链表简介
链表是很常见的数据结构,由一个个节点组成,每个节点中储存着数据和指针(地址引用),指针负责节点间的连接。
它是一种线性表,线性表有两种存储方式:顺序存储和链式存储。链表属于链式存储,顺序由元素间的指针决定,元素在内存中非连续存放,且链表长度可以改变。数组是顺序存储的线性表,元素在内存中连续存放的,且数组创建时大小已固定。
链表可以用来实现栈和队列数据结构(栈和队列可理解为逻辑类数据结构,链表属于存储类数据结构),实现缓存LRU算法,Java类库也使用了链表(如,LinkedList,LinkedHashMap)等。链表的形式有很多,常用的有单向链表、双向链表、循环链表 ...
单向链表
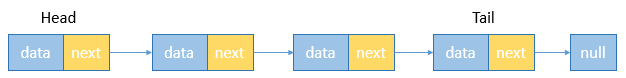
单链表中的节点分两部分,分别是数据(data)和指向下一个节点的地址(next),尾节点(tail)的next指向null。单向链表只能从头到尾一个方向遍历,查找节点时需要从头节点(head)开始向下查找。
插入节点首先遍历查找到插入的位置,然后将当前插入节点的next指向下一节点,上一节点的next指向当前插入节点。删除节点同样从头遍历找到要删除的节点,然后将当前删除节点的上一个节点next指向当前删除节点的下一个节点。
节点的伪代码:
class Node<E>{
private E item;
private Node<E> next; // 如果是尾节点,next指向null
Node(E data, Node<E> next) {
this.item = data;
this.next = next;
}
// ...
}
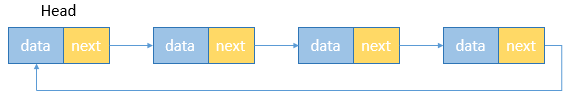
单向循环链表
循环链表和非循环链表基本一样,区别是首尾节点连在了一起,最后一个节点的next指向头节点,形成了一个闭环。
节点的伪代码:
class Node<E>{
private E item;
// 如果是末尾节点,指向首节点的引用地址
private Node<E> next;
Node(E data, Node<E> next) {
this.item = data;
this.next = next;
}
// ...
}
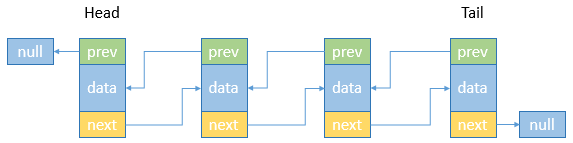
双向链表
顾名思义,与单向链表相比较,双向链表可以从头到尾或从尾到头两个方向来遍历数据。双向链表中的节点分三个部分,分别是指向上一个节点的地址(prev)和数据(data)以及指向下一个节点的地址(next),尾节点(tail)节点的next指向null,头节点(head)的prev指向null。
增加和删除节点和单向链表同理,只是增加了修改prev地址的操作。
节点的伪代码:
class Node<E>{
private E item;
private Node<E> prev; // 头节点prev指向null
private Node<E> next; // 尾节点next指向null
Node(Node<E> prev, E data, Node<E> next) {
this.item = data;
this.prev = prev;
this.next = next;
}
// ...
