1.背景
LRU-least recently used-最近最少使用算法,是一种内存数据淘汰策略,使用常见是当内存不足时,需要淘汰最近最少使用的数据。LRU常用语缓存系统的淘汰策略。
2.LRU原理
LRU最早实在操作系统接触到这个算法的,如下如所示。
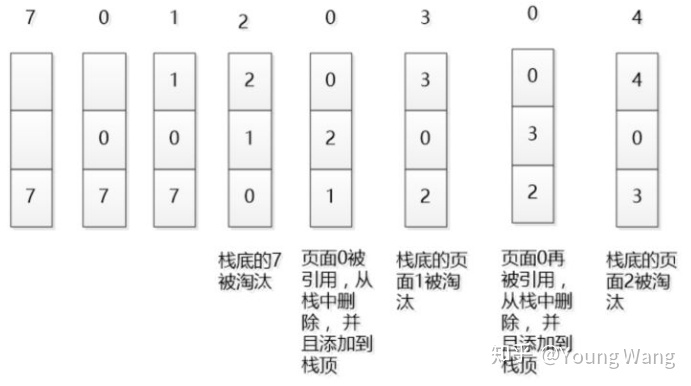
这里的栈有别于咱们后进先出的数据结构,主要用来描述原理本身。从途中可知LRU是如何实行淘汰的,同时,大家可能也意识到这种实现可能性能并不太好,存在大量的拷贝动作。
3.LRU算法实现
我们先从一道LRU设计算法题开始。
算法题:LRU缓存机制
运用你所掌握的数据结构,设计和实现一个 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存机制。它应该支持以下操作: 获取数据 get 和 写入数据 put 。
获取数据 get(key) - 如果关键字 (key) 存在于缓存中,则获取关键字的值(总是正数),否则返回 -1。
写入数据 put(key, value) - 如果关键字已经存在,则变更其数据值;如果关键字不存在,则插入该组「关键字/值」。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最久未使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间。
进阶: 你是否可以在 O(1) 时间复杂度内完成这两种操作?
示例要求:
LRUCache cache = new LRUCache( 2 /* 缓存容量 */ ); cache.put(1, 1); cache.put(2, 2); cache.get(1); // 返回 1 cache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废 cache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到) cache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废 cache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到) cache.get(3); // 返回 3 cache.get(4); // 返回 4
分析:
如果使用数组来实现一个基于LRU的缓存,按照LRU原理要求可以预知存在大量的拷贝操作,性能上可能无法满足。设计一个LRU缓存,满足放入和移出都是O(1),我们需要把访问次序维护好,但是这个次序的维护并不需要在内存中真正排序来反应,按照这种思路,有一种实现方法就是双向链表。
API定义
class LRUCache { public LRUCache(int capacity) { } public int get(int key) { } public void save(int key, int value) { } }
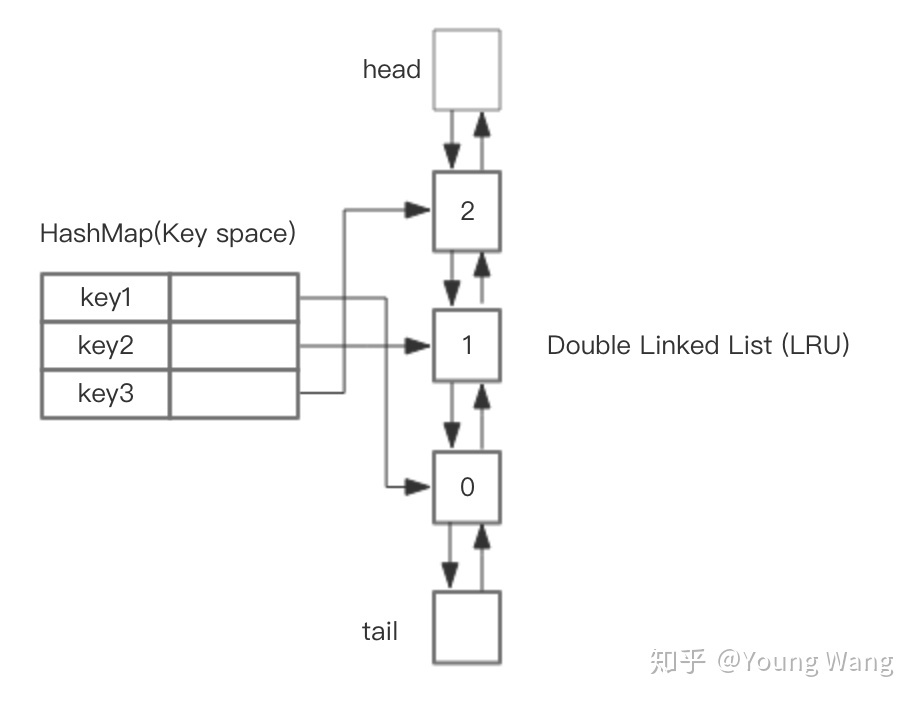
基于 HashMap + 双向链表 实现LRU
HahsMap用于快速查找到结点所在位置,然后将使用到的结点放在对头,这样最近最少使用的结点自然就落入到队尾。双向链表提供了良好的灵活性,两边可达。如下图所示。
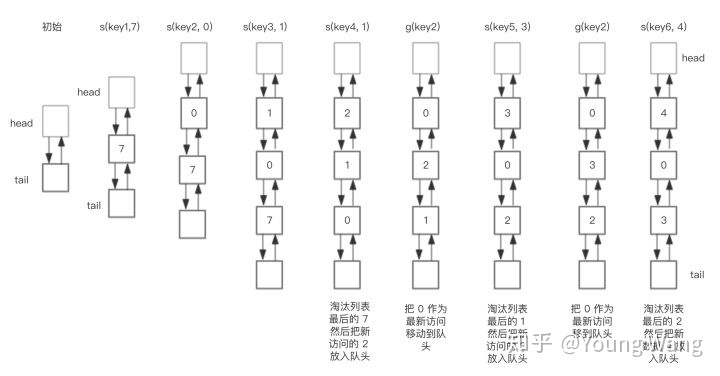
假设我们需要执行如下操作:
save("key1", 7)
save("key2", 0)
save("key3", 1)
save("key4", 2)
get("key2")
save("key5", 3)
get("key2")
save("key6", 4)
使用HashMap + 双向链表数据结构实现的LRU操作双向链表部分的轨迹如下。(下图中有一个错误,应该是 s(key4, 2) )
算法操作步骤如下:
