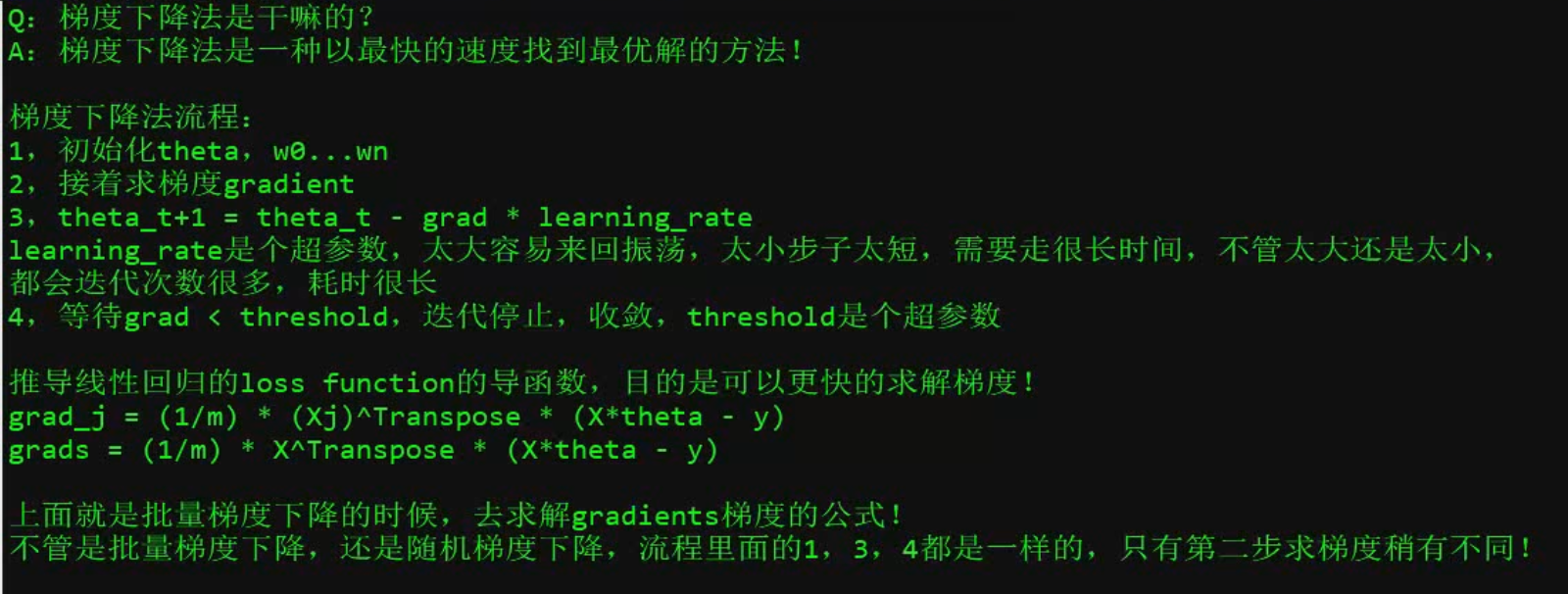
import numpy as np X=2*np.random.rand(100,1) #均匀分布取100,1向量 Y=4+3*X+np.random.randn(100,1) #标准正态分布,取得Y值 X_b=np.c_[np.ones((100,1)),X] #拼接X矩阵,每行的X0都是1 