}
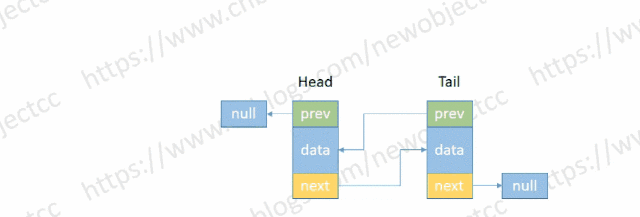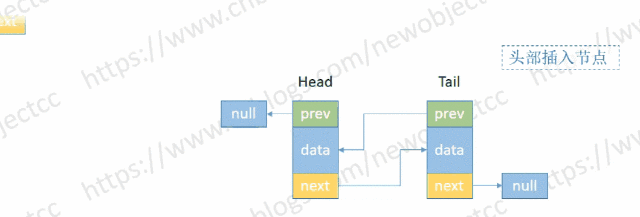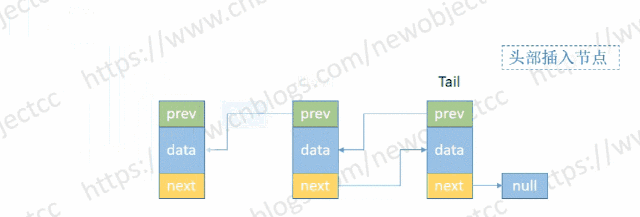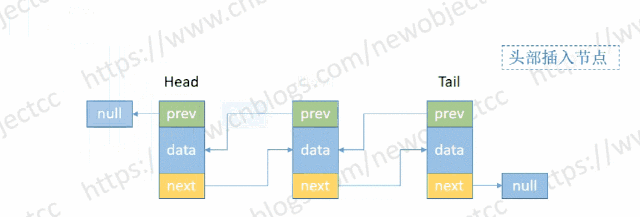
双向循环链表
尾节点的next指向头节点,头节点的prev指向尾节点,首尾节点连在一起形成闭环。

节点的伪代码:
class Node<E> {
private E item;
// 如果是第一个节点,其一用指向末尾节点
private Node<E> prev;
// 如果是末尾节点,指向第一个节点的引用地址,形成一个环形
private Node<E> next;
Node(Node<E> prev, E data, Node<E> next) {
this.item = data;
this.prev = prev;
this.next = next;
}
// ...
}
链表操作
链表的增删改查操作。链表查找节点需要从头或者尾部(单向链表只能从头开始)开始查找,删除或插入节点先查找到节点,然后改变相关节点的指针指向即可。
以双向链表为例:
添加节点
- 头部添加节点
伪代码:
Node<E> head;
Node<E> tail;
int size;
// 头部添加节点
void addHead(E e) {
Node<E> h = head;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, h); // (Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next)
head = newNode;
if(h == null) { // 空链表
tail = newNode;
} else {
h.prev = newNode;
}
size++; // 记录长度
}
- 尾部添加节点