1. save(key, value): 1. 首先在 HashMap 找到 Key 对应的节点,如果节点存在,更新节点的值,并把这个节点移动队头。 2. 如果不存在,需要构造新的节点,并且尝试把节点塞到队头。 3. 如果LRU空间不足,则通过 tail 淘汰掉队尾的节点,同时在 HashMap 中移除 Key。 2. get(key): 1. 通过 HashMap 找到 LRU 链表节点,因为根据LRU 原理,这个节点是最新访问的,所以要把节点插入到队头,然后返回缓存的值。
算法实现
由于可能存在并发读写LRUCache,因此需要保证线程安全。
public class LRUCache { class DLinkedNode { String key; int value; DLinkedNode pre; DLinkedNode post; } private ConcurrentMap<String, DLinkedNode> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, DLinkedNode>(); private int count; private int capacity; private DLinkedNode head, tail; public LRUCache(int capacity) { this.count = 0; this.capacity = capacity; head = new DLinkedNode(); head.pre = null; tail = new DLinkedNode(); tail.post = null; head.post = tail; tail.pre = head; } public int get(String key) { DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key); if(node == null){ return -1; // should raise exception here. } moveToHead(node); return node.value; } public void put(String key, int value) { DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key); if (node != null) { node.value = value; moveToHead(node); return; } DLinkedNode newNode = new DLinkedNode(); newNode.key = key; newNode.value = value; cache.put(key, newNode); addNode(newNode); ++count; if(count > capacity){ // pop the tail DLinkedNode tail = popTail(); cache.remove(tail.key); --count; } } private void addNode(DLinkedNode node){ node.pre = head; node.post = head.post; head.post.pre = node; head.post = node; } private void removeNode(DLinkedNode node){ DLinkedNode pre = node.pre; DLinkedNode post = node.post; pre.post = post; post.pre = pre; } private void moveToHead(DLinkedNode node){ removeNode(node); addNode(node); } private DLinkedNode popTail(){ DLinkedNode res = tail.pre; removeNode(res); return res; } }
采用HashMap + 双向链表,提供了很好的读写操作,且能在O(1)内完成读写操作。那么,Redis的淘汰策略是不是也是根据LRU,如果是,它的淘汰算法是不是也采用的这种数据结果?