learning_rate=0.1 #学习绿 n_iterations=10000#设置最大迭代次数 m=100#样本数 为了loss取平均,否则我数据量大的话loss反而大,不对,我要知道平均是不是大,就是把100 和 1000统一来看意思 theta=np.random.randn(2,1)#2因为X_b初始化俩个维度 count=0#当前迭代次数 for iteration in range(n_iterations): count+=1 gradients=1/m*X_b.T.dot(X_b.dot(theta)-Y)#各个点位的斜率 # print(gradients) theta=theta-learning_rate*gradients#theta赋予此次迭代的值 # print(gradients) print(count) print(theta)




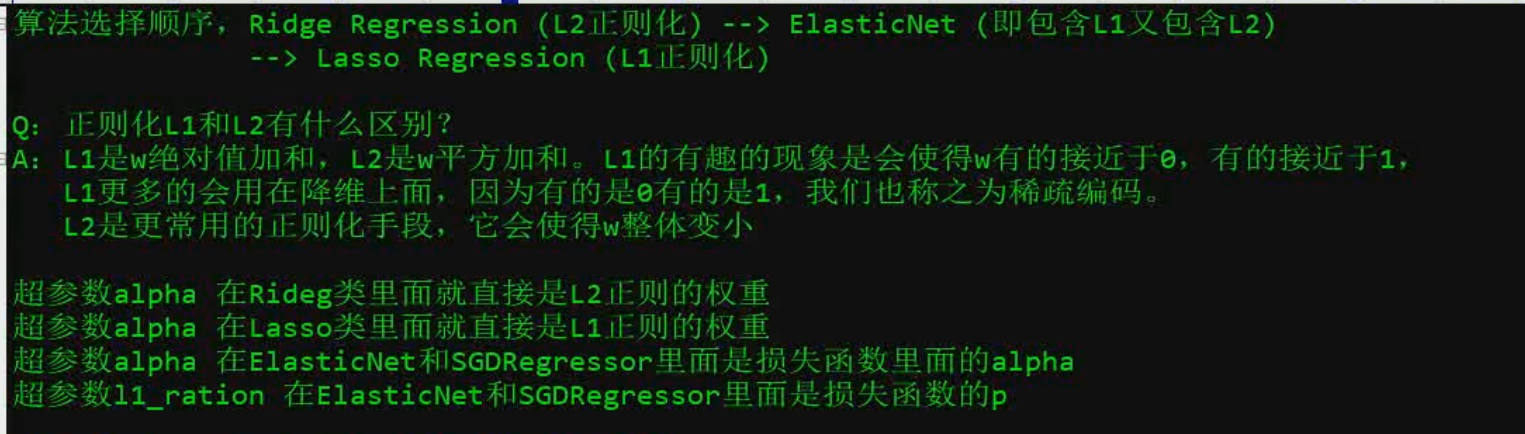



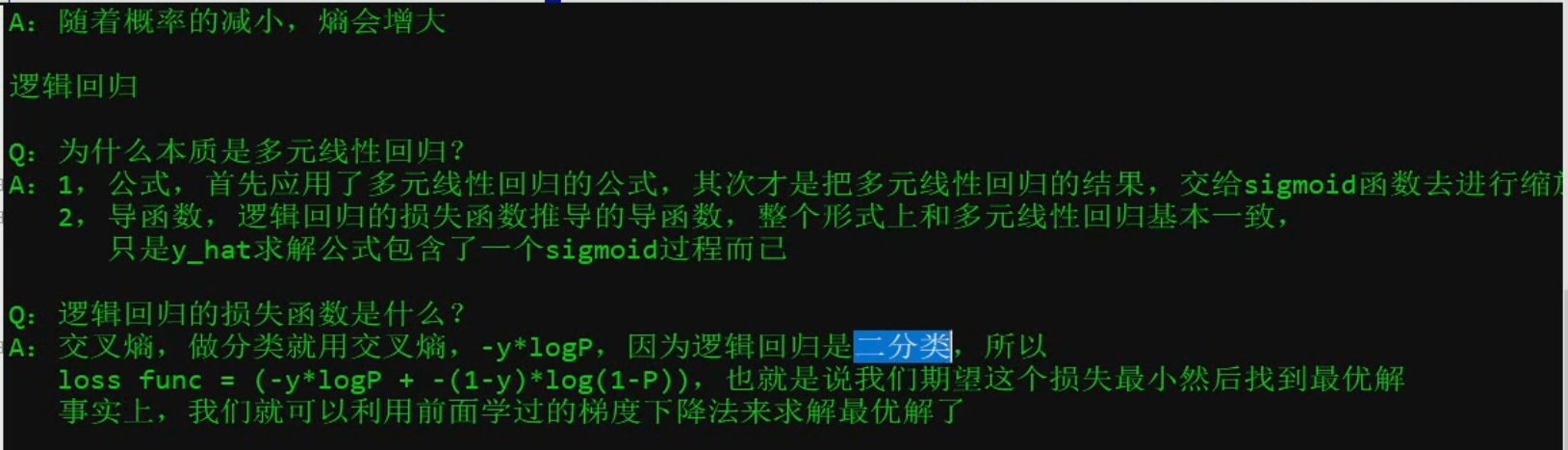
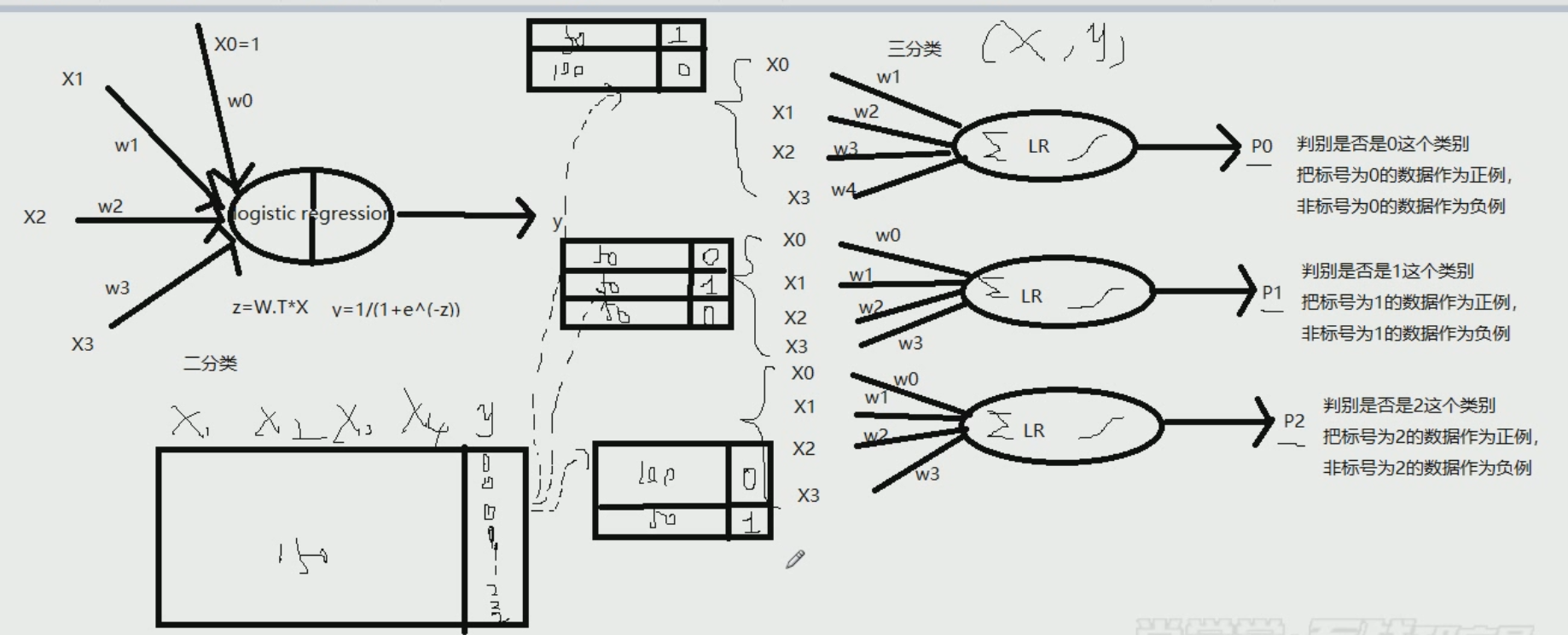
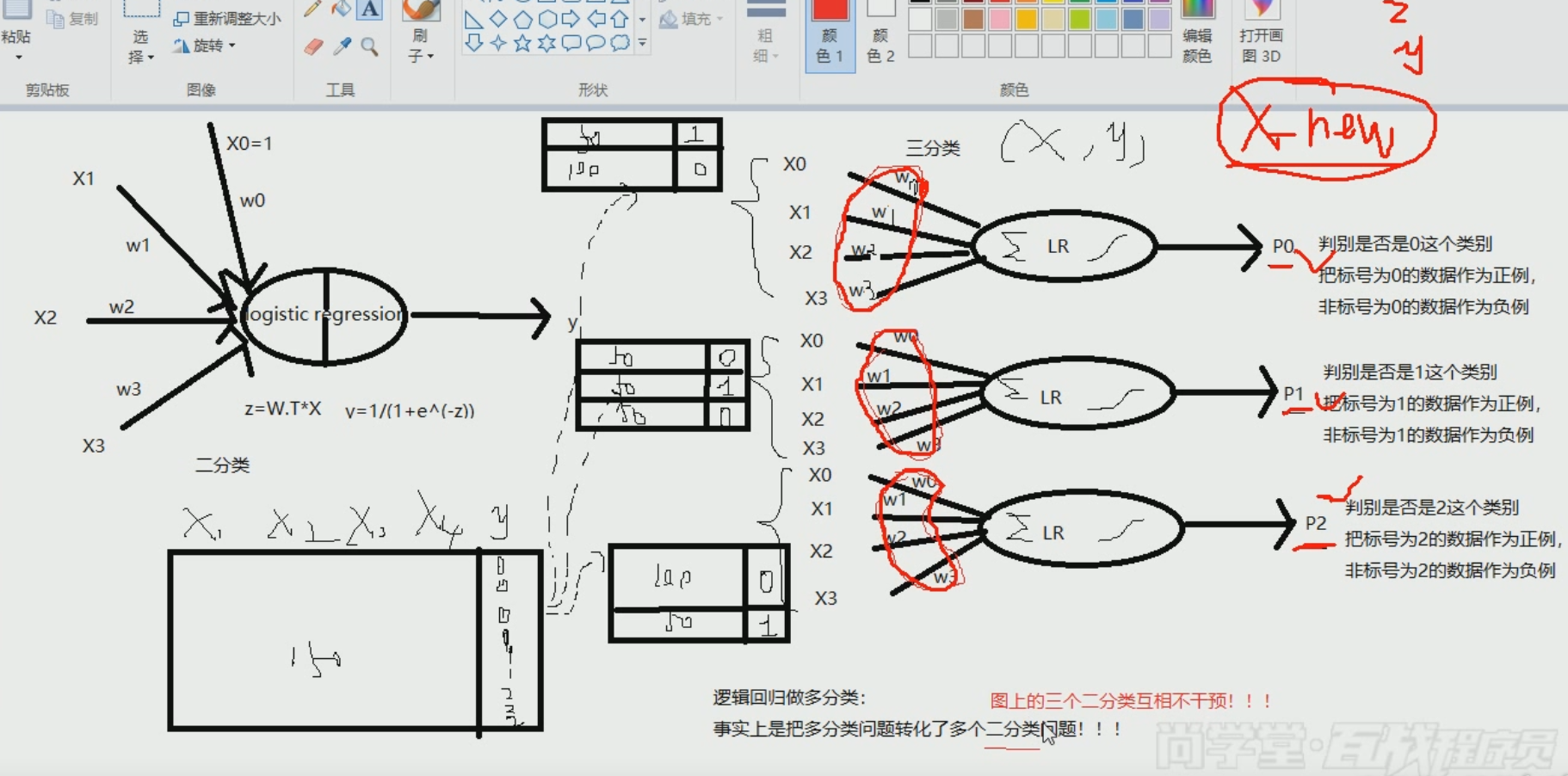