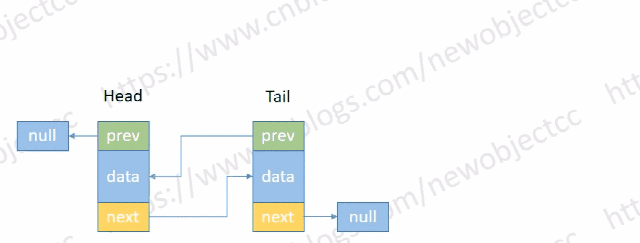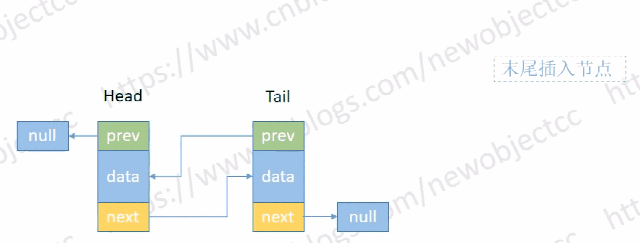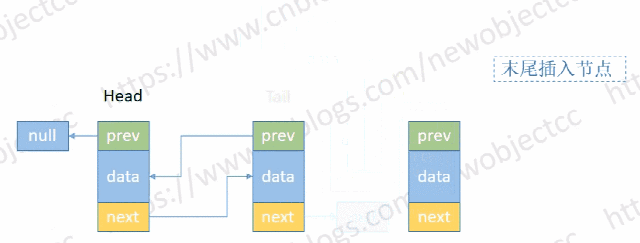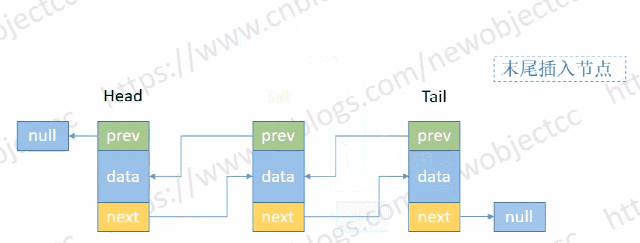
伪代码:
void addTail(E e) {
Node<E> t = tail;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(t, e, null);
tail = newNode;
if(t == null) {
head = newNode;
} else {
t.next = newNode;
}
size++;
}
- 按位置插入节点
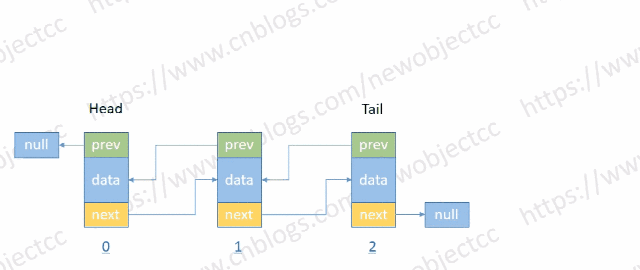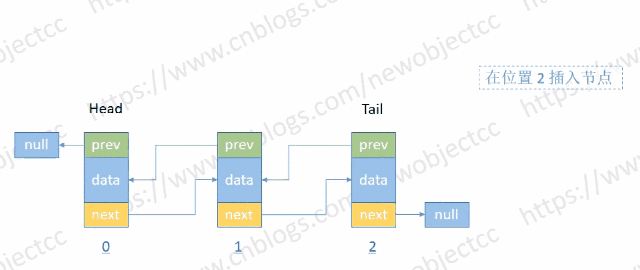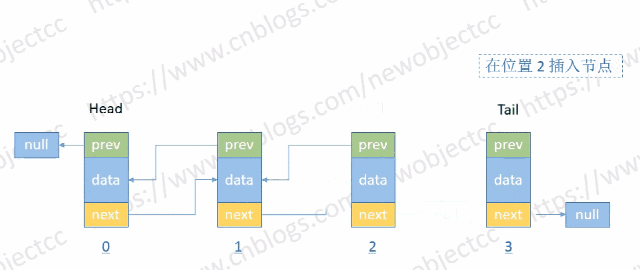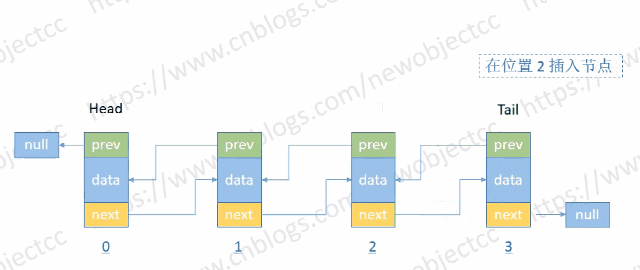
伪代码:
void add(int index, E element) {
if (index == size) {
// 直接在尾部添加节点
} else {
// 查找的节点
Node<E> temp = null;
if (index < (size >> 1)) {//由于双向链表,选择从离index位置最近端查找
Node<E> x = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
x = x.next;
}
temp = x;
} else {
Node<E> x = tail;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) {
x = x.prev;
}
temp = x;
}
// 插入节点
Node<E> pred = temp.prev;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, element, temp);