Python 算法实现:
class DLinkedNode: def __init__(self, key=0, value=0): self.key = key self.value = value self.prev = None self.next = None class LRUCache: def __init__(self, capacity: int): self.cache = dict() self.head = DLinkedNode() self.tail = DLinkedNode() self.head.next = self.tail self.tail.prev = self.head self.capacity = capacity self.size = 0 def get(self, key: int) -> int: if key not in self.cache: return -1 node = self.cache[key] # move this node to head self.moveToHead(node) return node.value def put(self, key: int, value: int) -> None: # old key if key in self.cache: node = self.cache[key] node.value = value self.moveToHead(node) # new key else: node = DLinkedNode(key, value) self.cache[key] = node self.addToHead(node) self.size += 1 if self.size > self.capacity: tail = self.removeTail() del self.cache[tail.key] self.size -= 1 def addToHead(self, node): node.next = self.head.next node.next.prev = node self.head.next = node node.prev = self.head def removeNode(self, node): prev_node = node.prev next_node = node.next prev_node.next = next_node next_node.prev = prev_node def moveToHead(self, node): self.removeNode(node) self.addToHead(node) def removeTail(self): node = self.tail.prev self.removeNode(node) return node # Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such: # obj = LRUCache(capacity) # param_1 = obj.get(key) # obj.put(key,value)
题目链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lru-cache/
4. Redis LRU算法实现
分析Redis LRU实现之前,我们先了解一下Redis缓存淘汰策略。
当Redis内存超出物理内存限制时,内存会频繁的磁盘swap区交换数据,而交换会导致redis对外服务性能的急剧下降,这在生产环境是不允许的。说得更明白些,在生产环境是不允许交换行为的,通过设置maxmemory可限制内存超过期望大小。
当实际需要的内存大于maxmemory时,Redis提供了6种可选策略:
- noeviction:不继续提供写服务,读请求可以继续;
- volatile-lru:尝试淘汰设置了过期时间的key,最少使用的key优先淘汰。也就是说没有设置过期时间的key不会被淘汰;
- volatile-ttl:也是淘汰设置了过期时间的key,只不过策略不是lru,而是根据剩余寿命的ttl值,ttl越小越优先被淘汰;
- volatile-random:同理,也是淘汰设置了过期时间的key,只不过策略是随机;
- allkeys-lru:类比volatile-lru,只不过未设置过期时间的key也在淘汰范围;
- allkeys-random:类比volatile-random,只不过未设置过期时间的key也在淘汰范围。
采用HashMap + 双向循环链表具有较好的读写性能,但是有没有发现什么问题呢?对,HashMap和链表都存在空间浪费的情况,HashMap本来就很耗内存,双向链表由于需要空间存储指针,两种数据结构空间使用率都不高,这显然很不划算。
针对这个问题,Redis采用了近似的做法,我们来分析分析。
首先,针对问题本身,我们需要淘汰的是最近未使用的相对比较旧的数据淘汰掉,那么,我们是否一定得非常精确地淘汰掉最旧的数据还是只需要淘汰掉比较旧的数据?
咱们来看下Redis是如何实现的。Redis做法很简单:随机取若干个key,然后按照访问时间排序,淘汰掉最不经常使用的数据。为此,Redis给每个key额外增加了一个24bit长度的字段,用于保存最后一次被访问的时钟(Redis维护了一个全局LRU时钟lruclock:REDIS_LUR_BITS,时钟分辨率默认1秒)。
下面我们看下采用volatile_lru和allkeys-lru是如何实现的,关键代码如下。
// 评估object空闲时间 unsigned long estimateObjectIdleTime(robj *o) { if (server.lruclock >= o->lru) { return (server.lruclock - o->lru) * REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION; } else { return ((REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_MAX - o->lru) + server.lruclock) * REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION; } } // LRU淘汰算法实现 ...... /* volatile-lru and allkeys-lru policy */ else if (server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_LRU || server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_LRU) { for (k = 0; k < server.maxmemory_samples; k++) { sds thiskey; long thisval; robj *o; de = dictGetRandomKey(dict); thiskey = dictGetKey(de); if (server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_LRU) de = dictFind(db->dict, thiskey); o = dictGetVal(de); thisval = estimateObjectIdleTime(o); /* Higher idle time is better candidate for deletion */ if (bestkey == NULL || thisval > bestval) { bestkey = thiskey; bestval = thisval; } } } ......