逻辑回归分析过程~~~~~

傅里叶变换:将时间轴拆分将频率分别分解出来,然后从侧面审视这些频率
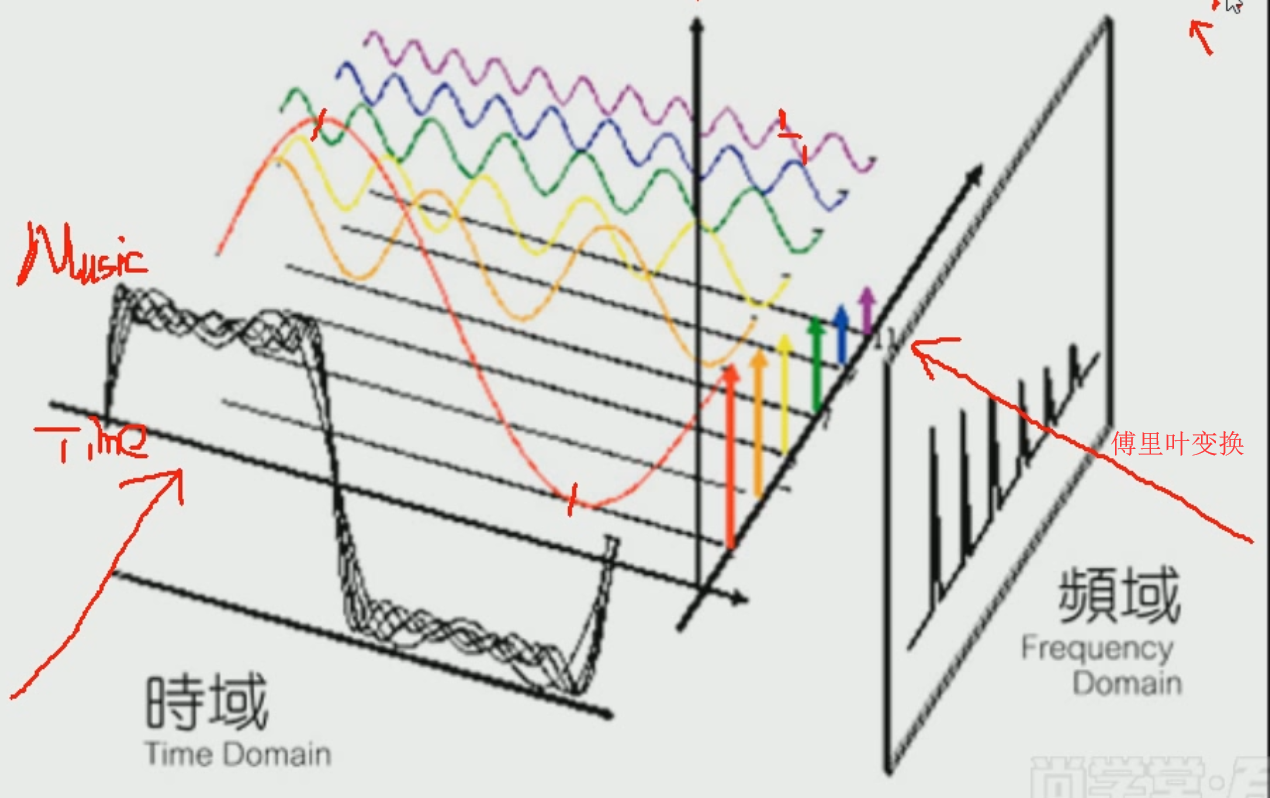
HZ太高就成噪声了,因此我们可以将维,比如就取前3000HZ
神经网络
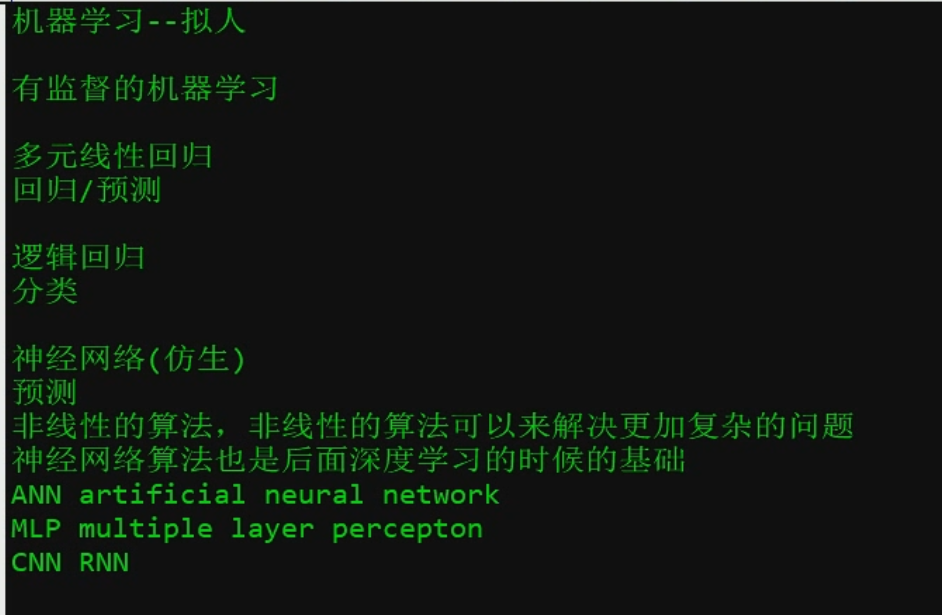

Relu 激活函数 max{0,x}