temp.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null) { // 查找到的节点为Head节点
head = newNode;
} else {
pred.next = newNode;
}
}
size++;
}
删除节点
- 删除头部节点
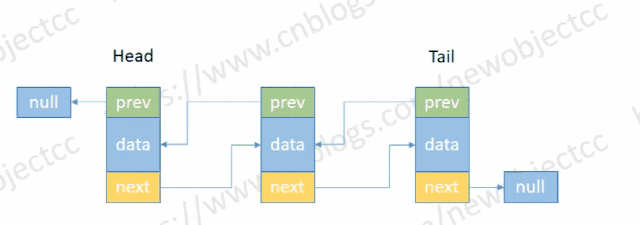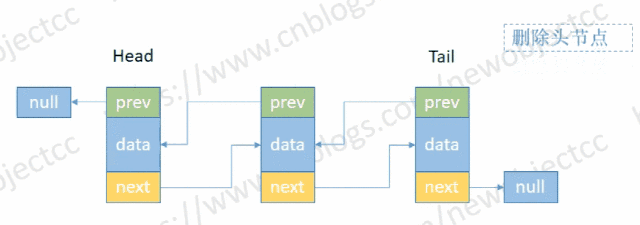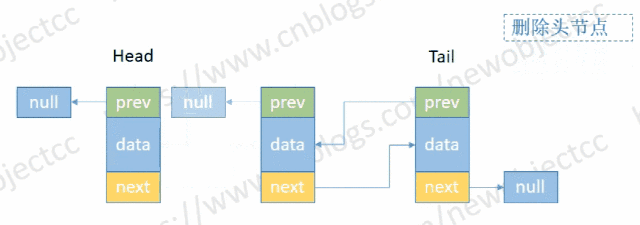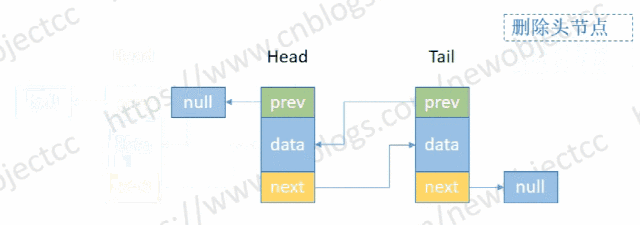
伪代码:
E removeHead() {
Node<E> h = head;
if (h != null){
E element = h.item;
Node<E> next = h.next;
head = next;
if (next == null) {
tail = null;
} else {
next.prev = null;
}
size--; // 减少长度
return element; // 返回删除元素
}
return null;
}
- 删除尾部节点
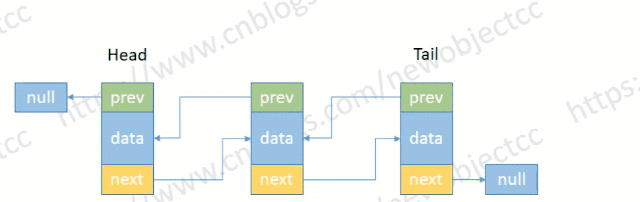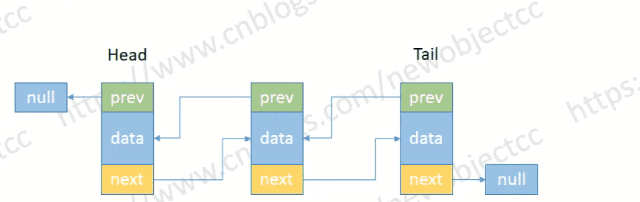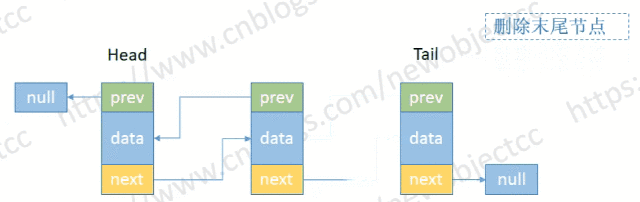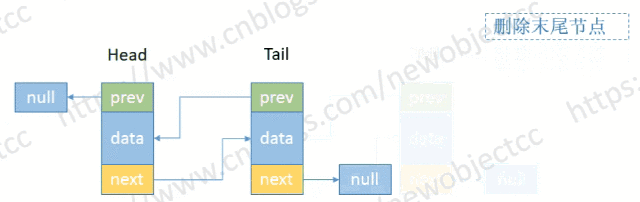
伪代码:
E removeTail() {
Node<E> t = tail;
if (t != null) {
E element = t.item;
Node<E> prev = t.prev;
tail = prev;
if (prev == null) {
head = null;
} else {
prev.next = null;
}
size--;
return element;