redis会基于server.maxmemory_samples配置选取固定数目的key,然后比较它们的lru访问时间,然后淘汰最近最久没有访问的key,maxmemory_samples的值越大,Redis的近似LRU算法就越接近于严格LRU算法,但是相应消耗也变高,对性能有一定影响,样本值默认为5。
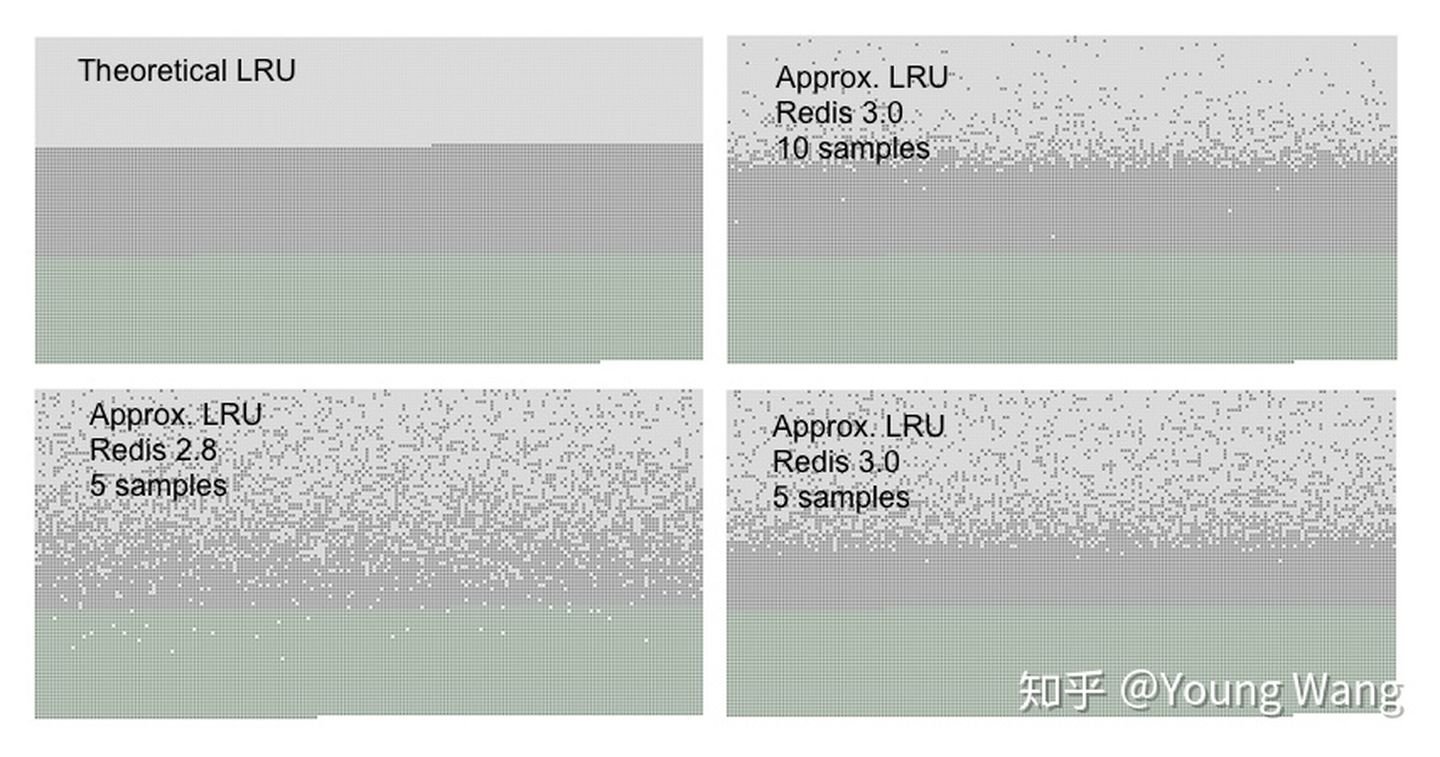

上图是Redis官网的一组LRU统计数据,Redis3.0以上采用近视LRU算法获得了不错的效果。从Redis实现我们看出,在商业世界,为了追求空间的利用率,也会采用权衡的实现方案。
总结
LRU是缓存系统中常见的淘汰策略,当内存不足时,我们需要淘汰掉最近最少使用的数据,LRU就是实现这种策略的统称。LRU算法实现可以基于HashMap + 双向链表的数据结构实现高效数据读写,于此同时,高效查询却带来了高内存消耗的的问题,为此Redis选择了近似LRU算法,随机采用一组key,选择最老的数据进行删除,能够达到类似的效果。
参考链接: