快速排序
步骤:(升序) 可在排序前将数组打乱
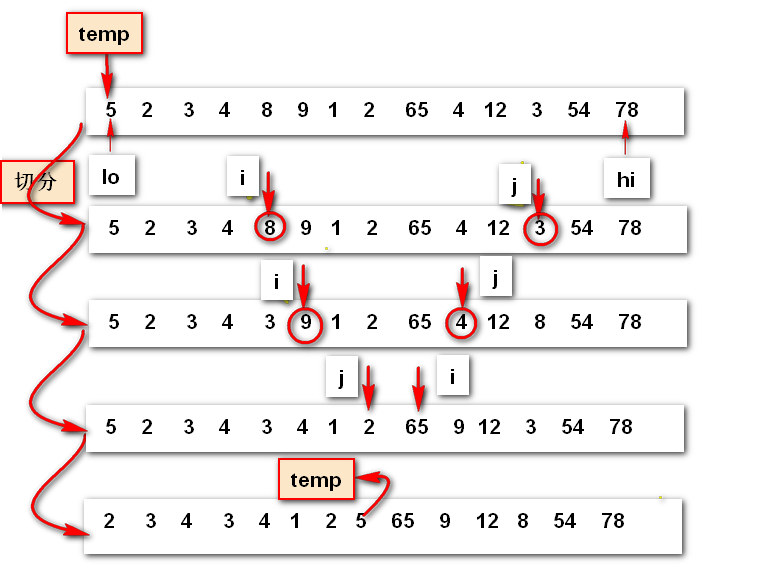
设a[lo]为切分元素temp(temp=a[lo]),将数组分为三部分:
- 不大于切分元素的小数组A
- A小数组与B小数组间插入temp
- 不小于切分元素的小数组B
如何切分:
设立一个从左到右扫描的指针i直到找大于等于切分元素的元素,同时一个从右到左的扫描指针j直到找小于等于切分元素的元素
两元素交换位置,继续扫描直到i>=j(A、B小数组已经排完整)时停止扫描。
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<malloc.h> 3 int sort(int *a,int lo,int hi); 4 int less(int a,int b); 5 void each(int *a,int *b); 6 int partition(int *a,int lo,int hi); 7 int main() 8 { 9 int n,i; 10 scanf("%d",&n); 11 int *a=(int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*n); 12 for(i=0;i<n;i++) 13 scanf("%d",&a[i]); 14 sort(a,0,n-1); 15 for(i=0;i<n;i++) 16 printf("%d ",a[i]); 17 return 0; 18 } 19 int sort(int *a,int lo,int hi) 20 { 21 if(lo>=hi) 22 return 0; 23 int j=partition(a,lo,hi); 24 sort(a,lo,j-1); 25 sort(a,j+1,hi); 26 } 27 int partition(int *a,int lo,int hi) 28 { 29 int i,j,temp; 30 temp=a[lo]; 31 i=lo; 32 j=hi+1; 33 34 while(1) 35 { 36 while(less(a[++i],temp)) 37 if (i==hi) //a[hi]大等于temp 38 break; 39 while(less(temp,a[--j])) 40 if(j==lo) 41 break; 42 if(i>=j)//两个小数组已分好 43 break; 44 each(&a[i],&a[j]); 45 } 46 each(&a[j],&a[lo]);//temp放到两小数组中间 47 return j; 48 } 49 int less(int a,int b) 50 { 51 if(a<b) 52 return 1; 53 return 0; 54 } 55 void each(int *a,int *b) 56 { 57 int temp; 58 temp=*a; 59 *a=*b; 60 *b=temp; 61 }
疑问:为什么返回 j,而不是i?切分元素是和a[j]交换,而不是a[i]?
答:切分数组占据的位置是小数组A的位置(小数组存储的是不大于切分元素的元素 ),而指针j在结束时指向的元素刚好是小数组A的最后一位元素。
改进后:
三向切分快速排序
设a[lo]为切分元素temp(temp=a[lo]),将待切分的数组分为四部分:
- a[lo]~a[lt-1]为小于切分元素的小数组
- a[lt]~a[i-1]为等于切分元素的小数组
- a[i]~a[gt]为待与切分元素比较的小数组
- a[gt+1]为大于切分元素的小数组
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<malloc.h> 3 int sort(int *a,int lo,int hi); 4 int less(int a,int b); 5 void each(int *a,int *b); 7 int main() 8 { 9 int n,i; 10 scanf("%d",&n); 11 int *a=(int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*n); 12 for(i=0;i<n;i++) 13 scanf("%d",&a[i]); 14 sort(a,0,n-1); 15 for(i=0;i<n;i++) 16 printf("%d ",a[i]); 17 return 0; 18 } 19 int sort(int *a,int lo,int hi) 20 { 21 int lt,gt,i,j,temp; 22 if(lo>=hi) 23 return 0; 24 temp=a[lo]; 25 i=lo+1; 26 lt=lo; 27 gt=hi; 28 while(i<=gt) 29 { 30 if(a[i]<temp) 31 each(&a[lt++],&a[i++]);//保证a[lt]到a[i-1]等于v 32 else if(a[i]>temp) 33 each(&a[gt--],&a[i]);//交换后再判断原a[gt]值的大小 34 else 35 i++; 36 } 37 sort(a,lo,lt-1); 38 sort(a,gt+1,hi); 39 } 40 int less(int a,int b) 41 { 42 if(a<b) 43 return 1; 44 return 0; 45 } 46 void each(int *a,int *b) 47 { 48 int temp; 49 temp=*a; 50 *a=*b; 51 *b=temp; 52 }
优势:
避免了与切分元素相同的元素参与到下一环节的递归运算,效率更高。
当存在主键重复时,三向切分比归并排序快。