}
return null;
}
- 按节点位置或值删除
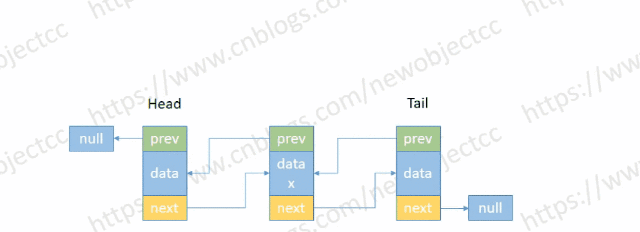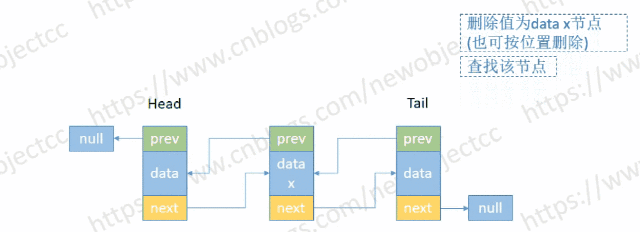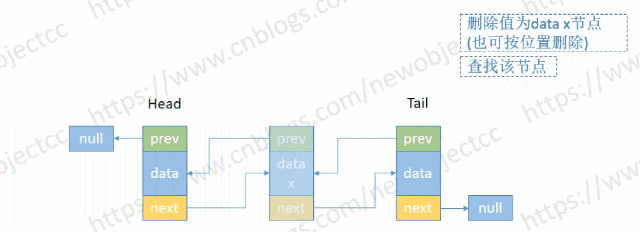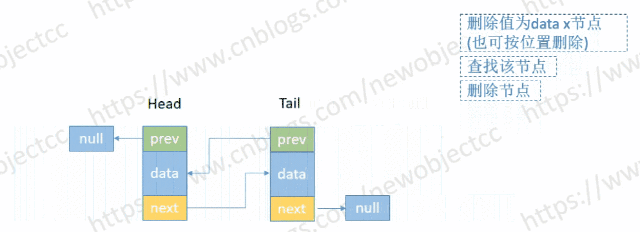
伪代码-按位置删除:
E remove(int index) {
// 根据index查找节点
Node<E> temp = null;
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
x = x.next;
}
temp = x;
} else {
Node<E> x = tail;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) {
x = x.prev;
}
temp = x;
}
// 删除节点
E element = temp.item;
Node<E> next = temp.next;
Node<E> prev = temp.prev;
if (prev == null) {
head = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
temp.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
tail= prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
temp.next = null;
}
temp.item = null;
size--;
return element;
}
查找节点
- 按位置或值查找节点
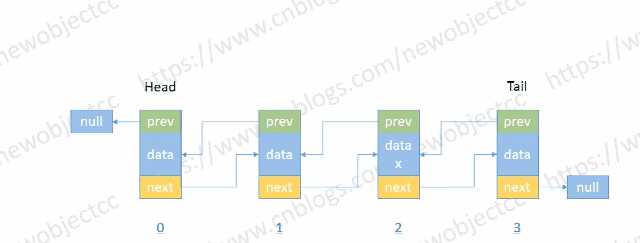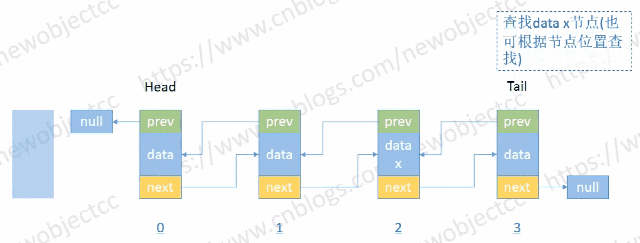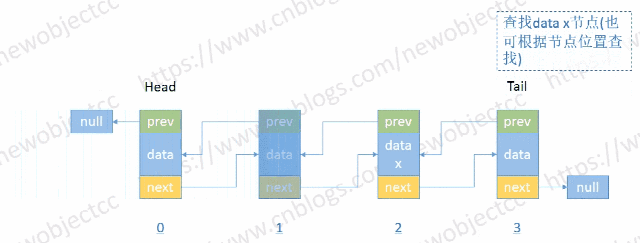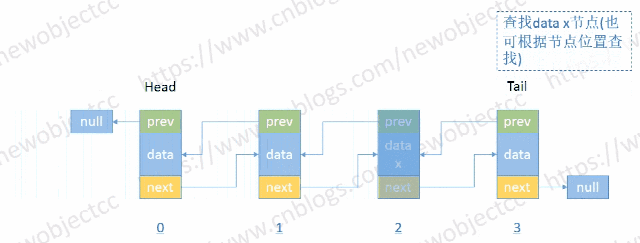
