前言
String和StringBuffer本质上都是修饰字符串的只是含义不同 StringBuffer叫做字符串缓冲区
首先看下string类的例子
public class Work1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
String s1 = s.substring(3);
System.out.println(s==s1);//结果为false
}
}
在来看下StringBuffer类的例子
public class Work1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer ab1 = new StringBuffer();
StringBuffer ab2 = ab1.append("hello");
System.out.println(ab1==ab2); //结果为true
}
}
在来看下二者的内存分布图如下:
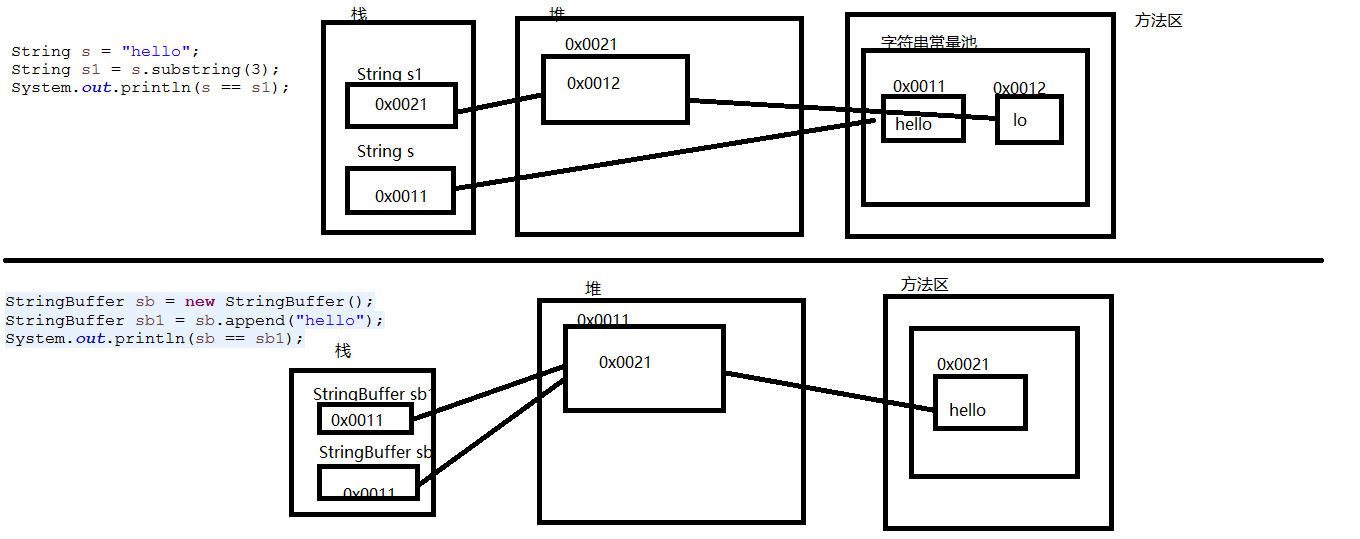
根据内存分布图来看 String 除了直接String s="hello" 这种方式之外不会创建新的对象 其它的不管是通过方法返回的String类型还是直接利用构造函数创建出来的字符串还是通过变量拼接(二边只要有一个变量拼接)都需要创建新的对象
而StringBuffer通过StringBuffer里面的方法 操作 返回一个StringBuffer类型的变量跟原StringBuffer变量是相等的 。
String stt1 = new String("hello");
String stt2 = new String("world");
System.out.println(stt1+stt2);
String stt1 = "hello"
String stt2 = new String("world");
System.out.println(stt1+"world");
//上面二种拼接都是可以的
//这种是可以拼接的
StringBuffer ab1 = new StringBuffer();
StringBuffer ab2 = ab1.append("hello");
System.out.println(ab2+"hello");
//这种是不可以拼接的
StringBuffer ab1 = new StringBuffer("abc");
StringBuffer ab2 = ab1.append("hello");
System.out.println(ab2+ab1);
最后总结三点不同:
1、String可以用+算术运算符拼接字符串(不管是二边有一个变量字符串还是都是常量字符串都可以拼接)StringBuffer不可以(除了二边只要有一个常量字符串对象就可以拼接 例如 ab2+"hello")
2、String表示线程不安全 执行效率高 StringBuffer相反
3、String对象中的值是不可变的 StringBuffer中的值是可变的(也就是可以通过方法修改原来的StringBuffer变量并赋值给一个新的StringBuffer变量 二者之间是相等的)
4、String创建对象时可以String a = "abc" 但是 StringBuffer不能直接这样创建 需要StringBuffer pj1 = new StringBuffer("abc");