伪代码-按位置索引查找:
E get(int index) {
Node<E> temp = null;
if (index < (size >> 1)) { // 从近的一端开始查找
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
x = x.next;
}
temp = x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) {
x = x.prev;
}
temp = x;
}
return temp.item;
}
如果是单向链表只能从头部开始向后查找。
更新节点
更新节点首先查找到节点,然后修改节点data的指针。
具体可参考LinkedList源码
链表实现栈和队列
栈和队列是一种对数据存取有严格顺序要求的线性数据结构,使用链表和数组都能实现。下面使用链表来实现栈和队列。
栈
栈只能从一端存取数据,遵循后进先出(LIFO)原则。进出栈的一端称为栈顶,另一封闭端称为栈底,数据进入栈称为入栈或压栈,取出数据称为出栈或弹栈。
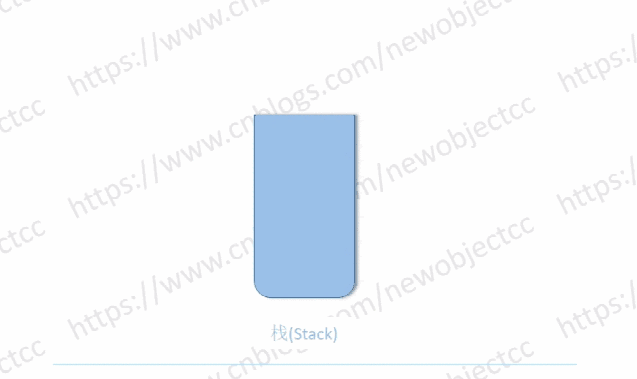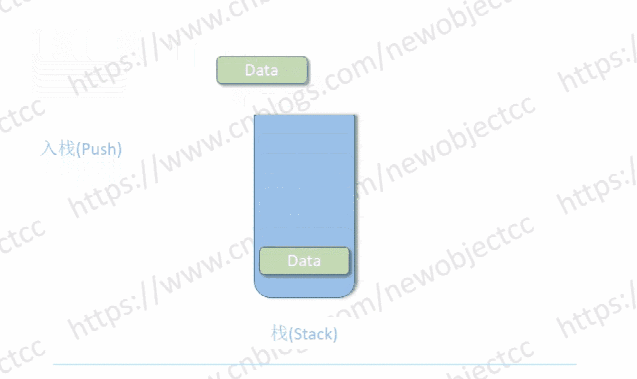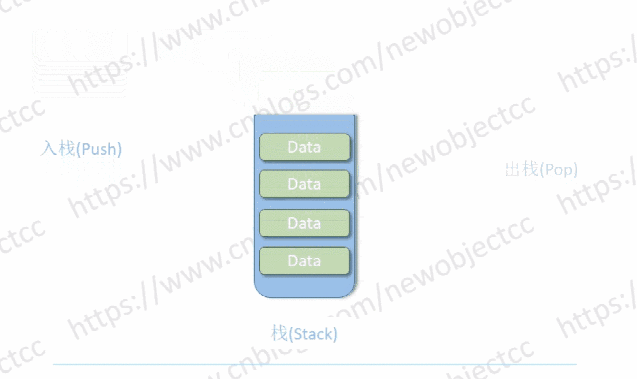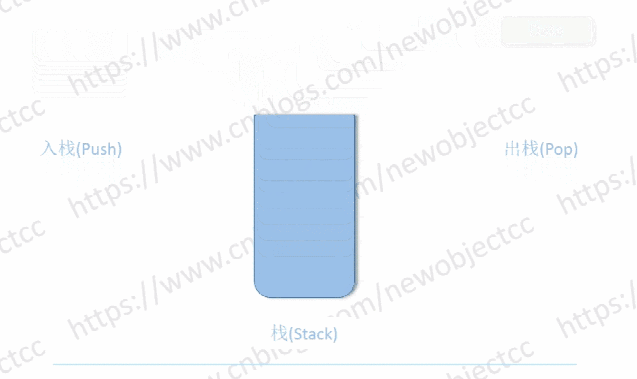
伪代码 - 基于双向链表实现简单的“栈”:
class Stack<E> {
// 返回栈顶元素值
public E peek() {
Node<E> h = head;
return (h == null) ? null : h.item;
}
// 入栈
public void push(E e) {
addHead(e); // 在头部添加节点
}
// 出栈
public E pop() {
// 移除头部节点并返回值
return removeHead();
}
// ...
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
}
队列
队列是从两端存取数据,并且从一端进,从另一端出,遵循先进先出(FIFO)原则。队列进数据一端称为队尾,出数据端称为队头,数据进队列称为入队,取出队列称为出队。

伪代码 - 基于链表实现“队列”:
class Queue {
// 入队
public boolean offer(E e) {
return addTail(e);
}
// 出队
public E poll() {
return removeHead();
}
// 返回头元素值
public E peek() {
Node<E> h = head;
return (h == null) ? null : h.item;
}
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
}
快慢指针
快慢指针是解决链表某些问题的常用方法,利用两个不同步频的指针fast指针和slow指针算法来解决很多问题,例如:
查找未知长度的单向链表倒数第N个值
由于链表长度未知,首先循环链表得到 length,然后再次循环链表到length-(N-1) 处得到元素。但是利用快慢指针来保持固定位置间隔,只需要循环一次链表即可查找到元素。
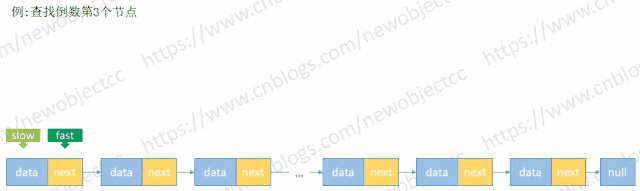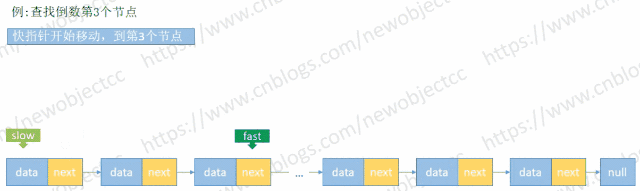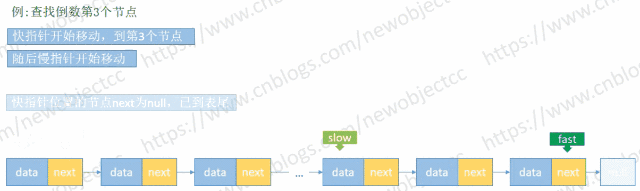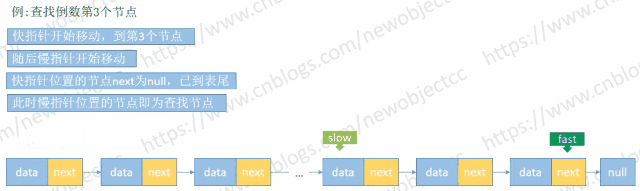
伪代码:
public E getLastN(int n) {
Node<E> h = head;
if (h == null || n < 1) {
return null;
}
Node<E> fast = h; // 快
Node<E> slow = h; // 慢
int count = 1;
while ((fast = fast.next) != null) {
// 倒数第k个节点与倒数第1个节点相隔 n-1 个位置,因此fast先走 n-1 个位置
if (count++ > n - 1) {
slow = slow.next;
}
}
// 链表中的元素个数小于 n
if (count < n) {
return null;
}
return slow.item;
}
找到链表中间节点值
使快指针移动步频是慢指针二倍,一次遍历即可快速找到中间节点。

伪代码:
public E getMiddle() {
Node<E> h = head;
if (h == null) {
return null;
}
Node<E> fast = h; // 快
Node<E> slow = h; // 慢
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
// 链表长度为偶数会两个中间节点,返回第一个
if (fast != null) {
slow = slow.next;
}
}
return slow.item;
}
源码:https://github.com/newobjectcc/code-example/blob/master/basic/datastructure/Linked.java
除此之外,还可以判断链表中是否有环等等问题,快慢指针在面试时可能会被问到,有兴趣朋友可以到网上找些链表的算法题。